
The Pacific sleeper shark is a sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found in the North Pacific on continental shelves and slopes in Arctic and temperate waters between latitudes 70°N and 22°N, from the surface to 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) deep. Records from southern oceans are likely misidentifications of relatives. Its length is up to 4.4 m (14 ft), although it could possibly reach lengths in excess of 7 m (23 ft).

The black dogfish is a species of dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae. It is common over the outer continental shelf and continental slope at depths of 180–2,250 m (590–7,380 ft). Females generally inhabit deeper water than males, and depending on the region, smaller sharks may occur at different depths than larger ones. This species is distributed widely in the Atlantic Ocean, from Greenland and Iceland to Virginia and West Africa in the north, and off southwestern Africa and Argentina in the south. The largest member of its family, the black dogfish, typically measures 60–75 cm (24–30 in) long. It has a stocky, dark brown body that is darker below than above, and bears scattered, minute bioluminescent organs. Its two dorsal fins are preceded by stout spines, and the anal fin is absent.
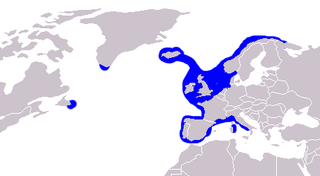
The common ling, also known as the white ling or simply the ling, is a large member of the family Lotidae, a group of cod-like fishes. It resembles the related rocklings, but it is much larger and has a single barbel. This species is unrelated to the pink ling, Genypterus blacodes, from the Southern Hemisphere. The common ling is found in the northern Atlantic, mainly off Europe, and into the Mediterranean Basin. It is an important quarry species for fisheries, especially in the northeastern Atlantic, although some doubts exist as the sustainability of the fisheries. As an edible species, it is eaten fresh, frozen, or dried, but also preserved in lye, while the roe is a delicacy in Spain.

The kitefin shark or seal shark is a species of squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae, and the only species in its genus. It is found sporadically around the world, usually close to the sea floor at depths of 200–600 m (660–1,970 ft). With a sizable oil-filled liver to maintain neutral buoyancy, this shark is able to cruise slowly through the water while expending little energy. The kitefin shark has a slender body with a very short, blunt snout, large eyes, and thick lips. Its teeth are highly differentiated between the upper and lower jaws, with the upper teeth small and narrow and the lower teeth large, triangular, and serrated. Its typical length is 1.0–1.4 m (3.3–4.6 ft).

The Izak catshark or simply Izak is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, common off the coasts of South Africa and southern Namibia. It typically inhabits the outer continental shelf at depths of 100–300 m (330–980 ft), with the males found deeper than the females and juveniles. The Izak catshark has a short, wide, flattened head and a robust body tapering to a long, slender tail. It can be identified by its ornate color pattern of dark brown spots or reticulations and blotches on a light yellowish background, as well as by the enlarged dermal denticles over its pectoral fins and along its dorsal midline from the snout to the second dorsal fin. This species reaches 69 cm (27 in) in length, with the males larger than females.

The Portuguese dogfish or Portuguese shark, is a species of sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae. This globally distributed species has been reported down to a depth of 3,675 m (12,057 ft), making it the deepest-living shark known. It inhabits lower continental slopes and abyssal plains, usually staying near the bottom. Stocky and dark brown in color, the Portuguese dogfish can be distinguished from similar-looking species by the small spines in front of its dorsal fins. Its dermal denticles are also unusual, resembling the scales of a bony fish. This species typically reaches 0.9–1 m (3.0–3.3 ft) in length; sharks in the Mediterranean Sea are much smaller and have distinct depth and food preferences.

The angular roughshark is a rough shark of the family Oxynotidae.

The smooth lanternshark or slender lanternshark is a species of dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae, found widely in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It inhabits benthic environments at a depth of 274–1,000 m (899–3,281 ft), and pelagic environments at a depth of 0–708 m (0–2,323 ft). The smooth lanternshark forms a species group with the larger blurred lanternshark, both of which are distinguished from other members of their family by small, irregularly arranged dermal denticles with a truncated shape. This species has a slender, dark brown body with an indistinct black band on the sides over the pelvic fins, and reaches 50 cm (20 in) in length. This slow-growing, ovoviviparous shark feeds on smaller squid, fishes, and fish eggs. Smooth lanternsharks are often caught as bycatch in eastern Atlantic and Japanese commercial fisheries. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has evaluated this species as of Least Concern because of its wide distribution and limited threats.

The sand devil or Atlantic angel shark is a species of angelshark, family Squatinidae, native to the northwestern Atlantic Ocean. It occurs off the eastern United States, in the northern Gulf of Mexico, and possibly in parts of the Caribbean Sea. This bottom-dwelling shark is found in shallow inshore waters in summer and fall, and deep offshore waters in winter and spring. The sand devil's flattened body and enlarged pectoral and pelvic fins give it a ray-like appearance. There is a band of enlarged thorns running along the middle of its back. It is gray or brown in color, with scattered small dark spots. This species reaches 1.2–1.5 m (3.9–4.9 ft) in length.

