
The hammerhead sharks are a group of sharks that form the family Sphyrnidae, named for the unusual and distinctive form of their heads, which are flattened and laterally extended into a cephalofoil. The shark's eyes are placed one on either end of this T-shaped structure, with their small mouths directly centered and underneath. Most hammerhead species are placed in the genus Sphyrna, while the winghead shark is placed in its own genus, Eusphyra. Many different— but not necessarily mutually exclusive—functions have been postulated for the cephalofoil, including sensory reception, manoeuvering, and prey manipulation. The cephalofoil gives the shark superior binocular vision and depth perception.

Mycteroperca bonaci, the black grouper, black rockfish or marbled rockfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. Other fish are sometimes called the black grouper including the similar gag grouper, the misty grouper, and the warsaw grouper. This species is found in the western Atlantic Ocean from the northeastern United States to Brazil.

Sphyrna is a genus of hammerhead sharks with a cosmopolitan distribution in the world's oceans. Members of Sphyrna have a tendency to inhabit coastal waters along the intertidal zone rather than the open ocean, as their prey such as invertebrates, fish, rays, small crustaceans, and other benthic organisms hide in the sands and sediment along these zones. Members of Sphyrna are also known by synonyms such as Zygaena, Cestracion, and Sphyrichthys. The earliest species described of this genus was Sphyrna zygaena by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, while the latest described member, Sphyrna gilberti, was discovered and described in 2013.

The great hammerhead is the largest species of hammerhead shark, belonging to the family Sphyrnidae, attaining an average length of 4.6 m (15 ft) and reaching a maximum length of 6.2 m (20 ft). It is found in tropical and warm temperate waters worldwide, inhabiting coastal areas and the continental shelf. The great hammerhead can be distinguished from other hammerheads by the shape of its "hammer", which is wide with an almost straight front margin, and by its tall, sickle-shaped first dorsal fin. A solitary, strong-swimming apex predator, the great hammerhead feeds on a wide variety of prey ranging from crustaceans and cephalopods, to bony fish, to smaller sharks. Observations of this species in the wild suggest that the cephalofoil functions to immobilize stingrays, a favored prey. This species has a viviparous mode of reproduction, bearing litters of up to 50 pups every two years.

The winghead shark is a species of hammerhead shark, and part of the family Sphyrnidae. Reaching a length of 1.9 m (6.2 ft), this small brown to gray shark has a slender body with a tall, sickle-shaped first dorsal fin. Its name comes from its exceptionally large "hammer", or cephalofoil, which can be as wide as half of the shark's total length. The function of this structure is unclear, but may relate to the shark's senses. The wide spacing of its eyes grants superb binocular vision, while the extremely long nostrils on the leading margin of the cephalofoil may allow for better detection and tracking of odor trails in the water. The cephalofoil also provides a large surface area for its ampullae of Lorenzini and lateral line, with potential benefits for electroreception and mechanoreception, respectively.

The smooth hammerhead is a species of hammerhead shark, and part of the family Sphyrnidae. This species is named "smooth hammerhead" because of the distinctive shape of the head, which is flattened and laterally extended into a hammer shape, without an indentation in the middle of the front margin. Unlike other hammerheads, this species prefers temperate waters and occurs worldwide at medium latitudes. In the summer, these sharks migrate towards the poles following cool water masses, sometimes forming schools numbering in the hundreds to thousands.

The smalleye hammerhead, also called the golden hammerhead or curry shark, is a small species of hammerhead shark in the family Sphyrnidae. This species was historically common in the shallow coastal waters of the western Atlantic Ocean, from Venezuela to Uruguay. It favors muddy habitats with poor visibility, reflected by its relatively small eyes. Adult males and juveniles are schooling and generally found apart from the solitary adult females. Typically reaching 1.2–1.3 m (3.9–4.3 ft) in length, this shark has a unique, bright golden color on its head, sides, and fins, which was only scientifically documented in the 1980s. As in all hammerheads, its head is flattened and laterally expanded into a hammer-shaped structure called the cephalofoil, which in this species is wide and long with an arched front margin bearing central and lateral indentations.

The bonnethead, also called a bonnet shark or shovelhead, is a small member of the hammerhead shark genus Sphyrna, and part of the family Sphyrnidae. It is an abundant species in the littoral zone of the North Atlantic and the Gulf of Mexico, is the only shark species known to display sexual dimorphism in the morphology of the head, and is the only shark species known to be omnivorous.

The daggernose shark is a little-known species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae, and the only extant member of its genus. It inhabits shallow tropical waters off northeastern South America, from Trinidad to northern Brazil, favoring muddy habitats such as mangroves, estuaries, and river mouths, though it is intolerant of fresh water. A relatively small shark typically reaching 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length, the daggernose shark is unmistakable for its elongated, flattened, and pointed snout, tiny eyes, and large paddle-shaped pectoral fins.

The scoophead is a little-known species of hammerhead shark, part of the family Sphyrnidae. It inhabits the tropical waters of the western Atlantic Ocean, from Panama to southern Brazil, and in the eastern Pacific Ocean from the Gulf of California to Ecuador, and probably northern Peru, as well. It is found in shallow, inshore habitats.

