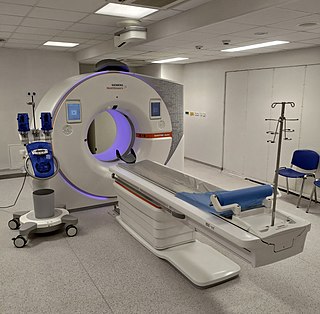
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.

Radiology is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography, but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation, as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above.

Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating and not passing gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital.

A lower gastrointestinal series is a medical procedure used to examine and diagnose problems with the human colon of the large intestine. Radiographs are taken while barium sulfate, a radiocontrast agent, fills the colon via an enema through the rectum.

Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common mesenchymal neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract. GISTs arise in the smooth muscle pacemaker interstitial cell of Cajal, or similar cells. They are defined as tumors whose behavior is driven by mutations in the KIT gene (85%), PDGFRA gene (10%), or BRAF kinase (rare). 95% of GISTs stain positively for KIT (CD117). Most (66%) occur in the stomach and gastric GISTs have a lower malignant potential than tumors found elsewhere in the GI tract.

An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as barium sulfate mixed with water, is ingested or instilled into the gastrointestinal tract, and X-rays are used to create radiographs of the regions of interest. The barium enhances the visibility of the relevant parts of the gastrointestinal tract by coating the inside wall of the tract and appearing white on the film. This in combination with other plain radiographs allows for the imaging of parts of the upper gastrointestinal tract such as the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine such that the inside wall lining, size, shape, contour, and patency are visible to the examiner. With fluoroscopy, it is also possible to visualize the functional movement of examined organs such as swallowing, peristalsis, or sphincter closure. Depending on the organs to be examined, barium radiographs can be classified into "barium swallow", "barium meal", "barium follow-through", and "enteroclysis". To further enhance the quality of images, air or gas is sometimes introduced into the gastrointestinal tract in addition to barium, and this procedure is called double-contrast imaging. In this case the gas is referred to as the negative contrast medium. Traditionally the images produced with barium contrast are made with plain-film radiography, but computed tomography is also used in combination with barium contrast, in which case the procedure is called "CT enterography".
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography, projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation.

Virtual colonoscopy is the use of CT scanning or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce two- and three-dimensional images of the colon, from the lowest part, the rectum, to the lower end of the small intestine, and to display the images on an electronic display device. The procedure is used to screen for colon cancer and polyps, and may detect diverticulosis. A virtual colonoscopy can provide 3D reconstructed endoluminal views of the bowel. VC provides a secondary benefit of revealing diseases or abnormalities outside the colon.

Diatrizoate, also known as amidotrizoate, is a contrast agent used during X-ray imaging. This includes visualizing veins, the urinary system, spleen, and joints, as well as computer tomography. It is given by mouth, injection into a vein, injection into the bladder, through a nasogastric tube, or rectally.

Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to image blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography is used to generate images of arteries in order to evaluate them for stenosis, occlusions, aneurysms or other abnormalities. MRA is often used to evaluate the arteries of the neck and brain, the thoracic and abdominal aorta, the renal arteries, and the legs.

An abdominal x-ray is an x-ray of the abdomen. It is sometimes abbreviated to AXR, or KUB.

High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing the lung parenchyma. On the other hand, HRCT of the temporal bone is used to diagnose various middle ear diseases such as otitis media, cholesteatoma, and evaluations after ear operations.
MRI contrast agents are contrast agents used to improve the visibility of internal body structures in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The most commonly used compounds for contrast enhancement are gadolinium-based. Such MRI contrast agents shorten the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues following oral or intravenous administration.
Endoexoenteric refers to a specific radiographic manifestation of lymphoma of the bowel.

Cone beam computed tomography is a medical imaging technique consisting of X-ray computed tomography where the X-rays are divergent, forming a cone.

Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis is an application of computed tomography (CT) and is a sensitive method for diagnosis of abdominal diseases. It is used frequently to determine stage of cancer and to follow progress. It is also a useful test to investigate acute abdominal pain. Renal stones, appendicitis, pancreatitis, diverticulitis, abdominal aortic aneurysm, and bowel obstruction are conditions that are readily diagnosed and assessed with CT. CT is also the first line for detecting solid organ injury after trauma.
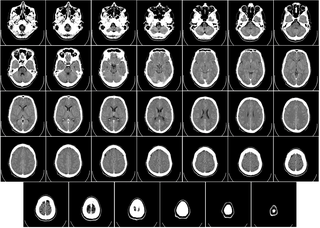
Computed tomography of the head uses a series of X-rays in a CT scan of the head taken from many different directions; the resulting data is transformed into a series of cross sections of the brain using a computer program. CT images of the head are used to investigate and diagnose brain injuries and other neurological conditions, as well as other conditions involving the skull or sinuses; it used to guide some brain surgery procedures as well. CT scans expose the person getting them to ionizing radiation which has a risk of eventually causing cancer; some people have allergic reactions to contrast agents that are used in some CT procedures.

Val Murray Runge is an American and Swiss professor of radiology and the editor-in-chief of Investigative Radiology. Runge was one of the early researchers to investigate the use of gadolinium-based contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), giving the first presentation in this field, followed two years later by the first presentation of efficacy. His research also pioneered many early innovations in MRI, including the use of tilted planes and respiratory gating. His publication on multiple sclerosis in 1984 represented the third and largest clinical series investigating the role of MRI in this disease, and the first to show characteristic abnormalities on MRI in patients whose CT was negative.

Medical imaging in pregnancy may be indicated because of pregnancy complications, intercurrent diseases or routine prenatal care.
Computed tomography enterography is a medical imaging technique which uses computed tomography scanner and contrast media to examine the small bowel. It was first introduced by Raptopoulos et al. in 1997. CT Enterography can be used to assess a variety of problems involving the small bowel, however it is mainly used to diagnosis and assess severity of Crohn's disease.















