History
The Moon has been observed for millennia. Over these ages, various levels of care and precision have been possible, according to the techniques of observation available at any time. There is a correspondingly long history of lunar theories: it stretches from the times of the Babylonian and Greek astronomers, down to modern lunar laser ranging.
The history can be considered to fall into three parts: from ancient times to Newton; the period of classical (Newtonian) physics; and modern developments.
Babylon
Of Babylonian astronomy, practically nothing was known to historians of science before the 1880s. [3] Surviving ancient writings of Pliny had made bare mention of three astronomical schools in Mesopotamia – at Babylon, Uruk, and 'Hipparenum' (possibly 'Sippar'). [4] But definite modern knowledge of any details only began when Joseph Epping deciphered cuneiform texts on clay tablets from a Babylonian archive: In these texts he identified an ephemeris of positions of the Moon. [5] Since then, knowledge of the subject, still fragmentary, has had to be built up by painstaking analysis of deciphered texts, mainly in numerical form, on tablets from Babylon and Uruk (no trace has yet been found of anything from the third school mentioned by Pliny).
To the Babylonian astronomer Kidinnu (in Greek or Latin, Kidenas or Cidenas) has been attributed the invention (5th or 4th century BC) of what is now called "System B" for predicting the position of the moon, taking account that the moon continually changes its speed along its path relative to the background of fixed stars. This system involved calculating daily stepwise changes of lunar speed, up or down, with a minimum and a maximum approximately each month. [6] The basis of these systems appears to have been arithmetical rather than geometrical, but they did approximately account for the main lunar inequality now known as the equation of the center.
The Babylonians kept very accurate records for hundreds of years of new moons and eclipses. [7] Some time between the years 500 BC and 400 BC they identified and began to use the 19 year cyclic relation between lunar months and solar years now known as the Metonic cycle. [8]
This helped them build a numerical theory of the main irregularities in the Moon's motion, reaching remarkably good estimates for the (different) periods of the three most prominent features of the Moon's motion:
- The synodic month, i.e. the mean period for the phases of the Moon. Now called "System B", it reckons the synodic month as 29 days and (sexagesimally) 3,11;0,50 "time degrees", where each time degree is one degree of the apparent motion of the stars, or 4 minutes of time, and the sexagesimal values after the semicolon are fractions of a time degree. This converts to 29.530594 days = 29d 12h 44m 3.33s, [9] to compare with a modern value (as at 1900 Jan 0) of 29.530589 days, or 29d 12h 44m 2.9s. [10] This same value was used by Hipparchos and Ptolemy, was used throughout the Middle Ages, and still forms the basis of the Hebrew calendar.
- The mean lunar velocity relative to the stars they estimated at 13° 10′ 35″ per day, giving a corresponding month of 27.321598 days, [11] to compare with modern values of 13° 10′ 35.0275″ and 27.321582 days. [10]
- The anomalistic month, i.e. the mean period for the Moon's approximately monthly accelerations and decelerations in its rate of movement against the stars, had a Babylonian estimate of 27.5545833 days, [12] to compare with a modern value 27.554551 days. [10]
- The draconitic month, i.e. the mean period with which the path of the Moon against the stars deviates first north and then south in ecliptic latitude by comparison with the ecliptic path of the Sun, was indicated by a number of different parameters leading to various estimates, e.g. of 27.212204 days, [13] to compare with a modern value of 27.212221, [10] but the Babylonians also had a numerical relationship that 5458 synodic months were equal to 5923 draconitic months, [13] which when compared with their accurate value for the synodic month leads to practically exactly the modern figure for the draconitic month.
The Babylonian estimate for the synodic month was adopted for the greater part of two millennia by Hipparchus, Ptolemy, and medieval writers (and it is still in use as part of the basis for the calculated Hebrew (Jewish) calendar).
Greece and Hellenistic Egypt
Thereafter, from Hipparchus and Ptolemy in the Bithynian and Ptolemaic epochs down to the time of Newton's work in the seventeenth century, lunar theories were composed mainly with the help of geometrical ideas, inspired more or less directly by long series of positional observations of the moon. Prominent in these geometrical lunar theories were combinations of circular motions – applications of the theory of epicycles. [14]
Hipparchus
Hipparchus, whose works are mostly lost and known mainly from quotations by other authors, assumed that the Moon moved in a circle inclined at 5° to the ecliptic, rotating in a retrograde direction (i.e. opposite to the direction of annual and monthly apparent movements of the Sun and Moon relative to the fixed stars) once in 182⁄3 years. The circle acted as a deferent, carrying an epicycle along which the Moon was assumed to move in a retrograde direction. The center of the epicycle moved at a rate corresponding to the mean change in Moon's longitude, while the period of the Moon around the epicycle was an anomalistic month. This epicycle approximately provided for what was later recognized as the elliptical inequality, the equation of the center, and its size approximated to an equation of the center of about 5° 1'. This figure is much smaller than the modern value: but it is close to the difference between the modern coefficients of the equation of the center (1st term) and that of the evection: the difference is accounted for by the fact that the ancient measurements were taken at times of eclipses, and the effect of the evection (which subtracts under those conditions from the equation of the center) was at that time unknown and overlooked. For further information see also separate article Evection.
