
Moa are an extinct group of flightless birds formerly endemic to New Zealand. During the Late Pleistocene-Holocene, there were nine species. The two largest species, Dinornis robustus and Dinornis novaezelandiae, reached about 3.6 metres (12 ft) in height with neck outstretched, and weighed about 230 kilograms (510 lb) while the smallest, the bush moa, was around the size of a turkey. Estimates of the moa population when Polynesians settled New Zealand circa 1300 vary between 58,000 and approximately 2.5 million.

Ratites are a polyphyletic group consisting of all birds within the infraclass Palaeognathae that lack keels and cannot fly. They are mostly large, long-necked, and long-legged, the exception being the kiwi, which is also the only nocturnal extant ratite.

Flightless birds are birds that cannot fly. They have, through evolution, lost the ability to fly. There are over 60 extant species, including the well-known ratites and penguins. The smallest flightless bird is the Inaccessible Island rail. The largest flightless bird, which is also the largest living bird in general, is the common ostrich.

The adzebills, genus Aptornis, were two closely related bird species, the North Island adzebill,, and the South Island adzebill,, of the extinct family Aptornithidae. The family was endemic to New Zealand. A tentative fossil species,, is known from the Miocene Saint Bathans fauna.

The bush moa, little bush moa, or lesser moa is an extinct species of moa from the family Emeidae endemic to New Zealand.

The upland moa is an extinct species of moa that was endemic to New Zealand. It is a ratite, a grouping of flightless birds with no keel on the sternum. It was the last moa species to become extinct, vanishing around 1500 CE, and was predominantly found in alpine and sub-alpine environments.

Dromornis is a genus of large to enormous prehistoric birds native to Australia during the Oligocene to Pliocene epochs. The species were flightless, possessing greatly reduced wing structures but with large legs, similar to the modern ostrich or emu. They were likely to have been predominantly, if not exclusively, herbivorous browsers. The male of the largest species, Dromornis stirtoni, is a contender for the tallest and heaviest bird, and possibly exhibited aggressive territorial behaviour. They belong to the family Dromornithidae, extinct flightless birds known as mihirungs.

Palaeognathae is an infraclass of birds, called paleognaths or palaeognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. It is one of the two extant infraclasses of birds, the other being Neognathae, both of which form Neornithes. Palaeognathae contains five extant orders consisting of four flightless lineages, termed ratites, and one flying lineage, the Neotropic tinamous. There are 47 species of tinamous, five of kiwis (Apteryx), three of cassowaries (Casuarius), one of emus (Dromaius), two of rheas (Rhea) and two of ostriches (Struthio). Recent research has indicated that paleognaths are monophyletic but the traditional taxonomic split between flightless and flighted forms is incorrect; tinamous are within the ratite radiation, meaning flightlessness arose independently multiple times via parallel evolution.

The giant moa (Dinornis) is an extinct genus of birds belonging to the moa family. As with other moa, it was a member of the order Dinornithiformes. It was endemic to New Zealand. Two species of Dinornis are considered valid, the North Island giant moa and the South Island giant moa. In addition, two further species have been suggested based on distinct DNA lineages.

The eastern moa is an extinct species of moa that was endemic to New Zealand.

The crested moa is an extinct species of moa. It is one of the 9 known species of moa to have existed.

The heavy-footed moa is a species of moa from the lesser moa family. The heavy-footed moa was widespread only in the South Island of New Zealand, and its habitat was the lowlands. The moa were ratites, flightless birds with a sternum without a keel. They also have a distinctive palate. The origin of these birds is becoming clearer as it is now believed that early ancestors of these birds were able to fly and flew to the southern areas in which they have been found.

The North Island giant moa is an extinct moa in the genus Dinornis, known in Māori as kuranui. Even though it might have walked with a lowered posture, standing upright, it would have been the tallest bird ever to exist, with a height estimated up to 3.6 metres (12 ft).
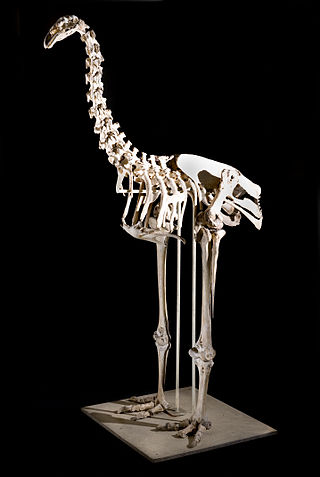
The South Island giant moa is an extinct species of moa in the genus Dinornis, known in Māori by the name moa nunui. It was one of the tallest-known bird species to walk the Earth, exceeded in weight only by the heavier but shorter elephant bird of Madagascar.

The broad-billed moa, stout-legged moa or coastal moa is an extinct species of moa that was endemic to New Zealand.

Mantell's moa also known as Mappin's moa or moa ruarangi is an extinct species of moa from the North Island of New Zealand. Its habitat was the lowlands. The moa were ratites, flightless birds with a sternum without a keel. They also have a distinctive palate. The origin of the ratites is becoming clearer as it is now believed that early ancestors of these birds were able to fly and flew to the southern areas that they have been found in.

The lesser moa were a family in the moa order Dinornithiformes. About two-thirds of all moa species are in the lesser moa family. The moa were ratites from New Zealand. Ratites are flightless birds with a sternum without a keel. They also have a distinctive palate. The origin of the ratites is becoming clearer as it is now believed that early ancestors of these birds were able to fly and flew to the southern areas that they have been found in.


