The smalltail shark is a species of requiem shark, and part of the family Carcharhinidae. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean, from the northern Gulf of Mexico to southern Brazil. It inhabits shallow waters close to shore, particularly over muddy bottoms around estuaries. It tends to swim low in the water column and forms large aggregations segregated by sex. A slim species generally not exceeding 1.1 m (3.6 ft) in length, the smalltail shark has a rather long, pointed snout, a broad, triangular first dorsal fin, and a second dorsal fin that originates over the midpoint of the anal fin base. It is plain gray in color, without prominent markings on its fins.
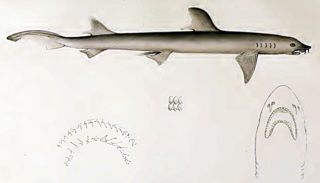
The barbeled houndshark is a species of ground shark and the only member of the family Leptochariidae. This demersal species is found in the coastal waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean from Mauritania to Angola, at depths of 10–75 m (33–246 ft). It favors muddy habitats, particularly around river mouths. The barbeled houndshark is characterized by a very slender body, nasal barbels, long furrows at the corners of the mouth, and sexually dimorphic teeth. Its maximum known length is 82 cm (32 in).
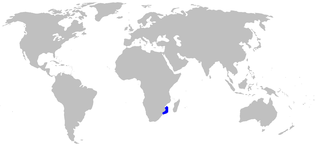
The balloon shark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to the southwestern Indian Ocean off South Africa and Mozambique. Benthic in nature, it is found over sandy and muddy flats at depths of 40–600 m (130–1,970 ft). This thick-bodied species has a broad, flattened head and a short tail; its distinguishing traits include narrow, lobe-like skin flaps in front of the nostrils, and a dorsal color pattern of faint darker saddles on a light grayish background.

The tiger catshark is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found over sandy areas and near reef peripheries off South Africa and perhaps Mozambique, from close to shore to usually no deeper than 100 m (330 ft). Reaching a length of 50 cm (20 in), this small, slim shark has a broad, flattened head with an upturned snout tip. It can additionally be identified by its dorsal colour pattern of ten dark brown saddles on a yellowish brown background.

The gecko catshark is a species of catshark, part of the family Scyliorhinidae, native to the northwestern Pacific Ocean from southern Japan to Taiwan, and possibly also off Vietnam. It is a common, demersal species found at depths of 100–900 m (330–2,950 ft). Its body is slender, with a pattern of dark saddles and blotches. The dorsal and caudal fins are edged in white, and there is a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the dorsal edge of the caudal fin. The gecko catshark is a schooling, opportunistic predator of bony fishes, cephalopods, and crustaceans. It is oviparous, with females producing two vase-shaped egg capsules at a time. This species is captured as bycatch, but does not appear to be threatened by fishery activities at present and has been assessed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

The broadfin sawtail catshark is a common species of catshark, part of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found on or near the bottom at depths of 150–540 m (490–1,770 ft), from southeastern Japan to the East China Sea. A slender species growing to 68 cm (27 in) long, this shark is characterized by a fairly long, pointed snout, a series of indistinct, dark saddles along its back and tail, and a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the dorsal edge of its caudal fin. In addition, adult males have very long claspers that reach past the anal fin. The broadfin sawtail catshark is an opportunistic predator of bony fishes, cephalopods, and crustaceans, with immature and mature sharks being primarily piscivorous. It is oviparous and reproduces year-round.

The scalloped hammerhead is a species of hammerhead shark in the family Sphyrnidae. It was originally known as Zygaena lewini. The Greek word sphyrna translates into "hammer" in English, referring to the shape of this shark's head, which is its most distinguishing characteristic. The shark's eyes and nostrils are at the tips of the extensions. It is a fairly large hammerhead, but is still smaller than both the great and smooth hammerheads.
The whitefin swellshark is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to southeastern Australia. It is found 126–554 m (413–1,818 ft) down, on the outer continental shelf and upper continental slope. Reaching 1.1 m (3.6 ft) in length, this shark has a very thick body and a short, broad, flattened head with a large mouth. It is characterized by a dorsal color pattern of dark saddles and blotches over a brown to gray background, and light fin margins. When threatened the whitefin swellshark can inflate itself with water or air to increase its size. Reproduction is oviparous. As of 2019 The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has assessed this species as Critically Endangered due to the significant decline of the population.

The broad stingray, also known as the brown stingray or Hawaiian stingray, is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. They range across the Indo-Pacific from southern Africa to Hawaii, and are the predominant species of stingray in the inshore waters of the Hawaiian Islands. This benthic fish also inhabits sandy or muddy flats at depths greater than 15 m (49 ft) in the Eastern Atlantic, from southern France to Angola, including the Mediterranean Sea. Usually growing to 1 m (3 ft) across, the broad stingray has a wide, diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc with a protruding snout tip and a long tail with a ventral fin fold. At night, this species actively forages for bottom-dwelling invertebrates and bony fishes, often near the boundaries of reefs. Reproduction is aplacental viviparous. As substantial threats to its population exist in many areas of its wide distribution, IUCN has listed this species as Vulnerable.

The Carolina hammerhead is a species of hammerhead shark, and part of the family Sphyrnidae, found in the western Atlantic Ocean. Their pupping grounds are in nearshore waters off the southeastern U.S. with the highest concentrations found in Bulls Bay, South Carolina. The Carolina hammerhead has also been found in nearshore waters off of Brazil. It was formally described in 2013. It is currently classified as Vulnerable (VU) on the IUCN Red List due to overfishing and habitat degradation.
























