
Omomyidae is a group of early primates that radiated during the Eocene epoch between about 55 to 34 million years ago (mya). Fossil omomyids are found in North America, Europe & Asia making it one of two groups of Eocene primates with a geographic distribution spanning holarctic continents, the other being the adapids. Early representatives of the Omomyidae and Adapidae appear suddenly at the beginning of the Eocene in North America, Europe, and Asia, and are the earliest known crown primates.

Purgatorius is a genus of seven extinct eutherian species typically believed to be the earliest example of a primate or a proto-primate, a primatomorph precursor to the Plesiadapiformes, dating to as old as 66 million years ago. The first remains were reported in 1965, from what is now eastern Montana's Tullock Formation, specifically at Purgatory Hill in deposits believed to be about 63 million years old, and at Harbicht Hill in the lower Paleocene section of the Hell Creek Formation. Both locations are in McCone County.

Plesiadapis is one of the oldest known primate-like mammal genera which existed about 58–55 million years ago in North America and Europe. Plesiadapis means "near-Adapis", which is a reference to the adapiform primate of the Eocene period, Adapis. Plesiadapis tricuspidens, the type specimen, is named after the three cusps present on its upper incisors.

Adapiformes is a group of early primates. Adapiforms radiated throughout much of the northern continental mass, reaching as far south as northern Africa and tropical Asia. They existed from the Eocene to the Miocene epoch. Some adapiforms resembled living lemurs.
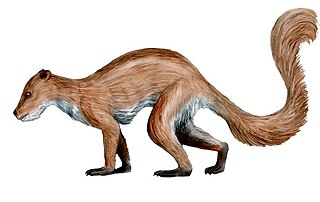
Plesiadapiformes is a group of Primates, a sister of the Dermoptera. While none of the groups normally directly assigned to this group survived, the group appears actually not to be literally extinct as the remaining primates appear to be derived Plesiadapiformes, as a sister of e.g. the Carpolestidae. The term Plesiadapiformes may still be used for all primates which are not crown primates, but this usage is paraphyletic. When the crown primates are cladistically granted, it becomes an obsolete junior synonym to primates. Purgatorius is believed to be a basal Plesiadapiformes.

Miacids are extinct primitive carnivoramorphans within the family Miacidae that lived during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs, about 62–34 million years ago. Miacids existed for approximately 28 million years.

Megalonychidae is an extinct family of sloths including the extinct Megalonyx. Megalonychids first appeared in the early Oligocene, about 35 million years (Ma) ago, in southern Argentina (Patagonia). There is actually one possible find dating to the Eocene, about 40 Ma ago, on Seymour Island in Antarctica. They first reached North America by island-hopping across the Central American Seaway, about 9 million years ago, prior to formation of the Isthmus of Panama about 2.7 million years ago. Some megalonychid lineages increased in size as time passed. The first species of these were small and may have been partly tree-dwelling, whereas the Pliocene species were already approximately half the size of the huge Late Pleistocene Megalonyx jeffersonii from the last ice age.

Teilhardina was an early marmoset-like primate that lived in Europe, North America and Asia during the Early Eocene epoch, about 56-47 million years ago. The paleontologist George Gaylord Simpson is credited with naming it after the French paleontologist, Jesuit and philosopher Teilhard de Chardin.

Plesiadapidae is a family of plesiadapiform mammals related to primates known from the Paleocene and Eocene of North America, Europe, and Asia. Plesiadapids were abundant in the late Paleocene, and their fossils are often used to establish the ages of fossil faunas.

Carpolestes is a genus of extinct primate-like mammals from the late Paleocene of North America. It first existed around 58 million years ago. The three species of Carpolestes appear to form a lineage, with the earliest occurring species, C. dubius, ancestral to the type species, C. nigridens, which, in turn, was ancestral to the most recently occurring species, C. simpsoni.
The Paleocene, or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek παλαιός palaiós meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch, translating to "the old part of the Eocene".
Altiatlasius is an extinct genus of mammal, which may have been the oldest known primate, dating to the Late Paleocene from Morocco. The only species, Altiatlasius koulchii, was described in 1990.

The Itaboraian age is a period within the Early Eocene geologic time epoch of the Paleogene, used more specifically with South American land mammal ages (SALMA). It follows the Riochican and precedes the Casamayoran age.
Microsyops is a plesiadapiform primate found in Middle Eocene in North America. It is in the family Microsyopidae. It appears to have had a more developed sense of smell than other early primates. It is believed to have eaten fruit, and its fossils show the oldest known dental cavities in a mammal.

Ignacius is a genus of extinct mammal from the early Cenozoic era. This genus is present in the fossil record from around 62-33 Ma. The earliest known specimens of Ignacius come from the Torrejonian of the Fort Union Formation, Wyoming and the most recent known specimen of Ignacius was found in the Medicine Pole Hills of North Dakota. Ignacius is one of ten genera within the family Paromomyidae, the longest living family of any plesiadapiforms, persisting for around 30 Ma during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. The analyses of postcranial fossils by paleontologists suggest that members of the family Paromomyidae, including the genus Ignacius, most likely possessed adaptations for arboreality.
Bownomomys was an early marmoset-like primate that lived in North America during the Early Eocene epoch, about 56-50 million years ago.
Wyonycteris is a genus of small mammals that existed in the late Paleocene and early Eocene epochs. The type species is Wyonycteris chalix, which lived in Wyoming during the Clarkforkian North American Land Mammal Age of the Paleocene and was originally proposed to be an early form of insectivorous bat. Later re-examination of the material has put this alliance in doubt, and the genus has instead been proposed as belonging to the subfamily Placentidentinae, within the family Nyctitheriidae. Similar fossil material of the same time period found in Europe was later discovered and described as new species, Wyonycteris richardi.
Navajovius is an extinct genus of plesiadapiforms that lived during the Paleocene epoch. Plesiadapiforms were small, arboreal mammals that are theorized to be either closely related to primates or dermopterans. Navajovius has only been documented from localities within North America. This genus was officially named in 1921 by Walter Granger and William Matthew and the type specimen is housed at the American Museum of Natural History.
Saxonella is a genus of extinct primate from the Paleocene Epoch, 66-56 Ma. The genus is present in the fossil record from around ~62-57 Ma. Saxonella has been found in fissure fillings in Walbeck, Germany as well as in the Paskapoo Formation in Alberta, Canada. Saxonella is one of five families within the superfamily Plesiadapoidae, which appears in the fossil record from the mid Paleocene to the early Eocene. Analyses of molars by paleontologists suggest that Saxonella most likely had a folivorous diet.
Torrejonia is a genus of extinct plesiadapiform that belongs to the family Palaechthonidae. There are currently two species known, T. wilsoni and T. sirokyi. This genus is present in the fossil record from around 62-58 Ma. Species belonging to this genus are suggested to be plesiadapiforms based on adaptations observed in the skeletal morphology consistent with arboreal locomotor behavior. Following the mass extinction event at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary (K-Pg), a large diversity of plesiadapiform families were documented beginning at the Torrejonian NALMA. Research has shown that T. wilsoni is one of the largest palaechthonids and is reconstructed as being more frugivorous than other palaechthonids.
















