
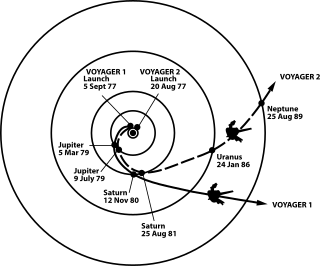
Voyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20,1977,as a part of the Voyager program. It was launched on a trajectory towards the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and enabled further encounters with the ice giants Uranus and Neptune. It remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets,and was the third of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity,which allowed it to leave the Solar System. Launched 16 days before its twin Voyager 1,the primary mission of the spacecraft was to study the outer planets and its extended mission is to study interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere.

Triton is the largest natural satellite of the planet Neptune. It is the only moon of Neptune massive enough to be rounded under its own gravity and hosts a thin,hazy atmosphere. Triton orbits Neptune in a retrograde orbit—revolving in the opposite direction to the parent planet's rotation—the only large moon in the Solar System to do so. Triton is thought to have once been a dwarf planet from the Kuiper belt,captured into Neptune's orbit by the latter's gravity.

Titania,also designated Uranus III,is the largest moon of Uranus. At a diameter of 1,578 kilometres (981 mi) it is the eighth largest moon in the Solar System,with a surface area comparable to that of Australia. Discovered by William Herschel in 1787,it is named after the queen of the fairies in Shakespeare's A Midsummer Night's Dream. Its orbit lies inside Uranus's magnetosphere.
The Grand Tour is a NASA program that would have sent two groups of robotic probes to all the planets of the outer Solar System. It called for four spacecraft,two of which would visit Jupiter,Saturn,and Pluto,while the other two would visit Jupiter,Uranus,and Neptune. The enormous cost of the project,around $1 billion,led to its cancellation and replacement with Mariner Jupiter-Saturn,which became the Voyager program.

An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium,such as oxygen,carbon,nitrogen,and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System:Uranus and Neptune.

The exploration of Uranus has,to date,been through telescopes and a lone probe by NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft,which made its closest approach to Uranus on January 24,1986. Voyager 2 discovered 10 moons,studied the planet's cold atmosphere,and examined its ring system,discovering two new rings. It also imaged Uranus' five large moons,revealing that their surfaces are covered with impact craters and canyons.

The exploration of Saturn has been solely performed by crewless probes. Three missions were flybys,which formed an extended foundation of knowledge about the system. The Cassini–Huygens spacecraft,launched in 1997,was in orbit from 2004 to 2017.

Neptune has been directly explored by one space probe,Voyager 2,in 1989. As of 2024,there are no confirmed future missions to visit the Neptunian system,although a tentative Chinese mission has been planned for launch in 2024. NASA,ESA,and independent academic groups have proposed future scientific missions to visit Neptune. Some mission plans are still active,while others have been abandoned or put on hold.

Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter,the third-most-massive planet,and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth. Compared to its fellow ice giant Uranus,Neptune is slightly more massive,but denser and smaller. Being composed primarily of gases and liquids,it has no well-defined solid surface,and orbits the Sun once every 164.8 years at an orbital distance of 30.1 astronomical units. It is named after the Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol , representing Neptune's trident.

The Planetary Science Decadal Survey is a serial publication of the United States National Research Council produced for NASA and other United States Government Agencies such as the National Science Foundation. The documents identify key questions facing planetary science and outlines recommendations for space and ground-based exploration ten years into the future. Missions to gather data to answer these big questions are described and prioritized,where appropriate. Similar decadal surveys cover astronomy and astrophysics,earth science,and heliophysics.

The Uranus Orbiter and Probe is an orbiter mission concept to study Uranus and its moons. The orbiter would also deploy an atmospheric probe to characterize Uranus's atmosphere. The concept is being developed as a potential large strategic science mission for NASA. The science phase would last 4.5 years and include multiple flybys of each of the major moons.

Argo was a 2009 spacecraft mission concept by NASA to the outer planets and beyond. The concept included flybys of Jupiter,Saturn,Neptune,and a Kuiper belt object. A focus on Neptune and its largest moon Triton would have helped answer some of the questions generated by Voyager 2's flyby in 1989,and would have provided clues to ice giant formation and evolution.
Planetary oceanography,also called astro-oceanography or exo-oceanography,is the study of oceans on planets and moons other than Earth. Unlike other planetary sciences like astrobiology,astrochemistry,and planetary geology,it only began after the discovery of underground oceans in Saturn's moon Titan and Jupiter's moon Europa. This field remains speculative until further missions reach the oceans beneath the rock or ice layer of the moons. There are many theories about oceans or even ocean worlds of celestial bodies in the Solar System,from oceans made of liquid carbon with floating diamonds in Neptune to a gigantic ocean of liquid hydrogen that may exist underneath Jupiter's surface.
MUSE is a European proposal for a dedicated mission to the planet Uranus to study its atmosphere,interior,moons,rings,and magnetosphere. It is proposed to be launched with an Ariane 6 in 2026,travel for 16.5 years to reach Uranus in 2044,and would operate until 2050.

The Ocean Worlds Exploration Program (OWEP) is a NASA program to explore ocean worlds in the outer Solar System that could possess subsurface oceans to assess their habitability and to seek biosignatures of simple extraterrestrial life.

OCEANUS is a mission concept conceived in 2016 and presented in 2017 as a potential future contestant as a New Frontiers program mission to the planet Uranus. The concept was developed in a different form by the astronautical engineering students of Purdue University during the 2017 NASA/JPL Planetary Science Summer School. OCEANUS is an orbiter,which would enable a detailed study of the structure of the planet's magnetosphere and interior structure that would not be possible with a flyby mission.

Trident is a space mission concept to the outer planets proposed in 2019 to NASA's Discovery Program. The concept includes flybys of Jupiter and Neptune with a focus on Neptune's largest moon Triton.
Shensuo,formerly Interstellar Express,is a proposed Chinese National Space Administration program designed to explore the heliosphere and interstellar space. The program will feature two or three space probes that were initially planned to be launched in 2024 and follow differing trajectories to encounter Jupiter to assist them out of the Solar System. The first probe,IHP-1,will travel toward the nose of the heliosphere,while the second probe,IHP-2,will fly near to the tail,skimming by Neptune and Triton in January 2038. There may be another probe—tentatively IHP-3—which would launch in 2030 to explore to the northern half of the heliosphere. IHP-1 and IHP-2 would be the sixth and seventh spacecraft to leave the Solar System,as well as first non-NASA probes to achieve this status.

The Enceladus Orbilander is a proposed NASA Flagship mission to Saturn's moon Enceladus. The Enceladus Orbilander would spend a year and a half orbiting Enceladus and sampling its water plumes,which stretch into space,before landing on the surface for a two-year mission to study materials for evidence of life. The mission,with an estimated cost of $4.9 billion,could launch in the late 2030s on a Space Launch System or Falcon Heavy with a landing in the early 2050s. It was proposed in the 2023–2032 Planetary Science Decadal Survey as the third highest priority Flagship mission,after the Uranus Orbiter and Probe and the Mars Sample Return program.



















