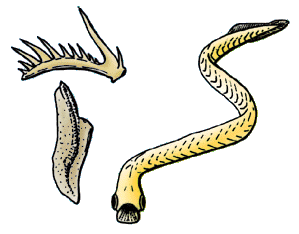
Conodonts are extinct agnathan chordates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from tooth-like microfossils found in isolation and now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. The animals are also called Conodontophora to avoid ambiguity.
Jay Wesley Osmond is a member of the Osmond family of performers. He was the drummer for the family male quintet The Osmonds.

The genus Cercartetus is a group of very small possums known as pygmy possums. Four species comprise this genus, which together with the genus Burramys make up the marsupial family Burramyidae.

Triviidae is a taxonomic family of small sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Littorinimorpha.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1933.
Helen Abbot Merrill was an American mathematician, educator and textbook author.

Methallenestril (INN), also known as methallenoestril (BAN) and as methallenestrol, as well as Horeau's acid, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen and a derivative of allenolic acid and allenestrol that was formerly used to treat menstrual issues but is now no longer marketed. It is a seco-analogue of bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, and although methallenestril is potently estrogenic in rats, in humans it is only weakly so in comparison. Vallestril was a brand of methallenestril issued by G. D. Searle & Company in the 1950s. Methallenestril is taken by mouth. By the oral route, a dose of 25 mg methallenestril is approximately equivalent to 1 mg diethylstilbestrol, 4 mg dienestrol, 20 mg hexestrol, 25 mg estrone, 2.5 mg conjugated estrogens, and 0.05 mg ethinylestradiol.
Maurice Goldsmith Mehl was an American paleontologist. A longtime professor in the Department of Geology at the University of Missouri, Mehl was a founding member and officer of the American Association of Petroleum Geologists. Mehl was a fellow of the Geological Society of America (1922), the Paleontological Society, and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Edward B. Branson was an American geologist and paleontologist. He worked at the University of Missouri.
Idiognathodontidae is an extinct conodont family.
Gondolella is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Gondolellidae.
Heinz Walter Kozur was a German paleontologist and stratigrapher.
Klaus Jürgen Müller was a German paleontologist.

Acanthodus is an extinct genus of conodonts.

Variabiloconus is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Conodonts are an extinct class of animals whose feeding apparatuses called teeth or elements are common microfossils found in strata dating from the Stage 10 of the Furongian, the fourth and final series of the Cambrian, to the Rhaetian stage of the Late Triassic. These elements can be used alternatively to or in correlation with other types of fossils in the subfield of the stratigraphy named biostratigraphy.
Neognathodus is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Idiognathoides is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Polygnathodella is an extinct genus of conodont.
Protoconodonts are an extinct taxonomic group of conodonts or, possibly, Chaetognaths.





