
The Squaliformes are an order of sharks that includes about 126 species in seven families.

The pygmy sperm whale is one of two extant species in the family Kogiidae in the sperm whale superfamily. They are not often sighted at sea, and most of what is known about them comes from the examination of stranded specimens.

The dwarf sperm whale is a sperm whale that inhabits temperate and tropical oceans worldwide, in particular continental shelves and slopes. It was first described by biologist Richard Owen in 1866, based on illustrations by naturalist Sir Walter Elliot. The species was considered to be synonymous with the pygmy sperm whale from 1878 until 1998. The dwarf sperm whale is a small whale, 2 to 2.7 m and 136 to 272 kg, that has a grey coloration, square head, small jaw, and robust body. Its appearance is very similar to the pygmy sperm whale, distinguished mainly by the position of the dorsal fin on the body–nearer the middle in the dwarf sperm whale and nearer the tail in the other.

The cookiecutter shark, also called the cigar shark, is a species of small squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae. This shark lives in warm, oceanic waters worldwide, particularly near islands, and has been recorded as deep as 3.7 km (2.3 mi). It migrates vertically up to 3 km (1.9 mi) every day, approaching the surface at dusk and descending with the dawn. Reaching only 42–56 cm (16.5–22 in) in length, the cookiecutter shark has a long, cylindrical body with a short, blunt snout, large eyes, two tiny spineless dorsal fins, and a large caudal fin. It is dark brown, with light-emitting photophores covering its underside except for a dark "collar" around its throat and gill slits.
The Dalatiidae are the family of kitefin sharks of the order Squaliformes. Members of this family are small, under 2 m (6.6 ft) long, and are found worldwide. They have cigar-shaped bodies with narrow heads and rounded snouts. Several species have specialized bioluminescent organs. Though eight genera are in this family, four of them are monotypic.

The pygmy shark, the second-smallest of all the shark species after the dwarf lanternshark, is a squaliform shark of the family Dalatiidae, the only member of the genus Euprotomicrus. Their lengths are up to about 25 cm (10 in) for females and about 22 cm (8.7 in) for males.

The finback catsharks are a small family, the Proscylliidae, of ground sharks. They can be found in warm seas worldwide and are often the most numerous and common shark in tropical regions. They are generally less than 1 m in length, and are slow-moving predators that feed on bony fish and small invertebrates. Although some bear live young, the majority lay eggs with almost fully developed young; these egg cases, known as "mermaid's purses", are unique in appearance to each species.

The pygmy ribbontail catshark is a species of finback catshark, family Proscylliidae, distributed patchily in the western Indo-Pacific from Tanzania to the Philippines. It occurs around the edges of continental and insular shelves at a depth of 71–766 m (233–2,513 ft), typically on or near mud bottoms. One of the smallest living shark species, the pygmy ribbontail catshark grows to a maximum known length of 24 cm (9.4 in). It has a slender body with a low, ribbon-like tail fin, and is dark brown in color with blackish dorsal fin markings and tail bands. This shark feeds mainly on bony fishes, followed by crustaceans and then squid. It is aplacental viviparous with females bearing litters of 1–2 relatively large pups. It is of minimal significance to fisheries, being caught as bycatch in some areas.

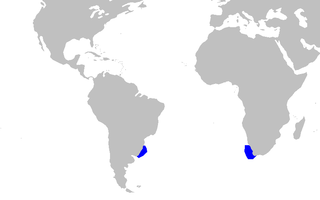
The longnose pygmy shark is a rare species of squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae and the only member its genus. It is known only from a handful of specimens collected from the cold oceanic waters of the Southern Hemisphere, between the surface and a depth of 502 m (1,647 ft). Reaching 37 cm (15 in) in length, this diminutive shark is characterized by a slender, dark brown body with a very long, bulbous snout. In addition, it has two spineless dorsal fins of nearly equal size, with the origin of the first lying over the pectoral fin bases. The longnose pygmy shark does not appear substantially threatened by fisheries, and has been assessed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
The taillight shark is a little-known species of shark in the family Dalatiidae and the only member of its genus. It is known from only four specimens collected from deep oceanic waters in the southern Atlantic Ocean and Pacific Ocean. A small shark with a laterally compressed body and a bulbous snout, this species has unusual adaptations that indicate a specialized lifestyle: its pectoral fins are paddle-like and may be used for propulsion, unlike other sharks and it has a pouch-like gland on its abdomen that emits clouds of luminescent blue fluid. This shark is likely aplacental viviparous and a formidable predator for its size.

