Melaleuca is a genus of nearly 300 species of plants in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae, commonly known as paperbarks, honey-myrtles, bottlebrushes or tea-trees. They range in size from small shrubs that rarely grow to more than 16 m (52 ft) high, to trees up to 35 m (115 ft). Their flowers generally occur in groups, forming a "head" or "spike" resembling a brush used for cleaning bottles, containing up to 80 individual flowers.

Melaleuca linariifolia is a plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae, and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is commonly known as snow-in-summer, narrow-leaved paperbark, flax-leaved paperbark and in the language of the Gadigal people as budjur. A hardy plant, it flowers prolifically in late spring or summer, making it a popular garden shrub or small tree in temperate places. Melaleuca trichostachya is a similar species but its leaves are arranged differently and the fruits have projecting valves.

Melaleuca styphelioides, known as the prickly-leaved paperbark or prickly paperbark, is a plant native to eastern Australia. It is a tree with spongy bark, prickly leaves and spikes of creamy-white flowers.

Melaleuca preissiana, commonly known as stout paperbark, modong or moonah, is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to coastal areas of southwest Australia. It is a shrub or small tree with papery bark, small leaves and spikes of usually white flowers. It occurs chiefly in areas that are seasonally wet.

Melaleuca leucadendra, commonly known as weeping paperbark, long-leaved paperbark or white paperbark is a species of woody plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae, and is widespread in northern Australia, Southeast Asia, New Guinea and the Torres Strait Islands. It grows as a tree to more than 20 m (70 ft) with a trunk covered with thick, white, papery bark and weeping thinner branches. It has a long flowering season, can flower at almost any time of the year and is often grown as a tree in parks and on roadsides. It was the first melaleuca to be described and was described from a specimen growing in Indonesia.

Melaleuca rhaphiophylla, commonly known as swamp paperbark is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south west of Western Australia. It has narrow, needle-like leaves and profuse spikes of white or yellowish flowers at variable times throughout the year. As its common name suggests, it is usually found in salt marshes, or swamps or along watercourses and occurs over wide areas of the south-west.

Melaleuca lanceolata commonly known as black paperbark, moonah, Rottnest Island teatree and western black tea tree is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is native to Australia where it occurs in Western Australia, South Australia, Victoria, New South Wales and Queensland. It is a densely foliaged tree with rough bark, which flowers prolifically in summer.

Melaleuca ericifolia, commonly known as swamp paperbark, is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and the genus Melaleuca, native to south-eastern Australia. It is a rather variable species and some specimens resemble Melaleuca armillaris but its papery bark and smaller, more prolific flower heads distinguish it from that species. It often grows in swampy areas and the draining and clearing of these has reduced the numbers of the species, especially around Port Philip Bay near Melbourne. It is also similar to Melaleuca pustulata, a Tasmanian endemic, but that species only grows in dry heath.

Melaleuca squarrosa, commonly known as scented paperbark, is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to south eastern parts of Australia, especially Tasmania. It is an attractive shrub with dense foliage and arching branches and it flowers profusely in spring or early summer, bearing spikes of perfumed yellow to white flowers.

Melaleuca linearifolia, commonly known as netted bottlebrush, is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to New South Wales in Australia.. It is a shrub with narrow, pointed leaves and red flower spikes in spring or summer.

Melaleuca squamophloia is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the black soil plains of south eastern Queensland in Australia. Like its close relative Melaleuca styphelioides, it is a small, erect tree with prickly leaves and spikes of cream or white flowers but its bark is hard rather than papery and the leaves have fewer veins than that species.

Melaleuca thymifolia, commonly known as thyme honey-myrtle, is a plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae and is native to eastern Australia. It is often noticed in spring, with its attractive, purple flowers and is one of the most commonly cultivated melaleucas. A fragrant shrub, it usually grows to about 1.0 m (3 ft) tall, has corky bark and slender, wiry stems.

Gaudium trinervium, commonly known as flaky-barked tea-tree, slender tea-tree or paperbark tree, is a species of shrub or small tree that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has papery bark that is shed in thin, flaking layers, narrow elliptic to broadly egg-shaped leaves with the narrower at the base, white flowers and silky-hairy fruit that falls from the plant when mature.

Melaleuca nodosa, commonly known as the prickly-leaved paperbark, is a plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae, and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a shrub or small tree with narrow, sometimes needle-like leaves and profuse heads of yellow flowers as early as April or as late as January.

Goodenia paniculata, commonly known as branched goodenia, is a species of plant in the family Goodeniaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a short-lived herb with egg-shaped to lance-shaped leaves with toothed edges and racemes of yellow flowers.

Melaleuca pustulata, commonly known as yellow paperbark, warty paperbark or Cranbrook paperbark is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to Tasmania in Australia. It is an uncommon shrub, one of only two melaleucas that are endemic to that state and one of only eight found naturally occurring there. It has thick, pimply leaves, hairy new growth and large numbers of heads of pale yellow, fragrant flowers in spring or early summer.

Melaleuca diosmatifolia, commonly known as rosy paperbark and pink honey-myrtle is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is native to Queensland and New South Wales in Australia. It was formerly known as Melaleuca erubescens but is not closely related to Melaleuca diosmifolia although the species name has the same meaning. It has pointed, non-prickly leaves and cylindrical spikes of pink or purple flowers.

Melaleuca groveana, commonly known as Grove's paperbark is a plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae and is endemic to New South Wales and Queensland in Australia. It is an uncommon species with relatively large heads of white flowers in spring, the styles of which are significantly longer than the stamens.

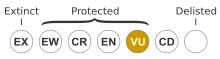
Melaleuca irbyana, commonly known as weeping paperbark, bushhouse paperbark and swamp paperbark, is a plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae and is endemic to New South Wales and Queensland in Australia. It is a shrub or small tree, often growing in pure stands in poorly drained areas. Its distribution is limited and it has been classified as an endangered species under legislation in both states and the forest as critically endangered under Australian government legislation.

Melaleuca tamariscina, commonly known as bush-house paperbark or tamarix honey-myrtle is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to central Queensland in Australia. It grows to the height of a small tree with small, scale-like leaves that are pressed against the branches, and has a papery bark and a weeping habit.