
Rapetosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur that lived in Madagascar from 70 to 66 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous Period. Only one species, Rapetosaurus krausei, has been identified.

Rajasaurus is a genus of carnivorous abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of India, containing one species: Rajasaurus narmadensis. The bones were excavated from the Lameta Formation in the Gujarat state of Western India, probably inhabiting what is now the Narmada River Valley. It was formally described by palaeontologist Jeffrey A. Wilson and colleagues in 2003 based on a partial skeleton comprising the braincase, spine, hip bone, legs, and tail–a first for an Indian theropod. The dinosaur likely measured 6.6 metres (22 ft), and had a single horn on the forehead which was probably used for display and head-butting. Like other abelisaurids, Rajasaurus was probably an ambush predator.

Masiakasaurus is a genus of small predatory noasaurid theropod dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. In Malagasy, masiaka means "vicious"; thus, the genus name means "vicious lizard". The type species, Masiakasaurus knopfleri, was named after the musician Mark Knopfler, whose music inspired the expedition crew. It was named in 2001 by Scott D. Sampson, Matthew Carrano, and Catherine A. Forster. Unlike most theropods, the front teeth of M. knopfleri projected forward instead of straight down. This unique dentition suggests that they had a specialized diet, perhaps including fish and other small prey. Other bones of the skeleton indicate that Masiakasaurus were bipedal, with much shorter forelimbs than hindlimbs. M. knopfleri was a small theropod, reaching 1.8–2.1 m (5.9–6.9 ft) long and weighing 20 kg (44 lb).

Majungasaurus is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in Madagascar from 70 to 66 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous Period, making it one of the last-known non-avian dinosaurs that went extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The genus contains a single species, Majungasaurus crenatissimus. This dinosaur is also called Majungatholus, a name which is considered a junior synonym of Majungasaurus.

Puertasaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous Period. It is known from a single specimen recovered from sedimentary rocks of the Cerro Fortaleza Formation in southwestern Patagonia, Argentina, which probably is Campanian or Maastrichtian in age. The only species is Puertasaurus reuili. Described by the paleontologist Fernando Novas and colleagues in 2005, it was named in honor of Pablo Puerta and Santiago Reuil, who discovered and prepared the specimen. It consists of four well-preserved vertebrae, including one cervical, one dorsal, and two caudal vertebrae. Puertasaurus is a member of Titanosauria, the dominant group of sauropods during the Cretaceous.

Hatzegopteryx is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur found in the late Maastrichtian deposits of the Densuş Ciula Formation, an outcropping in Transylvania, Romania. It is known only from the type species, Hatzegopteryx thambema, named by Buffetaut et al. in 2002 based on parts of the skull and humerus. Additional specimens, including a neck vertebra, were later placed in the genus, representing a range of sizes. The largest of these remains indicate it was among the biggest pterosaurs, with an estimated wingspan of 10 to 12 metres.

Simosuchus is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodyliforms from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown individuals were about 0.75 metres (2.5 ft) in length. The type species is Simosuchus clarki, found from the Maevarano Formation in Mahajanga Province, although one isolated multicuspid tooth of this genus was discovered in Kallamedu Formation of India.

Phosphatodraco is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous of what is now Morocco. In 2000, a pterosaur specimen consisting of five cervical (neck) vertebrae was discovered in the Ouled Abdoun Phosphatic Basin. The specimen was made the holotype of the new genus and species Phosphatodraco mauritanicus in 2003; the genus name means "dragon from the phosphates", and the specific name refers to the region of Mauretania. Phosphatodraco was the first Late Cretaceous pterosaur known from North Africa, and the second pterosaur genus described from Morocco. It is one of the only known azhdarchids preserving a relatively complete neck, and was one of the last known pterosaurs. Additional cervical vertebrae have since been assigned to the genus, and it has been suggested that fossils of the pterosaur Tethydraco represent wing elements of Phosphatodraco.
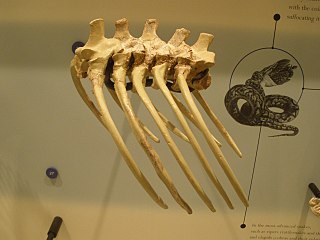
Madtsoiidae is an extinct family of mostly Gondwanan snakes with a fossil record extending from early Cenomanian to late Pleistocene strata located in South America, Africa, India, Australia and Southern Europe. Madtsoiidae include very primitive snakes, which like extant boas and pythons would likely dispatch their prey by constriction. Genera include some of the longest snakes known such as Vasuki, measuring at least 11–15 metres (36–49 ft) long, and the Australian Wonambi and Yurlunggur. As a grouping of basal forms the composition and even the validity of Madtsoiidae is in a state of flux as new pertinent finds are described, with more recent evidence suggesting that it is paraphyletic as previously defined.
The Maevarano Formation is a Late Cretaceous sedimentary rock formation found in the Mahajanga Province of northwestern Madagascar. It is most likely Maastrichtian in age, and records a seasonal, semiarid environment with rivers that had greatly varying discharges. Notable animal fossils recovered include the theropod dinosaur Majungasaurus, the early bird Vorona, the paravian Rahonavis, the titanosaurian sauropod Rapetosaurus, and the giant frog Beelzebufo.

Mahajangasuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform which had blunt, conical teeth. The type species, M. insignis, lived during the Late Cretaceous; its fossils have been found in the Maevarano Formation in northern Madagascar. It was a fairly large predator, measuring up to 4 metres (13 ft) long.

Madtsoia is an extinct genus of madtsoiid snakes. It is known from the Eocene of Argentina, the Paleocene of Brazil, the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of India, and the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Madagascar. The type species was the largest with an estimated length of 9–10 m (30–33 ft), and the other three species were smaller. A 5.1 m (17 ft) long M. madagascariensis would have weighed 50 kg (110 lb), but an isolated specimen suggests that this species reached 8 m (26 ft) in maximum length.
The Bluff Downs giant python is an extinct species of snake from Queensland, Australia, that lived during the Early Pliocene. Named in 2002, Liasis dubudingala was likely the biggest snake found in Australia, with a total length of up to 9 m (30 ft). This length rivals the largest extant snake species, the reticulated python from Asia and the green anaconda from South America. It may have fed on larger prey such as juvenile diprotodontids, but it is also possible that it was a skilled climber capable of catching birds and arboreal marsupials.

Sanajeh is a genus of late Cretaceous madtsoiid snake from western India. A fossil described in 2010 from the Lameta Formation was found coiled around an egg and an adjacent skeleton of a 50 cm (19 in) long sauropod dinosaur hatchling. This suggests that the snake preyed on hatchling sauropods at nesting sites.
Kelyophis is an extinct genus of nigerophiid snake which existed in Madagascar during the Late Cretaceous. The type species is Kelyophis hechti. Trunk vertebrae have been found from the Maastrichtian-age Maevarano Formation in the Mahajanga Basin. Kelyophis is similar to other nigerophiids in its small size, long centra with posterior surfaces that deflect slightly downward, tubercular-shaped neural spines that are directed toward the back of the neural arches, and several other features of the vertebrae.
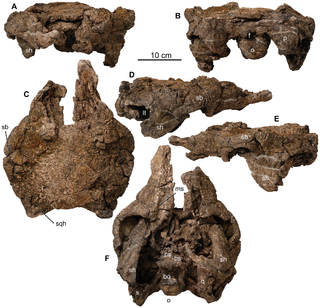
Europelta is a monospecific genus of nodosaurid dinosaur from Spain that lived during the Early Cretaceous in what is now the lower Escucha Formation of the Teruel Province. The type and only species, Europelta carbonensis, is known from two associated partial skeletons, and represents the most complete ankylosaur known from Europe. Europelta was named in 2013 by James I. Kirkland and colleagues. Europelta has an estimated length of 5 metres and weight of 1.3 tonnes, making it the largest member of the clade Struthiosaurini.

Tratayenia is an extinct genus of megaraptoran theropod dinosaurs known from remains found in the Santonian-age Bajo de la Carpa Formation of Argentina. The type and only species, Tratayenia rosalesi, was described in March 2018.

Changmiania is a genus of basal ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now China during the Early Cretaceous. It contains a single species, Changmiania liaoningensis.

Sahonachelys is an extinct genus of pelomedusoid turtle from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Maevarano Formation of Madagascar. The genus contains a single species, Sahonachelys mailakavava.

Stegouros is a genus of ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Dorotea Formation of southern Chile. The genus contains a single species, Stegouros elengassen, known from a semi-articulated, near-complete skeleton.
