The smalleye pygmy shark is a little-known species of squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae, found in water 150–2,000 m (490–6,560 ft) deep near Japan, the Philippines, and Australia. It migrates vertically daily, spending the day in deep water and the night in shallower water. One of the smallest shark species, the smalleye pygmy shark is known to reach only 22 cm (8.7 in) long. It has a blackish, spindle-shaped body with relatively small eyes, and a spine preceding the first dorsal fin, but not the second. Bioluminescent photophores occur on its underside, which may serve to disguise its silhouette from predators. This species feeds on small squid, krill, shrimp, and bony fishes. It is aplacental viviparous. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed it as Least Concern, citing its wide distribution and lack of threat from fisheries.

The spined pygmy shark is a species of squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae found widely in all oceans. Growing no larger than roughly 28 cm (11 in), it is one of the smallest sharks alive, with this record beaten by the dwarf lanternshark. This shark has a slender, cigar-shaped body with a sizable conical snout, a long but low second dorsal fin, and an almost symmetrical caudal fin. Its sister species S. aliae and it are the only sharks with a spine on the first dorsal fin and not the second. Spined pygmy sharks are dark brown to black, with numerous bioluminescent organs called photophores on their ventral surface. The shark is believed to use these photophores to match ambient light conditions, which break up its silhouette and help the shark to avoid being seen by predators below.

The dwarf lanternshark is a species of dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae and is the smallest shark in the world, reaching a maximum known length of 20 cm (8 in). It is known to be present only on the upper continental slopes off Colombia and Venezuela, at a depth of 283–439 m (928–1,440 ft). This species can be identified by its small size at maturity, long flattened head, and pattern of black ventral markings and a mid-dorsal line. Like other members of its genus, it is capable of producing light from a distinctive array of photophores. Reproduction is aplacental viviparous, with females gestating two or three young at a time. The dwarf lanternshark is not significant to commercial fisheries, but could be threatened by mortality from bycatch; the degree of impact from human activities on its population is unknown.
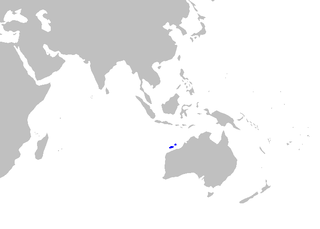
The pygmy lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the eastern Indian Ocean from northern Western Australia and possibly Java, at depths of between 430 and 550 m. Its length is up to 26 cm.

The false lanternshark or false pygmy shark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the western Pacific from the Norfolk Ridge and Lord Howe Ridge off New Caledonia.

Pocket God is a simulation game developed by Bolt Creative, in which the player manipulates an island and its inhabitants. It was released for the iPad, iPhone, and iPod Touch on January 9, 2009, and released for Verizon Wireless on September 1, 2010, Android on December 1, 2010, and Windows Phone on December 4, 2010. The Facebook version was released December 23, 2010.
The Sarawak pygmy swellshark is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found in the benthic zone near the edge of the Pacific continental shelf, at depths of 118–165 m.
The dwarf false catshark is a species of ground shark, which lives in the Indian Ocean near Socotra. This species is one of two known members of its genus, the other being the pygmy false catshark off the coast of India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. The pygmy false catshark is very closely related to the dwarf false catshark, but has some morphological differences. Two examples are its absence of an oral papillae and that it has more tooth rows in the lower jaw.
