The blackmouth catshark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, common in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean from Iceland to Senegal, including the Mediterranean Sea. It is typically found over the continental slope at depths of 150–1,400 m (490–4,590 ft), on or near muddy bottoms. The youngest sharks generally inhabit shallower water than the older juveniles and adults. This slim-bodied species is characterized by the black interior of its mouth, a marbled pattern of pale-edged brownish saddles or blotches along its back and tail, and a prominent saw-toothed crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the upper edge of its caudal fin. It reaches lengths of 50–79 cm (20–31 in), with sharks in the Atlantic growing larger than those in the Mediterranean.

The Atlantic sawtail catshark is a little-known species of catshark, part of the family Scyliorhinidae, found in a small area of the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, centered on the Strait of Gibraltar and the Alborán Sea. It is found on or close to the bottom over the continental slope, mostly at depths of 400–600 m (1,300–2,000 ft). This shark closely resembles, and was once thought to be the same species as, the blackmouth catshark ; both are slender with a series of dark saddles and blotches along the back and tail, and a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the dorsal edge of the caudal fin. It differs subtly from G. melastomus in characters including snout length, caudal peduncle depth, and the color of the furrows at the corner of its mouth.

The roughtail catshark or marbled catshark is a common species of catshark, part of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found at a depth of 36–702 m (118–2,303 ft) in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea, from North Carolina to Costa Rica. Individuals of different sexes and ages are segregated to some degree. A small species not exceeding 33 cm (13 in) in length, the roughtail catshark has a slender body with a marbled color pattern of dark saddles and spots, and a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the dorsal edge of its caudal fin. This species feeds mainly on shrimp and is oviparous. It is caught incidentally in shrimp trawls, though trawl fisheries within its range mostly do not operate at the depths it inhabits. As a result, the International Union for Conservation of Nature has listed it under Least Concern.

The Australian sawtail catshark is a common species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to southern Australian waters. It is found on or near the bottom of the outer continental shelf and upper continental slope, at depths of 85 to 823 m. This slim-bodied species is characterized by crests of enlarged dermal denticles along both the dorsal and ventral edges of its caudal fin and caudal peduncle, along with a color pattern of broad, dark saddles outlined in white. It can grow to 61 cm (24 in) in length. The Australian sawtail catshark feeds mainly on fishes, crustaceans, and cephalopods. Females are oviparous and lay eggs enclosed by capsules. This species is often caught incidentally by commercial bottom trawl fisheries, but is not significantly threatened by fishing activity. Thus, it has been assessed as of Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

Squatina squatina, the angelshark or monkfish, is a species of shark in the family Squatinidae, that were once widespread in the coastal waters of the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Well-adapted for camouflaging itself on the sea floor, the angelshark has a flattened form with enlarged pectoral and pelvic fins, giving it a superficial resemblance to a ray. This species can be identified by its broad and stout body, conical barbels, thornless back, and grayish or brownish dorsal coloration with a pattern of numerous small light and dark markings. It measures up to 2.4 m (7.9 ft) long.

Glyptocephalus cynoglossus, known in English by a variety of common names including the witch, witch flounder, pole flounder, craig fluke, Torbay sole and grey sole, is a species of flatfish from the family Pleuronectidae. It occurs on both sides of the North Atlantic Ocean on muddy sea beds in quite deep water. In northern Europe it has some importance in fisheries as a food fish.

Mullus barbatus is a species of goatfish found in the Mediterranean Sea, Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea and the eastern North Atlantic Ocean, where its range extends from Scandinavia to Senegal. They are fished, mostly by trawling, with the flesh being well regarded. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed their conservation status as being of "least concern".

The bottlenose skate, spearnose skate, or white skate is a species of skate in the family Rajidae. It is a benthic fish native to the coastal eastern Atlantic Ocean. Due to overfishing, it has been depleted or extirpated in many parts of its former range in the northeastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea, and is now endangered.
The frog shark is a very rare species of squaliform shark mainly found in deep water in the Pacific Ocean. It is in the sleeper shark family Somniosidae with the Greenland shark.

The blackbelly rosefish, Helicolenus dactylopterus, is a marine bony fish from the family Sebastidae, also known as bluemouth rockfish, and bluemouth seaperch. This Atlantic species is a typical sit-and-wait predator with a highly cryptic coloration.

The Cape horse mackerel is a mackerel-like species in the family Carangidae. It is a pelagic species of the south eastern Atlantic Ocean which is a target of fisheries, mainly as bycatch.





















