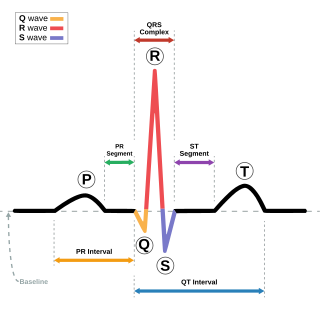
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram, a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances, inadequate coronary artery blood flow, and electrolyte disturbances.

An artificial cardiac pacemaker is a medical device, nowadays always implanted, that generates electrical pulses delivered by electrodes to one or more of the chambers of the heart, the upper atria or lower ventricles. Each pulse causes the targeted chamber(s) to contract and pump blood, thus regulating the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart.

Cardioversion is a medical procedure by which an abnormally fast heart rate (tachycardia) or other cardiac arrhythmia is converted to a normal rhythm using electricity or drugs. Synchronized electrical cardioversion uses a therapeutic dose of electric current to the heart at a specific moment in the cardiac cycle, restoring the activity of the electrical conduction system of the heart. Pharmacologic cardioversion, also called chemical cardioversion, uses antiarrhythmia medication instead of an electrical shock.

Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current to the heart. Although not fully understood, this process depolarizes a large amount of the heart muscle, ending the arrhythmia. Subsequently, the body's natural pacemaker in the sinoatrial node of the heart is able to re-establish normal sinus rhythm. A heart which is in asystole (flatline) cannot be restarted by a defibrillator, but would be treated only by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and medication. Like this asystole sometimes converts into a shockable rhythm, which can be treated by cardioversion or defibrillation.

Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms, caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is mainly decided based on ejection fraction and also measured by the severity of symptoms. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease.

Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echocardiogram, a cardiac echo, or simply an echo.

An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) or automated implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) is a device implantable inside the body, able to perform defibrillation, and depending on the type, cardioversion and pacing of the heart. The ICD is the first-line treatment and prophylactic therapy for patients at risk for sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.

Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat.

Cardiac catheterization is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
In cardiology, ventricular remodeling refers to changes in the size, shape, structure, and function of the heart. This can happen as a result of exercise or after injury to the heart muscle. The injury is typically due to acute myocardial infarction, but may be from a number of causes that result in increased pressure or volume, causing pressure overload or volume overload on the heart. Chronic hypertension, congenital heart disease with intracardiac shunting, and valvular heart disease may also lead to remodeling. After the insult occurs, a series of histopathological and structural changes occur in the left ventricular myocardium that lead to progressive decline in left ventricular performance. Ultimately, ventricular remodeling may result in diminished contractile (systolic) function and reduced stroke volume.

The coronary sinus is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begins at the junction of the great cardiac vein, and oblique vein of the left atrium. It receives multiple tributaries. It passes across the backside of the heart along a groove between left atrium and left ventricle, then drains into the right atrium at the orifice of the coronary sinus.

T wave alternans (TWA) is a periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave in an electrocardiogram TWA was first described in 1908. At that time, only large variations could be detected. Those large TWAs were associated with increased susceptibility to lethal ventricular tachycardias.
The Dor procedure is a medical technique used as part of heart surgery and originally introduced by the French cardiac surgeon Vincent Dor (b.1932). It is also known as endoventricular circular patch plasty (EVCPP).
Morton Maimon Mower was an American cardiologist specializing in electrophysiology and the co-inventor of the automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator. He served in several professional capacities at Sinai Hospital and Cardiac Pacemakers Inc. In 1996, he became the chairman and chief executive officer of Mower Research Associates. He was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 2002 for the development of the automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator with Michel Mirowski in the 1970s. He continued his research in the biomechanical engineering laboratories at Johns Hopkins University.
Management of heart failure requires a multimodal approach. It involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and possibly the use of devices or surgery.
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) is a non-invasive, external device for patients at risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). It allows physicians time to assess their patient's arrhythmic risk and make appropriate plans. It is a leased device. A summary of the device, its technology and indications was published in 2017 and reviewed by the EHRA Scientific Documents Committee.
Cardiac contractility modulation is a therapy which is intended for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe heart failure with symptoms despite optimal medical therapy who can benefit from an improvement in cardiac output. The short- and long-term use of this therapy enhances the strength of ventricular contraction and therefore the heart's pumping capacity by modulating (adjusting) the myocardial contractility. This is provided by a pacemaker-like device that applies non-excitatory electrical signals adjusted to and synchronized with the electrical action in the cardiac cycle.

Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the left ventricle is maximally filled – is normal, defined as greater than 50%; this may be measured by echocardiography or cardiac catheterization. Approximately half of people with heart failure have preserved ejection fraction, while the other half have a reduction in ejection fraction, called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
In cardiology, ventricular dyssynchrony is a difference in the timing, or lack of synchrony, of contractions in different ventricles in the heart. Large differences in timing of contractions can reduce cardiac efficiency and is correlated with heart failure.
Yaariv Khaykin is a Canadian cardiologist and a clinical researcher in the area of electrophysiology. He is the director of the Newmarket Electrophysiology Research Group at the Southlake Regional Health Centre. He has published research into complex ablation and pioneered cardiac ablation methods.














