
Borneo is the third-largest island in the world, with an area of 748,168 km2 (288,869 sq mi). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda Islands, located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and east of Sumatra.
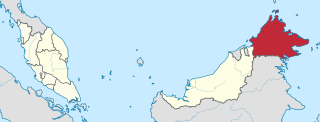
Sabah is a state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah has land borders with the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and Indonesia's North Kalimantan province to the south. The Federal Territory of Labuan is an island just off Sabah's west coast. Sabah shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the west and the Philippines to the north and east. Kota Kinabalu is the state capital and the economic centre of the state, and the seat of the Sabah State government. Other major towns in Sabah include Sandakan and Tawau. The 2020 census recorded a population of 3,418,785 in the state. It has an equatorial climate with tropical rainforests, abundant with animal and plant species. The state has long mountain ranges on the west side which forms part of the Crocker Range National Park. Kinabatangan River, the second longest river in Malaysia runs through Sabah. The highest point of Sabah, Mount Kinabalu is also the highest point of Malaysia.

East Malaysia, or the Borneo States, also known as Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia on and near the island of Borneo, the world's third-largest island. East Malaysia comprises the states of Sabah, Sarawak, and the Federal Territory of Labuan. The small independent nation of Brunei comprises two enclaves in Sarawak. To the south and southeast is the Indonesian portion of Borneo, Kalimantan. East Malaysia lies to the east of Peninsular Malaysia, the part of the country on the Malay Peninsula. The two are separated by the South China Sea.

Labuan, officially the Federal Territory of Labuan, is an island federal territory of Malaysia. Its territory includes Labuan Island and six smaller islands, off the coast of the state of Sabah in East Malaysia. Labuan's capital is Victoria and is best known as an offshore financial centre offering international financial and business services via Labuan IBFC since 1990 as well as being an offshore support hub for deepwater oil and gas activities in the region. It is also a tourist destination for people travelling through Sabah, nearby Bruneians and scuba divers. The name Labuan derives from the Malay word labuhan which means harbour.

The Sultanate of Sulu was a Sunni Muslim state that ruled the Sulu Archipelago, coastal areas of Zamboanga City and certain portions of Palawan in the today's Philippines, alongside parts of present-day Sabah and North Kalimantan in north-eastern Borneo.

Lahad Datu is the capital of the Lahad Datu District in the Dent Peninsula on Tawau Division of Sabah, Malaysia. Its population was estimated to be around 27,887 in 2010. The town is surrounded by stretches of cocoa and palm oil plantations. It is also an important timber exporting port. The town has an airport for domestic flights.

The North Borneo Chartered Company (NBCC), also known as the British North Borneo Company (BNBC), was a British chartered company formed on 1 November 1881 to administer and exploit the resources of North Borneo. The territory became a protectorate of the British Empire in 1888 but the company remained involved with the territory until 1946, when administration was fully assumed by the Crown colony government.

Lawas is a small town and the capital of Lawas District, Limbang Division, Sarawak, Malaysia. This district area is 3,811.90 square kilometres, and population was 46,200. It is 1,200 km from the state capital, Kuching and 200 km from the capital city of Sabah, Kota Kinabalu.

Semporna is the capital of the Semporna District in the Tawau Division of Sabah, Malaysia. Its population was estimated to be around 35,301 in 2010.

The North Borneo dispute, also known as the Sabah dispute, is the territorial dispute between Malaysia and the Philippines over much of the eastern part of the state of Sabah. Sabah was previously known as North Borneo prior to the formation of the Malaysian federation.

The Raj of Sarawak, Kingdom of Sarawak or State of Sarawak, was a kingdom founded in 1841 in northwestern Borneo and was in a treaty of protection with the United Kingdom from 1888. It was formed from a series of land concessions acquired by the Englishman James Brooke from the Sultan of Brunei. Sarawak was recognised as a sovereign state by the United States in 1850, and by the United Kingdom in 1864. The territory of the kingdom is now the Malaysian state of Sarawak.

