Carpet sharks are sharks classified in the order Orectolobiformes. Sometimes the common name "carpet shark" is used interchangeably with "wobbegong", which is the common name of sharks in the family Orectolobidae. Carpet sharks have five gill slits, two spineless dorsal fins, and a small mouth that does not extend past the eyes. Many species have barbels.

The bluegrey carpetshark or Colclough's shark, is an uncommon species of carpet shark endemic to shallow inshore waters off northeastern Australia. It is one of the two extant members of the family Brachaeluridae. The bluegrey carpetshark has a stocky body with a wide, slightly flattened head, dorsally placed eyes, and a pair of long barbels with posterior skin flaps. It has large pectoral fins, two dorsal fins of unequal size placed far back on the body, and a sizable space between the anal fin and the base of the caudal fin. Growing to 76 cm (30 in) long, this species has a black-and-white color pattern as a juvenile, which largely fades with age such as that adults are brownish.
The rasptooth dogfish is a dogfish, found on the Kyushu–Palau Ridge in the northwest Pacific Ocean at depths of 360 m. Its maximum length is unknown. This species was originally described as Centroscyllium sheikoi, and subsequently allocated to the newly named genus Miroscyllium based on anatomical features not shared with other Centroscyllium. More recent molecular data suggest this species belongs to the genus Etmopterus, but as of June 2014 Miroscyllium sheikoi remains the valid name recognized by FishBase, the Catalog of Fishes World Register of Marine Species, and the IUCN

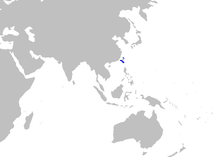
The spotless smooth-hound is a species of houndshark, in the family Triakidae, found on the continental shelves of the northwest Pacific, between latitudes 40° N and 11° N, from the surface to a depth of 300 m. It can grow to a length of up to 1 m.

The blackspotted catshark is a catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found in the waters off the coasts of Japan, Korea, China, and Taiwan between latitudes 39° N and 20° N, at the depths of between 80 and 100 m. It can grow up to 49 cm in length.

The Taiwan angelshark is an angelshark in the family Squatinidae. The Taiwan angelshark is one of four species of Squatina in the waters around Taiwan and Japan. It is a demersal, ray-like shark that grows to 1–2 meters in length.

The ocellated angelshark is an angelshark of the family Squatinidae found only from the Taiwan Straits in the western Pacific between latitudes 28 and 22°N and in northern Malaysia. Its length is up to 63 cm.

The clouded angelshark is an angelshark of the family Squatinidae found in the northwest Pacific from the southeastern Sea of Japan to Taiwan between latitudes 47° N and 22° N. Its length is up to 1.63 m.

The barbelthroat carpetshark is a carpetshark of the family Parascylliidae found in the South China Sea between Luzon in the Philippines and China, between latitudes 23°N and 10°N, at depths between 180 and 190 m. Its length is up to 34 cm.

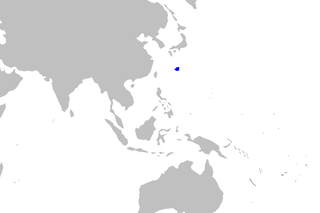
The saddle carpetshark is a carpet shark of the family Parascylliidae found around Japan, between latitudes 35°N and 24°N, at depths between 250 and 290 m. The saddle carpetshark is known to grow up to 49 cm (19 in) in length, and it is an oviparous.

The rusty carpetshark is a carpetshark of the family Parascylliidae found off southern Australia between latitudes 31°S and 41°S near the ocean floor on the continental shelf. It inhabits rocky reefs and seagrass beds 5–150 m (16–492 ft) in depth by night, hiding in caves by day. Its length is up to 80 cm (2.6 ft) TL and it feeds on crustaceans and molluscs. Reproduction is oviparous, with pups being born at 17 cm (6.7 in) in length.

The collared carpetshark is a poorly understood species of carpetshark of the family Parascylliidae endemic to the waters of eastern Australia between latitudes 26°S and 38°S. It is typically found 55–128 m (180–420 ft) in depth near the floor of rocky reefs on the continental shelf, though its depth range can extend between 20 and 230 m. At a maximum length of only 85 cm (2.79 ft), it poses no threat to humans. It is common within its range and is not targeted species. This, combined with high survival rates after discardment and a significant portion of habitat untouched by fishing are why it is listed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Reproduction is oviparous and embryos feed solely on yolk.
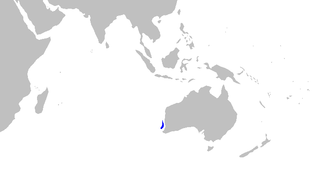
The ginger carpetshark is a species of carpetshark of the family Parascylliidae endemic to the waters off western Australia. It is a small fish at only 78.1 cm (2.56 ft) TL in length in females and harmless to humans. Its depth range is 204–245 m (669–804 ft) on the upper continental shelf. It is known from only three specimens, and so biological and population data are lacking. It is likely not under threat due to its depth range, but its limited range may make it vulnerable to fishing. Reproduction is oviparous and embryos feed solely on yolk.

The necklace carpetshark, also known as the varied carpetshark, is a carpetshark of the family Parascylliidae endemic to the waters off Australia's southern coast between latitudes 37°S and 41°S. It is found near the ocean floor over sand, rock, coral reefs, and kelp and seagrass beds at depths down to 180 m (590 ft). It is almost exclusively seen at night and spends the day hidden in caves or camouflaged on the ocean floor.

The Arabian carpetshark is a species of carpet shark in the family Hemiscylliidae, inhabiting coral reefs and other shallow coastal habitats from the Persian Gulf to India. Reaching 78 cm (31 in) long, this shark is characterized by a slender, plain brown body, and by two dorsal fins with straight trailing margins and the second smaller but longer-based than the first. The Arabian carpetshark feeds on bony fishes and invertebrates. Reproduction is oviparous with an annual cycle; females deposit egg capsules four at a time and the young hatch after 70–80 days. This small shark is often captured as bycatch but rarely used by humans. It has been assessed as Near Threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), as there is increasing fishing pressure and habitat degradation within its range. It does well in aquariums and has been bred in captivity.

The Indonesian speckled carpetshark, Hemiscyllium freycineti, is a species of bamboo shark in the family Hemiscylliidae. It is found in the shallow ocean around the Raja Ampat Islands in West Papua, Indonesia, but was formerly believed to be more widespread. This was due to confusion with H. michaeli, a species described from eastern Papua New Guinea in 2010. Compared to that species, the spots on H. freycineti are smaller, more rounded or slightly elongated in shape, and tend to darken at regular intervals forming 8-9 vertical bars on the body and tail. Furthermore, the large black spot behind the pectoral fin is more clearly defined in H. michaeli than in H. freycineti. Confusingly, some books with illustrations and photos labelled as H. freycineti actually show H. michaeli.

Hemiscyllium is a genus of sharks in the family Hemiscylliidae.

The Formosan lady's slipper or beautiful cypripedium, Cypripedium formosanum, is a species of orchid endemic to Taiwan.
Cirrhoscyllium is a genus of carpetsharks in the family Parascylliidae.