Ptolemy
Ptolemy's work the Almagest had wide and long-lasting acceptance and influence for over a millennium. He gave a geometrical lunar theory that improved on that of Hipparchus by providing for a second inequality of the Moon's motion, using a device that made the apparent apogee oscillate a little – prosneusis of the epicycle. This second inequality or second anomaly accounted rather approximately, not only for the equation of the center, but also for what became known (much later) as the evection. But this theory, applied to its logical conclusion, would make the distance (and apparent diameter) of the Moon appear to vary by a factor of about 2, which is clearly not seen in reality. [15] (The apparent angular diameter of the Moon does vary monthly, but only over a much narrower range of about 0.49°–0.55°. [16] ) This defect of the Ptolemaic theory led to proposed replacements by Ibn al-Shatir in the 14th century [17] and by Copernicus in the 16th century. [18]
Ibn al-Shatir and Copernicus
Significant advances in lunar theory were made by the Arab astronomer, Ibn al-Shatir (1304–1375). Drawing on the observation that the distance to the Moon did not change as drastically as required by Ptolemy's lunar model, he produced a new lunar model that replaced Ptolemy's crank mechanism with a double epicycle model that reduced the computed range of distances of the Moon from the Earth. [17] [19] A similar lunar theory, developed some 150 years later by the Renaissance astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus, had the same advantage concerning the lunar distances. [20] [21]
Tycho Brahe, Johannes Kepler, and Jeremiah Horrocks
Tycho Brahe and Johannes Kepler refined the Ptolemaic lunar theory, but did not overcome its central defect of giving a poor account of the (mainly monthly) variations in the Moon's distance, apparent diameter and parallax. Their work added to the lunar theory three substantial further discoveries.
- The nodes and the inclination of the lunar orbital plane both appear to librate, with a monthly (according to Tycho) or semi-annual period (according to Kepler).
- The lunar longitude has a twice-monthly Variation , by which the Moon moves faster than expected at new and full moon, and slower than expected at the quarters.
- There is also an annual effect, by which the lunar motion slows down a little in January and speeds up a little in July: the annual equation.
The refinements of Brahe and Kepler were recognized by their immediate successors as improvements, but their seventeenth-century successors tried numerous alternative geometrical configurations for the lunar motions to improve matters further. A notable success was achieved by Jeremiah Horrocks, who proposed a scheme involving an approximate 6 monthly libration in the position of the lunar apogee and also in the size of the elliptical eccentricity. This scheme had the great merit of giving a more realistic description of the changes in distance, diameter and parallax of the Moon.
Newton
This section needs additional citations for verification .(January 2023) |
A first gravitational period for lunar theory started with the work of Newton. He was the first to define the problem of the perturbed motion of the Moon in recognisably modern terms. His groundbreaking work is shown for example in the Principia [22] in all versions including the first edition published in 1687.
Newton's biographer, David Brewster, reported that the complexity of Lunar Theory impacted Newton's health: "[H]e was deprived of his appetite and sleep" during his work on the problem in 1692–3, and told the astronomer John Machin that "his head never ached but when he was studying the subject". According to Brewster, Edmund Halley also told John Conduitt that when pressed to complete his analysis Newton "always replied that it made his head ache, and kept him awake so often, that he would think of it no more" [Emphasis in original]. [23]
Solar perturbation of lunar motion
This section possibly contains original research .(January 2023) |
Newton identified how to evaluate the perturbing effect on the relative motion of the Earth and Moon, arising from their gravity towards the Sun, in Book 1, Proposition 66, [24] and in Book 3, Proposition 25. [25] The starting-point for this approach is Corollary VI to the laws of motion. [26] This shows that if the external accelerative forces from some massive body happens to act equally and in parallel on some different other bodies considered, then those bodies would be affected equally, and in that case their motions (relative to each other) would continue as if there were no such external accelerative forces at all. It is only in the case that the external forces (e.g. in Book 1, Prop. 66, and Book 3, Prop. 25, the gravitational attractions towards the Sun) are different in size or in direction in their accelerative effects on the different bodies considered (e.g. on the Earth and Moon), that consequent effects are appreciable on the relative motions of the latter bodies. (Newton referred to accelerative forces or accelerative gravity due to some external massive attractor such as the Sun. The measure he used was the acceleration that the force tends to produce (in modern terms, force per unit mass), rather than what we would now call the force itself.)
Thus Newton concluded that it is only the difference between the Sun's accelerative attraction on the Moon and the Sun's attraction on the Earth that perturbs the motion of the Moon relative to the Earth.
Newton then in effect used vector decomposition of forces, [27] to carry out this analysis. In Book 1, Proposition 66 and in Book 3, Proposition 25, [28] he showed by a geometrical construction, starting from the total gravitational attraction of the Sun on the Earth, and of the Sun on the Moon, the difference that represents the perturbing effect on the motion of the Moon relative to the Earth. In summary, line LS in Newton's diagram as shown below represents the size and direction of the perturbing acceleration acting on the Moon in the Moon's current position P (line LS does not pass through point P, but the text shows that this is not intended to be significant, it is a result of the scale factors and the way the diagram has been built up).