Darvel Bay or Lahad Datu Bay is a bight on the east side of Sabah, Malaysia. It is the largest semi-enclosed bay on the east coast of Borneo and faces the Sulawesi Sea. Administratively, it is within Tawau Division, with Lahad Datu District on the north side, Kunak District in the middle and Semporna District to the south of the bay.

The history of Sabah can be traced back to about 23–30,000 years ago when evidence suggests the earliest human settlement in the region existed. The history is interwoven with the history of Brunei and the history of Malaysia, which Sabah was previously part of and is currently part of respectively. The earliest recorded history of Sabah being part of any organised civilisation began in the early 15th century during the thriving era of the Sultanate of Brunei. Prior to this, early inhabitants of the land lived in predominantly tribal societies, although such tribal societies had continued to exist until the 1900s. The eastern part of Sabah was ceded to the Sultan of Sulu by the Sultan of Brunei in 1658 for the former helping a victory over Brunei enemies, but many sources stated it had not been ceded at all. By the late 19th century, both territories previously owned by Sultan of Brunei and Sultan of Sulu was granted to British syndicate and later emerged as British North Borneo under the management of the North Borneo Chartered Company. Sabah became a protectorate of the United Kingdom in 1888 and subsequently became a Crown colony from 1946 until 1963, during which time it was known as Crown Colony of North Borneo. On 16 September 1963, Sabah merged with Malaya, Sarawak and Singapore to form Malaysia.

The Crown Colony of Labuan was a Crown colony off the northwestern shore of the island of Borneo established in 1848 after the acquisition of the island of Labuan from the Sultanate of Brunei in 1846. Apart from the main island, Labuan consists of six smaller islands; Burung, Daat, Kuraman, Papan, Rusukan Kecil, and Rusukan Besar.
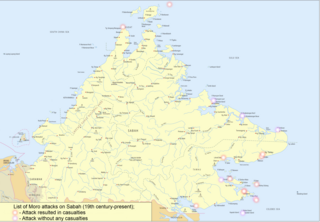
The cross border attacks in Sabah are a series of cross border terrorist attacks perpetrated by Moro pirates from Mindanao, Philippines, in the state of Sabah, Malaysia, that began even before the British colonial period. Many civilians have died or suffered during these incidents, causing an increase in anti-Filipino sentiment among the native peoples of Sabah, especially after major attacks in 1985, 2000 and 2013. The attacks were more intense during the presidential terms of Diosdado Macapagal and Ferdinand Marcos, who supported irredentist claims to include eastern Sabah as part of the Philippines territory. In addition, recent infiltration and attacks by militants as well as uncontrolled human migration from Mindanao to Sabah has led to more unease sentiments among the local residents of Sabah, with around 78% of prison inmates that were caught in the state due to involvement in criminal activities and lawlessness issues mainly originating from the southern Philippines.

The Batu Tinagat Lighthouse is a lighthouse on Batu Tinagat of Tawau District, Tawau Division in Sabah, Malaysia. It is located approximately 10 kilometres from the Tawau town centre.

The Nabawan District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Interior Division which includes the districts of Beaufort, Keningau, Kuala Penyu, Nabawan, Sipitang, Tambunan and Tenom. The capital of the district is in Nabawan Town.

The Kudat District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Kudat Division which includes the districts of Kota Marudu, Kudat and Pitas. The capital of the district is in Kudat Town.

The Lahad Datu District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Tawau Division which includes the districts of Kunak, Lahad Datu, Semporna and Tawau. The capital of the district is in Lahad Datu Town.

The Papar River is a river in West Coast Division, northwestern Sabah of Malaysia. It has a total length of 60 km from its headwaters in the mountains of northwest Sabah to its outlet at the South China Sea, northwest of Papar town. It originates in the mountains in the interior Papar, Penampang and Tuaran Districts, which form part of the Crocker Range system. This includes the areas of Babagon, Bonobukan, Buayan, Central Papar, Gramatoi, Himpangno, Kaiduan, Kalangan, Kawari, Kogopon, Lingan, Mandalipau, Marahang, Padawan, Terian, Tiku and Ulu Papar.






















