
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. The aortic valve normally has three cusps or leaflets, although in 1–2% of the population it is found to congenitally have two leaflets. The aortic valve is the last structure in the heart the blood travels through before stopping the flow through the systemic circulation.

The mitral valve, also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-way valves allowing blood flow in just one direction. The mitral valve and the tricuspid valve are known as the atrioventricular valves because they lie between the atria and the ventricles.

Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. It is the primary form of myxomatous degeneration of the valve. There are various types of MVP, broadly classified as classic and nonclassic. In severe cases of classic MVP, complications include mitral regurgitation, infective endocarditis, congestive heart failure, and, in rare circumstances, cardiac arrest.

Mitral stenosis is a valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the opening of the mitral valve of the heart. It is almost always caused by rheumatic valvular heart disease. Normally, the mitral valve is about 5 cm2 during diastole. Any decrease in area below 2 cm2 causes mitral stenosis. Early diagnosis of mitral stenosis in pregnancy is very important as the heart cannot tolerate increased cardiac output demand as in the case of exercise and pregnancy. Atrial fibrillation is a common complication of resulting left atrial enlargement, which can lead to systemic thromboembolic complications such as stroke.
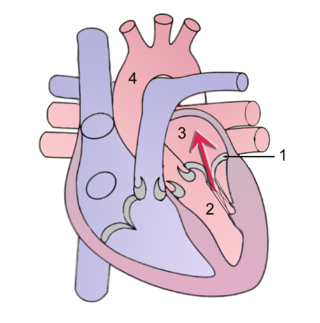
Mitral regurgitation (MR), also known as mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence, is a form of valvular heart disease in which the mitral valve is insufficient and does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood. It is the abnormal leaking of blood backwards – regurgitation from the left ventricle, through the mitral valve, into the left atrium, when the left ventricle contracts. Mitral regurgitation is the most common form of valvular heart disease.
Aortic valve replacement is a cardiac surgery procedure whereby a failing aortic valve is replaced with an artificial heart valve. The aortic valve may need to be replaced because of aortic regurgitation, or if the valve is narrowed by stenosis.

An artificial heart valve is a one-way valve implanted into a person's heart to replace a heart valve that is not functioning properly. Artificial heart valves can be separated into three broad classes: mechanical heart valves, bioprosthetic tissue valves and engineered tissue valves.

Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart. These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging, but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy.

Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" or "endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the heart that creates connections between all four of its chambers. It is a very specific combination of 3 defects:

Aortic valve repair or aortic valve reconstruction is the reconstruction of both form and function of a dysfunctional aortic valve. Most frequently it is used for the treatment of aortic regurgitation. It can also become necessary for the treatment of aortic aneurysm, less frequently for congenital aortic stenosis.
Mitral valve replacement is a procedure whereby the diseased mitral valve of a patient's heart is replaced by either a mechanical or tissue (bioprosthetic) valve.
Tricuspid regurgitation (TR), also called tricuspid insufficiency, is a type of valvular heart disease in which the tricuspid valve of the heart, located between the right atrium and right ventricle, does not close completely when the right ventricle contracts (systole). TR allows the blood to flow backwards from the right ventricle to the right atrium, which increases the volume and pressure of the blood both in the right atrium and the right ventricle, which may increase central venous volume and pressure if the backward flow is sufficiently severe.

Lutembacher's syndrome is a very rare form of congenital heart disease that affects one of the chambers of the heart as well as a valve. It is commonly known as both congenital atrial septal defect (ASD) and acquired mitral stenosis (MS). Congenital atrial septal defect refers to a hole being in the septum or wall that separates the two atria; this condition is usually seen in fetuses and infants. Mitral stenosis refers to mitral valve leaflets sticking to each other making the opening for blood to pass from the atrium to the ventricles very small. With the valve being so small, blood has difficulty passing from the left atrium into the left ventricle. Septal defects that may occur with Lutembacher's syndrome include: Ostium primum atrial septal defect or ostium secundum which is more prevalent.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cardiology, the branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the human heart. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiology are called cardiologists.
David H. Adams is an American cardiac surgeon and the Marie-Josée and Henry R. Kravis Professor and Chairman of the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. Dr. Adams is a recognized leader in the field of heart valve surgery and mitral valve reconstruction. As director of Mount Sinai Mitral Valve Repair Center, he has set national benchmarks with >99% degenerative mitral valve repair rates, while running one of the largest valve repair programs in the United States. Dr. Adams is the co-inventor of 2 mitral valve annuloplasty repair rings – the Carpentier-McCarthy-Adams IMR ETlogix Ring and the Carpentier-Edwards Physio II Annuloplasty Ring, and is a senior consultant with royalty agreements with Edwards Lifesciences. He is also the inventor of the Tri-Ad Adams Tricuspid Annuloplasty ring with a royalty agreement with Medtronic. He is a co-author with Professor Alain Carpentier of the benchmark textbook in mitral valve surgery Carpentier's Reconstructive Valve Surgery. He is also the National Co-Principal Investigator of the FDA pivotal trial of the Medtronic-CoreValve transcatheter aortic valve replacement device.
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery, encompasses various aspects of cardiac surgical procedures that can be performed with minimally invasive approach either via mini-thoracotomy or mini-sternotomy. MICS CABG or the McGinn technique is heart surgery performed through several small incisions instead of the traditional open-heart surgery that requires a median sternotomy approach, and can be performed in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease. MICS CABG is a beating-heart multi-vessel procedure performed under direct vision through an anterolateral mini-thoracotomy.

A hybrid cardiac surgical procedure in a narrow sense is defined as a procedure that combines a conventional, more invasive surgical part with an interventional part, using some sort of catheter-based procedure guided by fluoroscopy imaging in a hybrid operating room (OR) without interruption. The hybrid technique has a reduced risk of surgical complications and has shown decreased recovery time. It can be used to treat numerous heart diseases and conditions and with the increasing complexity of each case, the hybrid surgical technique is becoming more common.
Mitral valve annuloplasty is a surgical technique for the repair of leaking mitral valves. Due to various factors, the two leaflets normally involved in sealing the mitral valve to retrograde flow may not coapt properly. Surgical repair typically involves the implantation of a device surrounding the mitral valve, called an annuloplasty device, which pulls the leaflets together to facilitate coaptation and aids to re-establish mitral valve function.

Edwards Lifesciences is an American medical technology company headquartered in Irvine, California, specializing in artificial heart valves and hemodynamic monitoring. It developed the SAPIEN transcatheter aortic heart valve made of cow tissue within a balloon-expandable, cobalt-chromium frame, deployed via catheter. The company has manufacturing facilities at the Irvine headquarters, as well as in Draper, Utah; Costa Rica; the Dominican Republic; Puerto Rico; and Singapore; and is building a new facility due to be completed in 2021 in Limerick, Ireland.

MitraClip is a medical device used to treat mitral valve regurgitation for individuals who should not have open-heart surgery. It is implanted via a tri-axial transcatheter technique and involves suturing together the anterior and posterior mitral valve leaflets.