Shown here is Newton's diagram from the first (1687) Latin edition of the Principia (Book 3, Proposition 25, p. 434). Here he introduced his analysis of perturbing accelerations on the Moon in the Sun-Earth-Moon system. Q represents the Sun, S the Earth, and P the Moon.
Parts of this diagram represent distances, other parts gravitational accelerations (attractive forces per unit mass). In a dual significance, SQ represents the Earth-Sun distance, and then it also represents the size and direction of the Earth-Sun gravitational acceleration. Other distances in the diagram are then in proportion to distance SQ. Other attractions are in proportion to attraction SQ.
The Sun's attractions are SQ (on the Earth) and LQ (on the Moon). The size of LQ is drawn so that the ratio of attractions LQ:SQ is the inverse square of the ratio of distances PQ:SQ. (Newton constructs KQ=SQ, giving an easier view of the proportions.) The Earth's attraction on the Moon acts along direction PS. (But line PS signifies only distance and direction so far, nothing has been defined about the scale factor between solar and terrestrial attractions).
After showing solar attractions LQ on the Moon and SQ on the Earth, on the same scale, Newton then makes a vector decomposition of LQ into components LM and MQ. Then he identifies the perturbing acceleration on the Moon as the difference of this from SQ. SQ and MQ are parallel to each other, so SQ can be directly subtracted from MQ, leaving MS. The resulting difference, after subtracting SQ from LQ, is therefore the vector sum of LM and MS: these add up to a perturbing acceleration LS.
Later Newton identified another resolution of the perturbing acceleration LM+MS = LS, into orthogonal components: a transverse component parallel to LE, and a radial component, effectively ES.

Newton's diagrammatic scheme, since his time, has been re-presented in other and perhaps visually clearer ways. Shown here is a vector presentation [29] indicating, for two different positions, P1 and P2, of the Moon in its orbit around the Earth, the respective vectors LS1 and LS2 for the perturbing acceleration due to the Sun. The Moon's position at P1 is fairly close to what it was at P in Newton's diagram; corresponding perturbation LS1 is like Newton's LS in size and direction. At another position P2, the Moon is farther away from the Sun than the Earth is, the Sun's attraction LQ2 on the Moon is weaker than the Sun's attraction SQ=SQ2 on the Earth, and then the resulting perturbation LS2 points obliquely away from the Sun.
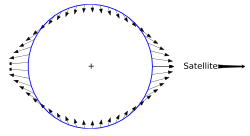
Constructions like those in Newton's diagram can be repeated for many different positions of the Moon in its orbit. For each position, the result is a perturbation vector like LS1 or LS2 in the second diagram. Shown here is an often-presented form of the diagram that summarises sizes and directions of the perturbation vectors for many different positions of the Moon in its orbit. Each small arrow is a perturbation vector like LS, applicable to the Moon in the particular position around the orbit from which the arrow begins. The perturbations on the Moon when it is nearly in line along the Earth-Sun axis, i.e. near new or full moon, point outwards, away from the Earth. When the Moon-Earth line is 90° from the Earth-Sun axis they point inwards, towards the Earth, with a size that is only half the maximum size of the axial (outwards) perturbations. (Newton gave a rather good quantitative estimate for the size of the solar perturbing force: at quadrature where it adds to the Earth's attraction he put it at 1⁄178.725 of the mean terrestrial attraction, and twice as much as that at the new and full moons where it opposes and diminishes the Earth's attraction.) [28]
Newton also showed that the same pattern of perturbation applies, not only to the Moon, in its relation to the Earth as disturbed by the Sun, but also to other particles more generally in their relation to the solid Earth as disturbed by the Sun (or by the Moon); for example different portions of the tidal waters at the Earth's surface. [a] The study of the common pattern of these perturbing accelerations grew out of Newton's initial study of the perturbations of the Moon, which he also applied to the forces moving tidal waters. Nowadays this common pattern itself has become often known as a tidal force whether it is being applied to the disturbances of the motions of the Moon, or of the Earth's tidal waters – or of the motions of any other object that suffers perturbations of analogous pattern.
After introducing his diagram 'to find the force of the Sun to perturb the Moon' in Book 3, Proposition 25, Newton developed a first approximation to the solar perturbing force, showing in further detail how its components vary as the Moon follows its monthly path around the Earth. He also took the first steps in investigating how the perturbing force shows its effects by producing irregularities in the lunar motions. [b]
For a selected few of the lunar inequalities, Newton showed in some quantitative detail how they arise from the solar perturbing force.
Much of this lunar work of Newton's was done in the 1680s, and the extent and accuracy of his first steps in the gravitational analysis was limited by several factors, including his own choice to develop and present the work in what was, on the whole, a difficult geometrical way, and by the limited accuracy and uncertainty of many astronomical measurements in his time.

















