
The Sardinian pika is an extinct species of lagomorph that was endemic to the islands of Sardinia, Corsica and neighbouring Mediterranean islands until its extinction likely in Roman times. It was the last surviving member of Prolagus, a genus of lagomorph with a fossil record spanning 20 million years once widespread throughout Europe during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs. Its closest living relatives are modern pikas, from which it is estimated to have diverged around 30 million years ago.

The Erycinae, also known as the Old World sand boas, are a subfamily of nonvenomous snakes in the family Boidae. Species of the subfamily Erycinae are found in Europe, Asia Minor, Africa, Arabia, central and southwestern Asia, India, Sri Lanka, and western North America. Four genera comprising 18 species are currently recognized as being valid.

Psammophis is a genus of snakes in the family Psammophiidae. The genus comprises 33 species, which are found in Africa and Asia. Psammophis are diurnal and prey on lizards and rodents which they actively hunt. All species in the genus are venomous, and the venom is considered mild and not dangerous to humans.
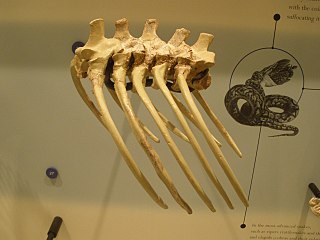
Madtsoiidae is an extinct family of mostly Gondwanan snakes with a fossil record extending from early Cenomanian to late Pleistocene strata located in South America, Africa, India, Australia and Southern Europe. Madtsoiidae include very primitive snakes, which like extant boas and pythons would likely dispatch their prey by constriction. Genera include some of the longest snakes known such as Vasuki, measuring at least 11–15 metres (36–49 ft) long, and the Australian Wonambi and Yurlunggur. As a grouping of basal forms the composition and even the validity of Madtsoiidae is in a state of flux as new pertinent finds are described, with more recent evidence suggesting that it is paraphyletic as previously defined.

Diplocynodon is an extinct genus of alligatoroid crocodilian that lived during the Paleocene to Middle Miocene in Europe. Some species may have reached lengths of 3 metres (9.8 ft), while others probably did not exceed 1 metre (3.3 ft). They are almost exclusively found in freshwater environments. The various species are thought to have been opportunistic aquatic predators.

Crocodylus falconensis is an extinct species of crocodile known from the early Pliocene of the lower part of the Vergel Member of the San Gregorio Formation of Venezuela. C. falconensis was named in 2013 after Falcón State and is thought to be the basalmost species of Crocodylus found in the Neotropics.

The Messel Formation is a geologic formation in Hesse, central Germany, dating back to the Eocene epoch. Its geographic range is restricted to the Messel pit. There it unconformably overlies crystalline Variscan basement and its Permian cover (Rotliegend) as well as Eocene volcanic breccias derived from the basement rocks. The formation mainly comprises lacustrine laminated bituminous shale renowned for its content of fossils in exceptional preservation, particularly plants, arthropods and vertebrates.

Casaleia is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Amblyoponinae described by Pagliano & Scaramozzino in 1990 from fossils found in Europe. The genus contains four species dating from the Eocene to Miocene, Casaleia eocenica, Casaleia inversa, Casaleia longiventris, Casaleia orientalis.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2018.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2017.
This list of fossil reptiles described in 2020 is a list of new taxa of fossil reptiles that were described during the year 2020, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to reptile paleontology that occurred in 2020.

Eoconstrictor is an extinct genus of booid snake, which supposedly had infrared vision, from the Eocene of Germany. The type species, E. fischeri is known from multiple well-preserved specimens found in the Messel Pit of Germany. It was originally named as Palaeopython fischeri by Stephan Schaal in 2004, but examination of the genus showed that it represented a distinct lineage; it was renamed as the new genus Eoconstrictor in 2020. In a subsequent study Georgalis, Rabi & Smith (2021) reinterpreted "Paleryx" spinifer from the Eocene Geiseltal Lagerstätte as the second species belonging to the genus Eoconstrictor. Palci et al. (2023) named the third species belonging to this genus, E. barnesi described on the basis of fossils from the Geiseltal Lagerstätte.
This list of fossil reptiles described in 2021 is a list of new taxa of fossil reptiles that were described during the year 2021, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to reptile paleontology that occurred in 2021.
This list of fossil reptiles described in 2022 is a list of new taxa of fossil reptiles that were described during the year 2022, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to reptile paleontology that occurred in 2022.

Titanochelon is an extinct genus of giant tortoises known from the Early Miocene to the beginning of the Pleistocene in Europe, extending from the Iberian Peninsula to Anatolia. Some members of the genus were larger than extant giant tortoises, with a shell length of up to 2 m.

Drazinderetes is a large bodied genus of soft shell turtle from the Middle Eocene Drazinda Formation of Pakistan. Its presence in the shallow marine deposits of the Drazinda Formation suggests that Drazinderetes may have been a partially or fully marine animal. Indetermined trionychine remains from the same formation may suggest that Drazinderetes could have been among the largest known turtles, with one entoplastron indicating a potential length of 1.5 to 2.1 meters. Drazinderetes currently consists of only a single species: Drazinderetes tethyensis.
Falcontoxodon is an extinct genus of toxodontid notoungulate that lived from the late Pliocene to the Pleistocene in what is now Venezuela. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Chapadmalalan-Uquian Codore Formation, as well as in the more recent Ensenadan San Gregorio Formation.
This is an overview of the paleofauna of the Eocene Messel Formation as explored by the Messel Pit excavations in Germany. A former quarry and now UNESCO World Heritage Site, the Messel Formation preserves what once were a series of anoxic lakes surrounded by a sub-tropical rainforest during the Middle Eocene, approximately 47 Ma.
This list of fossil reptiles described in 2023 is a list of new taxa of fossil reptiles that were described during the year 2023, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to reptile paleontology that occurred in 2023.
This list of fossil reptiles described in 2016 is a list of new taxa of fossil reptiles that were described during the year 2016, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to reptile paleontology that occurred in 2016.











