A tetrose is a monosaccharide with 4 carbon atoms. They have either an aldehyde functional group in position 1 (aldotetroses) or a ketone functional group in position 2 (ketotetroses).
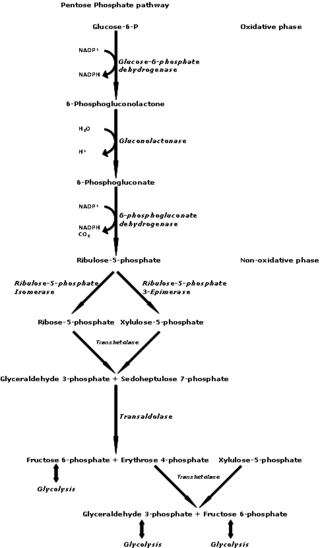
The pentose phosphate pathway is a metabolic pathway parallel to glycolysis. It generates NADPH and pentoses as well as ribose 5-phosphate, a precursor for the synthesis of nucleotides. While the pentose phosphate pathway does involve oxidation of glucose, its primary role is anabolic rather than catabolic. The pathway is especially important in red blood cells (erythrocytes). The reactions of the pathway were elucidated in the early 1950s by Bernard Horecker and co-workers.

D-Xylulose 5-phosphate (D-xylulose-5-P) is an intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway. It is a ketose sugar formed from ribulose-5-phosphate by ribulose-5-phosphate epimerase. In the non-oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway, xylulose-5-phosphate acts as a donor of two-carbon ketone groups in transketolase reactions.

Phosphopentose epimerase encoded by the RPE gene is a metalloprotein that catalyzes the interconversion between D-ribulose 5-phosphate and D-xylulose 5-phosphate.
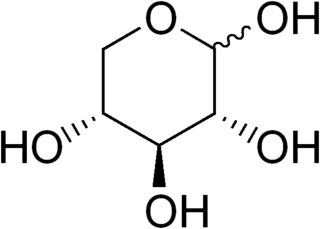
D-Xylose is a five-carbon aldose that can be catabolized or metabolized into useful products by a variety of organisms.

In enzymology, a D-xylulose reductase (EC 1.1.1.9) is an enzyme that is classified as an Oxidoreductase (EC 1) specifically acting on the CH-OH group of donors (EC 1.1.1) that uses NAD+ or NADP+ as an acceptor (EC 1.1.1.9). This enzyme participates in pentose and glucuronate interconversions; a set of metabolic pathways that involve converting pentose sugars and glucuronate into other compounds.

In enzymology, a L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of ribulose 5-phosphate and xylulose 5-phosphate in the oxidative phase of the Pentose phosphate pathway.
The enzyme 3-dehydro-L-gulonate-6-phosphate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.85) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase (EC 4.1.2.22) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme L-fuculose-phosphate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.19) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.111) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme gluconate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.39) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme mannonate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.8) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme mannitol-1-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.22) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase (EC 3.5.99.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (EC 2.2.1.7) is an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylneuraminate synthase (EC 2.5.1.56) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a rhamnulokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a ribulokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction









