
The treeshrews are small mammals native to the tropical forests of South and Southeast Asia. They make up the entire order Scandentia, which split into two families: the Tupaiidae, and the Ptilocercidae.

Rails are a large, cosmopolitan family of small- to medium-sized terrestrial and/or semi-amphibious birds. The family exhibits considerable diversity in its forms, and includes such ubiquitous species as the crakes, coots, and gallinule; other rail species are extremely rare or endangered. Many are associated with wetland habitats, some being semi-aquatic like waterfowl, but many more are wading birds or shorebirds. The ideal rail habitats are marsh areas, including rice paddies, and flooded fields or open forest. They are especially fond of dense vegetation for nesting. The rail family is found in every terrestrial habitat with the exception of dry desert, polar or freezing regions, and alpine areas. Members of Rallidae occur on every continent except Antarctica. Numerous unique island species are known.

Struthionidae is a family of flightless birds, containing the extant ostriches and their extinct relatives. The two extant species of ostrich are the common ostrich and Somali ostrich, both in the genus Struthio, which also contains several species known from Holocene fossils such as the Asian ostrich. The common ostrich is the more widespread of the two living species, and is the largest living bird species. The extinct genus Pachystruthio from the Late Pliocene-Early Pleistocene of Eurasia is one of the largest birds ever.

The bird family Sulidae comprises the gannets and boobies. Collectively called sulids, they are medium-large coastal seabirds that plunge-dive for fish and similar prey. The 10 species in this family are often considered congeneric in older sources, placing all in the genus Sula. However, Sula and Morus (gannets) can be readily distinguished by morphological, behavioral, and DNA sequence characters. Abbott's booby (Papasula) is given its own genus, as it stands apart from both in these respects. It appears to be a distinct and ancient lineage, maybe closer to the gannets than to the true boobies.

Galeocerdo is a genus of ground shark. Only a single species, G. cuvier, the tiger shark is extant. The earliest fossils date back to the early Eocene epoch, (Ypresian), around 56–47.8 Million years ago. While historically considered a member of the requiem shark family Carcharhinidae, it is currently considered to be the only member of the family Galeocerdonidae. While this genus was historically considered diverse, including 21 extinct species, morphometric analysis conducted in 2021 suggested that the diversity of the genus included only 5 extinct species much lower than previously assumed. The oldest fossils of the extant G. cuvier date to the middle Miocene.

Thylacinidae is an extinct family of carnivorous marsupials from the order Dasyuromorphia. The only species to survive into modern times was the thylacine, which became extinct in 1936.

Dipteronia is a genus with two living and one extinct species in the soapberry family Sapindaceae. The living species are native to central and southern China, The fossil species has been found in Middle Paleocene to Early Oligocene sediments of North America and China.

Ground squirrels are rodents of the squirrel family (Sciuridae) that generally live on the ground or in burrows, rather than in trees like the tree squirrels. The term is most often used for the medium-sized ground squirrels, as the larger ones are more commonly known as marmots or prairie dogs, while the smaller and less bushy-tailed ground squirrels tend to be known as chipmunks.

Anseranatidae, the magpie-geese, is a biological family of waterbirds. The only living species, the magpie goose, is a resident breeder in northern Australia and in southern New Guinea.

Nimravidae is an extinct family of carnivorans, sometimes known as false saber-toothed cats, whose fossils are found in North America and Eurasia. Not considered to belong to the true cats, the nimravids are generally considered closely related and classified as a distinct family in the suborder Feliformia. Fossils have been dated from the Middle Eocene through the Late Miocene epochs, spanning about 33.2 million years.

Paraceratherium is an extinct genus of hornless rhinocerotoids belonging to the family Paraceratheriidae. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has ever existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch. The first fossils were discovered in what is now Pakistan, and remains have been found across Eurasia between China and the Balkans. Paraceratherium means "near the hornless beast", in reference to Aceratherium, the genus in which the type species P. bugtiense was originally placed.

Squalodon is an extinct genus of whales of the Oligocene and Miocene epochs, belonging to the family Squalodontidae. Named by Jean-Pierre Sylvestre de Grateloup in 1840, it was originally believed to be an iguanodontid dinosaur but has since been reclassified. The name Squalodon comes from Squalus, a genus of shark. As a result, its name means "shark tooth". Its closest modern relative is the South Asian river dolphin.

Sciurini is a tribe that includes about forty species of squirrels, mostly from the Americas. It includes five living genera—the American dwarf squirrels, Microsciurus; the Bornean Rheithrosciurus; the widespread American and Eurasian tree squirrels of the genus Sciurus, which includes some of the best known squirrel species; the Central American Syntheosciurus; and the American pine squirrels, Tamiasciurus. Like other arboreal squirrels, they are sometimes referred to as tree squirrels.
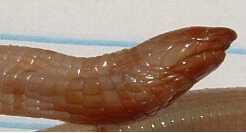
Rhineuridae is a family of amphisbaenians that includes one living genus and species, Rhineura floridana, as well as many extinct species belonging to both Rhineura and several extinct genera. The living R. floridana is found only in Georgia and Florida, but extinct species ranged across North America, some occurring as far west as Oregon. The family has a fossil record stretching back 60 million years to the Paleocene and was most diverse in the continental interior during the Eocene and Oligocene.

The pen-tailed treeshrew is a treeshrew of the family Ptilocercidae native to southern Thailand, the Malay Peninsula, Borneo, and some Indonesian islands.

The Cameroon scaly-tail, also referred to as the Cameroon anomalure, flightless anomalure or flightless scaly-tail, is a rodent species endemic to West Central Africa. The scientific literature has never reported observations of live individuals. The taxonomic classification of the species has been subject to recent revision.

Tupaia is a treeshrew genus in the family Tupaiidae that was first described by Thomas Stamford Raffles in 1821. The name of this genus derives from the Malay word tupai meaning squirrel or small animal resembling a squirrel.

Tupaiidae is one of two families of treeshrews, the other family being Ptilocercidae. The family contains three living genera and 19 living species. The family name derives from tupai, the Malay word for treeshrew and also for squirrel which tupaiids superficially resemble. The former genus Urogale was disbanded in 2011 when the Mindanao treeshrew was moved to Tupaia based on a molecular phylogeny.
Tupaia miocenica is a fossil treeshrew from the Miocene of Thailand. Known only from a single tooth, an upper first or second molar, it is among the few known fossil treeshrews. With a length of 3.57 mm, the tooth is large for a treeshrew. At the back lingual corner, the tooth shows a small cusp, the hypocone, that is separated from the protocone in front of it by a narrow valley. The condition of the hypocone distinguishes this species from various other treeshrews. In addition, the presence of a well-developed but simple mesostyle is distinctive.
Laomaki is a genus of adapiform primate that lived during the Early Oligocene in Asia, containing only the species Laomaki yunnanensis. It was described from a right maxilla fragment. Its molars and premolars are somewhat similar to those of Rencunius and Anthradapis respectively. Its placement within the family Sivaladapidae is uncertain; it has not been placed in a subfamily. It has been found at sites in Jammu and Kashmir and Yunnan, having lived around the time of the Eocene–Oligocene transition.























