
The Nahuan or Aztecan languages are those languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family that have undergone a sound change, known as Whorf's law, that changed an original *t to before *a. Subsequently, some Nahuan languages have changed this to or back to, but it can still be seen that the language went through a stage. The best known Nahuan language is Nahuatl. Nahuatl is spoken by about 1.7 million Nahua peoples.

The Otomi are an Indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the central Mexican Plateau (Altiplano) region.

Otomi is an Oto-Pamean language spoken by approximately 240,000 indigenous Otomi people in the central altiplano region of Mexico. Otomi consists of several closely related languages, many of which are not mutually intelligible. The word Hñähñu has been proposed as an endonym, but since it represents the usage of a single dialect, it has not gained wide currency. Linguists have classified the modern dialects into three dialect areas: the Northwestern dialects are spoken in Querétaro, Hidalgo and Guanajuato; the Southwestern dialects are spoken in the State of Mexico; and the Eastern dialects are spoken in the highlands of Veracruz, Puebla, and eastern Hidalgo and villages in Tlaxcala and Mexico states.
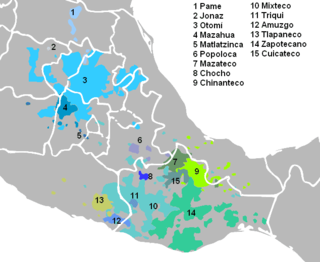
The Pame languages are a group of languages in Mexico that is spoken by around 12,000 Pame people in the state of San Luis Potosí. It belongs to the Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family.
Chichimeca or Chichimeca Jonaz is an indigenous language of Mexico spoken by around 200 Chichimeca Jonaz people in Misión de Chichimecas near San Luis de la Paz in the state of Guanajuato. The Chichimeca Jonaz language belongs to the Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family. The Chichimecos self identify as úza and call their language eza'r.

Conín was a Native American conquistador of the Otomí people, who helped the Spaniards conquer territories in the central part of Mexico during the 16th century. In the Otomí language his name means "Thunder."

Huamango is an early Postclassical archaeological site located about 4 kilometers northwest of the modern city of Acambay in the State of Mexico. The archaeological area is on the San Miguel plateau, in the vicinity of the Peña Picuda hill, at an approximate altitude of 2,850 meters above sea level. It is rich in legends, stories and ancestral traditions.
Sierra Otomia.k.a.Highland Otomi is a dialect cluster of the Otomi language spoken in Mexico by ca. 70,000 people in the highlands of Eastern Hidalgo, Western Veracruz and Northern Puebla. The speakers themselves call the language Yųhų or Ñųhų. Lastra 2001 classifies it as an Eastern Otomi language together with Ixtenco Otomi, Tilapa Otomi, and Acazulco Otomi. The three varieties of Sierra Otomi—Eastern Highland, Texcatepec, and Tenango—are above 70% lexically similar; the Eastern Highland dialects are above 80%, and will be considered here.
The grammar of the Otomi language displays a mixture of elements of synthetic and analytic structures. Particularly the phrase-level morphology is synthetic, whereas the sentence-level is analytic. Simultaneously, the language is head-marking in terms of its verbal morphology, but not in its nominal morphology, which is more analytic. Otomi recognizes three large open word classes of nouns, verbs, and particles. There is a small closed class of property words, variously analyzed as adjectives or stative verbs.
Temoaya Otomi, also known as Toluca Otomi or Otomi of San Andrés Cuexcontitlan, is a variety of the Otomi language spoken in Mexico by ca. 37,000 people in and around the municipality of Temoaya, and in three communities within the municipality of Toluca: San Andrés Cuexcontitlán, San Pablo Autopan and San Cristobal Huichochitlan. The two varieties are quite different. The speakers themselves call the language Ñatho. Lastra (2001) classifies it as a southwestern dialect along with the dialects of Mexico state. Lastra also notes that the endangered Otomí dialect of San Felipe in eastern Michoacán is most similar to the Otomí spoken in San Andrés Cuexcontitlan.
Classical Otomi is the name used for the Otomi language as spoken in the early centuries of Spanish colonial rule in Mexico and documented by Spanish friars who learned the language in order to catechize the Otomi peoples. During the colonial period, many Otomis learned to write their language in Roman letters. As a consequence, a significant number of documents in Otomi, both secular and religious, exist from the period, and the most well-known documents are the Codices of Huichapan and Jilotepec. Text in classical Otomi is not easily accessible since the Spanish speaking friars failed to differentiate the varied vowel and consonant sounds of the Otomi language.

Huexotla or Huexotla is an archaeological site located 5 kilometers south of Texcoco, at the town of San Luis Huexotla, close to Chapingo, in the state of Mexico.
Central Otomi is a Native American language spoken by 10,000 in San Felipe Santiago and in several neighboring towns in the Mexican state of Mexico, such as Chapa de Mota and Jilotepec de Abasolo. Also called 'State of Mexico Otomi', there are other varieties spoken in the state, such as Temoaya Otomi. The autonym is Hñatho or Hñotho.
Tilapa Otomi is a seriously endangered native American language spoken by less than a dozen people in the village of Santiago Tilapa, between Toluca and the DF in Mexico State. It has been classified as Eastern Otomi by Lastra (2006). but in reality "Eastern Otomi" in Lastra's classification is a broader term for a "conservative variety". It is a language closely related to Acazulco and Atlapulco Otomi. It also shows a number of idiosyncratic innovations which make it stand as a different language, probably the closest one to Colonial Otomi. Its system of verbal conjugations is highly complex compared to the Mezquital varieties.
Ixtenco Otomi, also known as Tlaxcala Otomi, is a native American language spoken in the town of San Juan Bautista Ixtenco in the state of Tlaxcala, Mexico. It has been classified as Eastern Otomi by Lastra (2006). Lastra considers Ixtenco Otomí to be a very conservative dialect.
Santa Ana Hueytlalpan Otomi is a native American language spoken in Santa Ana Hueytlalpan town of Tulancingo de Bravo municipality of Hidalgo, Mexico. It has been classified as Eastern Otomi by Lastra (2006), but is not included in Ethnologue.
San Jeronimo Acazulco Otomi, or Ocoyoacac Otomí, is a moribund and seriously endangered dialect of the Otomi language spoken by a hundred or so people in the town of San Jerónimo Acazulco in Ocoyoacac, Mexico State.

The Iranun language, also known as Iranon or Illanun, is an Austronesian language belonging to the Danao languages spoken in the provinces of Maguindanao del Norte and other part of Lanao del Sur and Lanao del Norte, coastal municipalities of Zamboanga del Sur from Tukuran to Dumalinao and Cotabato in southern Philippines and the Malaysian state of Sabah. It is the second most spoken language in Maguindanao after the Maguindanao language.
Chayuco-Jamiltepec Mixtec is a Mixtec language of Oaxaca, spoken in the towns of San Agustín Chayuco, Santa Catarina Mechoacán, Santiago Jamiltepec, San Andrés Huaxpaltepec, Santa María Huazolotitlán, Santiago Tetepec, and Santa Elena Comaltepec.
Teotlalpan was the pre-Columbian name of a region in the north of Valley of Mexico comprising what is today the Mezquital Valley in the state of Hidalgo and adjacent areas in the State of Mexico. The region was one of two regions settled by Otomí people, the other being the region around Jilotepec and Tula, Hidalgo. In the 18th century the name of the main part of the region came to be known as Mezquital.







