
East Malaysia, or the Borneo States, also known as Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia on and near the island of Borneo, the world's third-largest island. East Malaysia comprises the states of Sabah, Sarawak, and the Federal Territory of Labuan. The small independent nation of Brunei comprises two enclaves in Sarawak. To the south and southeast is the Indonesian portion of Borneo, Kalimantan. East Malaysia lies to the east of Peninsular Malaysia, the part of the country on the Malay Peninsula. The two are separated by the South China Sea.

The geography of Malaysia includes both the physical and the human geography of Malaysia, a Southeast Asian country made up of two major landmasses separated by water—Peninsular Malaysia to the west and East Malaysia to the east—and numerous smaller islands that surround those landmasses. Peninsular Malaysia is on the southernmost part of the Malay Peninsula, south of Thailand, north of Singapore and east of the Indonesian island of Sumatra; East Malaysia comprises most of the northern part of Borneo, and shares land borders with Brunei to the north and Indonesian Borneo to the south.

Mount Kinabalu is the highest mountain in Borneo and Malaysia. With an elevation of 4,095 metres (13,435 ft), it is the third-highest peak of an island on Earth, the 28th highest peak in Southeast Asia, and 20th most prominent mountain in the world. The mountain is located in Ranau district, West Coast Division of Sabah, Malaysia. It is protected as Kinabalu Park, a World Heritage Site.

Kota Kinabalu, colloquially referred to as KK, is the state capital of Sabah, Malaysia. It is also the capital of the Kota Kinabalu District as well as the West Coast Division of Sabah. The city is located on the northwest coast of Borneo facing the South China Sea. The Tunku Abdul Rahman National Park lies to its west and Mount Kinabalu, which gave the city its name, is located to its east. Kota Kinabalu has a population of 452,058 according to the 2010 census; when the adjacent Penampang and Tuaran districts are included, the metro area has a combined population of 628,725. The 2020 Census revealed an increase in the municipal population to 500,421, while the wider area including the Penampang and Putatan districts had a population of 731,406.

Kinabalu Park, established as one of the first national parks of Malaysia in 1964, is Malaysia's first World Heritage Site designated by UNESCO in December 2000 for its "outstanding universal values" and the role as one of the most important biological sites in the world with more than 4,500 species of flora and fauna, including 326 bird and around 100 mammal species, and over 110 land snail species.

The Bornean ferret badger, also known as Everett's ferret badger or the Kinabalu ferret badger, is a small, nocturnal and omnivorous mammal that is endemic to the island of Borneo. It is a member of the family Mustelidae and is one of six species of the genus Melogale. It is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species due to its small distribution range, which includes Kinabalu National Park and Crocker Range National Park.

Mount Tambuyukon or Tamboyukon is a mountain located at the West Coast and Kudat divisions of Sabah, Malaysia. It is considered the third-highest mountain in the country with height at 2,579 metres (8,461 ft), lying north of the highest Mount Kinabalu.

Nepenthes lowii, or Low's pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is named after Hugh Low, who discovered it on Mount Kinabalu. This species is perhaps the most unusual in the genus, being characterised by its strongly constricted upper pitchers, which bear a greatly reduced peristome and a reflexed lid with numerous bristles on its lower surface.

Nepenthes fusca, or the dusky pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is found throughout a wide altitudinal range and is almost always epiphytic in nature, primarily growing in mossy forest.

The Crocker Mountains form a range that separates the West Coast and Interior divisions of Sabah, Malaysia. At an average height of 1,800 metres (5,906 ft), it is the highest mountain range in the state. It is named after a 19th century British administrator of North Borneo, William Maunder Crocker.

Nepenthes macrophylla, the large-leaved pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant known only from a very restrictive elevation on Mount Trusmadi in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo.
Mount Trusmadi or Trus Madi is a mountain located at the Interior Division of Sabah, Malaysia. It is considered as the second highest mountain in both Sabah and Malaysia at 2,642 metres (8,668 ft), after Mount Kinabalu with Trusmadi offering a tougher climbing challenge than the latter.

The Trusmadi Range or Trus Madi Range is a mountain range in Interior Division and parts of West Coast Division of Sabah, Malaysia that also separates the west and east coast of Sabah aside from the main Crocker Mountains. With a length of about 80 kilometres, the range includes the state's second highest peak, Mount Trusmadi, after which it is named.

Nepenthes chaniana is a tropical pitcher plant species belonging to the genus Nepenthes. It is characterised by a dense indumentum of long, white hairs. Pitchers are cylindrical and mostly white to yellow in colouration. Nepenthes chaniana belongs to the loosely defined "N. maxima complex", which also includes, among other species, N. boschiana, N. epiphytica, N. eymae, N. faizaliana, N. fusca, N. klossii, N. maxima, N. platychila, N. stenophylla, and N. vogelii.

Mount Pueh, also known as Mount Pueh-Berumput, Mount Poi and Mount Poe, is a mountain located near Lundu, Sarawak on the Malaysia-Indonesia border. Mount Pueh was known to biologists for the collections made there by Eric Mjöberg (1882–1938), a Swedish naturalist, who was Curator of the Sarawak Museum between 1922 and 1924. Mjöberg's herpetological collections from Gunung Pueh between October and December 1923, and other localities in Borneo, were reported by Smith (1925). Mjöberg, unfortunately, left little by way of written records, of his ascent of Pueh and the collections he made.
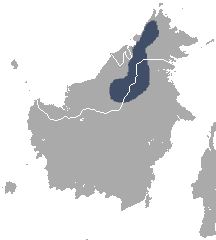
The Bornean smooth-tailed treeshrew is a species of treeshrew in the family Tupaiidae. It is endemic to Borneo. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The Borneo montane rain forests is an ecoregion on the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. It includes montane tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, also known as a cloud forests. The ecoregion is partly in East Malaysia and Indonesia (Kalimantan).
The Semporna Peninsula is a peninsula in Tawau Division, Sabah, Malaysia. It consists of coastal areas and numerous isolated hills and mountains rising to over 305 metres (1,001 ft). The Peninsula is also considered as a volcanic arc of the region with several volcanoes active during the Holocene period is located on the area.

Greater Kota Kinabalu refers to the dense clusters of regional populated areas surrounding the city of Kota Kinabalu in Malaysia. It comprises the districts of Kota Kinabalu, Penampang, Tuaran and Papar. These districts are also part of the West Coast Division. It was forecasted that in 2019, the combined population of these districts was 1.1 million people, in a combined area of 3,277 km2.

The Sugut River is a river located in the northeastern part of Sabah, Malaysia, between the tripoint of the West Coast, Sandakan as well as a portion of the Kudat division. It has a total length of 178 km from its headwaters in the mountains of northwest Sabah to its outlet at the Sulu Sea, northeastern of Beluran town. Its source is originated from the mountains in the eastern slopes of Mount Kinabalu National Park in Ranau District, which part of the Mount Kinabalu system.


















