Related Research Articles
In the geologic timescale, the Asselian is the earliest geochronologic age or lowermost chronostratigraphic stage of the Permian. It is a subdivision of the Cisuralian epoch or series. The Asselian lasted between 298.9 and 295 million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Gzhelian and followed by the Sakmarian.
The Bashkirian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Pennsylvanian. The Bashkirian age lasted from 323.2 to 315.2 Ma, is preceded by the Serpukhovian and is followed by the Moscovian.
The Tournaisian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Mississippian, the oldest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Tournaisian age lasted from 358.9 Ma to 346.7 Ma. It is preceded by the Famennian and is followed by the Viséan.
The Visean, Viséan or Visian is an age in the ICS geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the second stage of the Mississippian, the lower subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Visean lasted from 346.7 to 330.9 Ma. It follows the Tournaisian age/stage and is followed by the Serpukhovian age/stage.
The Serpukhovian is in the ICS geologic timescale the uppermost stage or youngest age of the Mississippian, the lower subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Serpukhovian age lasted from 330.9 Ma to 323.2 Ma. It is preceded by the Visean and is followed by the Bashkirian.
The Gzhelian is an age in the ICS geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest stage of the Pennsylvanian, the youngest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Gzhelian lasted from 303.7 to 298.9 Ma. It follows the Kasimovian age/stage and is followed by the Asselian age/stage, the oldest subdivision of the Permian system.
Taphrognathus is an extinct genus of conodonts from the Dinantian.
The Exshaw Formation is a stratigraphic unit in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It takes the name from the hamlet of Exshaw, Alberta in the Canadian Rockies, and was first described from outcrops on the banks of Jura Creek north of Exshaw by P.S. Warren in 1937. The formation is of Late Devonian to Early Mississippian age as determined by conodont biostratigraphy, and it straddles the Devonian-Carboniferous boundary.
The Moscovian is in the ICS geologic timescale a stage or age in the Pennsylvanian, the youngest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Moscovian age lasted from 315.2 to 307 Ma, is preceded by the Bashkirian and is followed by the Kasimovian. The Moscovian overlaps with the European regional Westphalian stage and the North American Atokan and Desmoinesian stages.
Maurice Goldsmith Mehl was an American paleontologist. A longtime professor in the Department of Geology at the University of Missouri, Mehl was a founding member and officer of the American Association of Petroleum Geologists. Mehl was a fellow of the Geological Society of America (1922), the Paleontological Society, and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
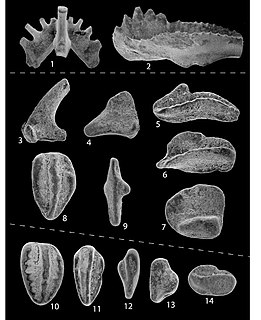
Polygnathus is an extinct genus of conodonts.

Gnathodus is an extinct conodont genus in the family Idiognathodontidae.
Streptognathodus is an extinct genus of conodonts from the Late Carboniferous to Early Permian.
Conodonts are an extinct class of animals whose feeding apparatuses called teeth or elements are common microfossils found in strata dating from the Stage 10 of the Furongian, the fourth and final series of the Cambrian, to the Rhaetian stage of the Late Triassic. These elements can be used alternatively to or in correlation with other types of fossils in the subfield of the stratigraphy named biostratigraphy.
Scaliognathus is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Dollymae is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Siphonodella is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Neognathodus is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Declinognathodus is an extinct genus of platform conodonts.
Idiognathoides is an extinct genus of conodonts.
References
- ↑ British Avonian (Carboniferous) conodont faunas, and their value in local and intercontinental correlation. FHT Rhodes, RL Austin, EC Druce, 1969, British Museum (Natural History)