
The New Zealand greater short-tailed bat is one of two species of New Zealand short-tailed bats, a family (Mystacinidae) unique to New Zealand. Larger than the New Zealand lesser short-tailed bat, there have been no confirmed sightings of this species since 1965 and it is considered to be critically endangered, if not extinct. In prehistoric times it lived in the North and South Islands but by the time of European arrival was restricted to small islands near Stewart Island/Rakiura. It is thought that a rat invasion of Taukihepa/Big South Cape Island in 1963 led to the species extinction.

Chalinolobus is a genus of bats, commonly known as pied, wattled, or long-tailed bats. They have fleshy lobes at the bottom edge of their ears and on their lower lips. The bats otherwise classified in the genus Glauconycteris are included in Chalinolobus by some zoologists.

The New Zealand long-tailed bat, also known as the long-tailed wattled bat or pekapeka-tou-roa (Māori), is one of 15 species of bats in the genus Chalinolobus variously known as "pied bats", "wattled bats" or "long-tailed bats". It is one of the two surviving bat species endemic to New Zealand, but is closely related to five other wattled or lobe-lipped bats in Australia and elsewhere.

Gould's wattled bat is a species of Australian wattled bat named after the English naturalist John Gould.

The large-eared pied bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae.

The chocolate wattled bat, species Chalinolobus morio, is a bat allied to the family Vespertilionidae. It is found only in Australia, including the island Tasmania, and widespread in southern regions. It is known to reside from sea level to at least 1,570 metres (5,150 ft) in Victoria.

The hoary wattled bat is a species of vesper bat found in northern Australia and Papua New Guinea. Two subspecies are currently recognised:
The little pied bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found only in semi-arid woodlands in eastern Australia.

Genoways's yellow bat is a species of vesper bat. It is found only in Mexico. It is threatened by habitat loss. Due to its imperiled status, it is identified by the Alliance for Zero Extinction as a species in danger of imminent extinction.

Nyctophilus geoffroyi is a vespertilionid bat, a flying nocturnal mammal found in Australia, The species is relatively common. They have been referred to as the lesser long-eared bat.

Brandt's bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is native throughout most of Europe and parts of Asia. It is known for its high life expectancy relative to its body size, approximately twice that of humans and holds the record for the oldest bat; in 2005, one individual was discovered in a cave in Siberia that had been banded in 1964, making the bat at least 41 years old.
The dark-brown serotine is a species of vesper bat found in Central and West Africa.
The large forest bat is a vespertilionid bat found in southeast Australia, Tasmania, and Lord Howe Island. They are classified as common.
The southern forest bat is a vespertilionid bat found in Australia.

The New Caledonia blossom bat is an uncommon species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. The species lives in caves in northern New Caledonia, and forms colonies of up to 300.
Myotis nyctor is a species of bat found in the Lesser Antilles. It was previously considered a subspecies of Schwartz's myotis, Myotis martiniquensis, but was elevated to species rank in 2012.
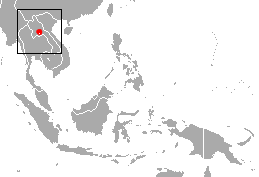
The Phou Khao Khouay leaf-nosed bat is a species of bat endemic to Laos. It was described as a new species in 2006. It is considered vulnerable to extinction by the IUCN.
The Chocoan long-tongued bat is a species of bat found in South America. It was described as a new species in 2004.

The Tasmanian long-eared bat is a species of vesper bat endemic to Tasmania.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.













