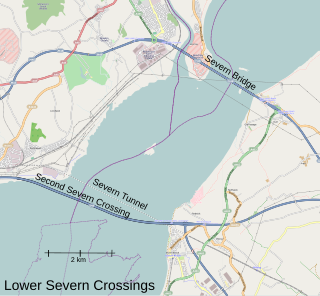
Severn crossing is a term used to refer to the two motorway crossings over the River Severn estuary between England and Wales operated by England's National Highways. The two crossings are:

The M4, originally the London-South Wales Motorway, is a motorway in the United Kingdom running from west London to southwest Wales. The English section to the Severn Bridge was constructed between 1961 and 1971; the Welsh element was largely complete by 1980, though a non-motorway section around Briton Ferry bridge remained until 1993. On the opening of the Second Severn Crossing in 1996, the M4 was rerouted over it.

The A483, officially described as the Swansea to Manchester Trunk Road, although now ending in Chester, is a major road in the United Kingdom. It runs from Swansea in Wales to Chester in England via Llandovery, Llandrindod Wells, Oswestry and Wrexham, a distance of around 153 miles (246 km).

The fuel protests in the United Kingdom were a series of campaigns held in response to the rising petrol and diesel fuel prices for road vehicle use. There have been three major campaigns amongst many other protests in the 21st century. The first major protest in 2000 was primarily led by independent lorry owner-operators. One group of lorry owner-operators from the South East of England formed a protest group called "TransAction" that protested at oil refineries and fuel depots in Essex. Protests and blockades of oil facilities caused widespread disruption to the supply of petroleum products. The aim of the protests was to secure a reduction in the fuel duty rate on petrol and diesel, which the government refused to enact. After the protest ended, the government did announce a freeze on fuel duties, and promised changes would be made to the way that goods vehicles were taxed, which would include the taxing of foreign vehicles operating on British roads.

The A48 is a trunk road in Great Britain running from the A40 at Highnam, 3 miles (4.8 km) west of Gloucester, England, to the A40 at Carmarthen, Wales. Before the Severn Bridge opened on 8 September 1966, it was a major route between England and South Wales. For most of its route, it runs almost parallel to the M4 motorway. During times of high winds at the Severn Bridge, the A48 is used as part of the diversion route and is still marked as a Holiday Route.

The M48 is a 13-mile-long (21 km) motorway in Great Britain, which crosses the Severn near Chepstow, Monmouthshire, linking England with Wales via the Severn Bridge. This road used to be the M4, and as a result is anomalously numbered: as it lies to the north of the M4 and to the west of the M5, it is in the Motorway Zone 5. The M4, M48 and the A48(M) motorway are the only motorways in Wales.

European route E30 is an A-Class European route from the port of Cork in Ireland in the west to the Russian city of Omsk, near the border with Kazakhstan in the east. For much of the Russian stretch, it follows the Trans-Siberian Highway and, east of the Ural Mountains, with AH6 of the Asian Highway Network, which continues to Busan, South Korea. The total length is 6,530 km (4,060 mi)—3,300 km (2,100 mi) from Cork to Moscow, and 3,230 km (2,010 mi) from Moscow to Omsk. The naming is by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE).

The A48(M) motorway in Wales links Cardiff with Newport. It is a 2-mile-long (3 km) spur of the M4 motorway. At St Mellons, it runs continuously into the dual-carriageway A48, which also has (albeit narrow) hard shoulders. The A48(M) has no other junctions and opened in 1977. The M4 was extended west from junction 29 in 1980.

Pontarddulais, also spelled Pontardulais, is town and community in Swansea, Wales. It is 10 miles (16 km) northwest of the city centre. It is in the Pontarddulais ward of the City and County of Swansea Council. Pontarddulais adjoins the village of Hendy in Carmarthenshire. The built-up population was 9,073.

Transport in Wales is heavily influenced by the country's geography. Wales is predominantly hilly or mountainous, and the main settlements lie on the coasts of north and south Wales, while mid Wales and west Wales are lightly populated. The main transport corridors are east–west routes, many continuing eastwards into England.

Hydrocarbon Oil Duty is a fuel tax levied on some fuels used by most road motor vehicles in the United Kingdom; with exceptions for local bus services, some farm and construction vehicles and aviation, which pay reduced or no fuel duty.

The M4 Motorway is a 55-kilometre (34 mi) series of partially tolled dual carriageway motorways in Sydney designated as route M4. The M4 designation is part of the wider A4 and M4 route designation, the M4 runs parallel and/or below ground to Great Western Highway, Parramatta Road and City West Link, which are part of route A44.

Pontlliw is a village in the community of Pontlliw and Tircoed, part of the City and County of Swansea in Wales. The village is located near Pontarddulais, off Junction 47 of the M4 motorway.

Castleton is a hamlet in the city of Newport, South Wales.

The M4 relief road, also known as M4 Corridor around Newport (M4CaN), was a proposed motorway, south of the city of Newport, South Wales, intended to relieve traffic congestion on the M4 motorway.

The Brynglas Tunnels carry the M4 under Brynglas Hill in Newport, Wales. The 360-metre-long (390 yd) tunnels are the first and only twin–bored tunnels in the UK motorway network.

The A4232, which is also known either as the Peripheral Distributor Road (PDR) (Welsh: Ffordd Ddosbarthu Ymylol) or the Cardiff Link Road (Welsh: Ffordd Gyswllt Caerdydd), is a distributor road in Cardiff, the capital of Wales.
Hendy is a village in the community of Llanedi in Carmarthenshire, Wales. It is situated at the Carmarthenshire and Swansea border, and lies on Afon Gwili, just across the River Loughor from Pontarddulais. Together with Fforest to the north, it forms part of a continuous built-up area centred on Pontarddulais. Most of the village sits between the M4 Motorway junction 48 and the A48 road north of the motorway.

A smart motorway, also known in Scotland as an intelligent transport system, is a section of motorway in the United Kingdom that employs active traffic management (ATM) techniques to increase capacity through the use of MIDAS technology including variable speed limits and occasionally hard shoulder running and ramp metering at busy times. They were developed at the turn of the 21st century as a cost-effective alternative to traditional carriageway widening, with intended benefits ranging from more reliable journey times to lower vehicle emissions. However, despite the risk of a collision occurring between two moving vehicles being found to be decreased, there has been an acknowledged rise in the incidence of collisions involving vehicles where at least one was stationary in the first few years following the widespread removal of the hard shoulder on the country's busiest sections of motorway. Smart motorways garnered intense criticism from politicians, police representatives and motoring organisations, particularly from 2020 onwards, after a surge in near miss incidents and dozens of fatalities were revealed, and as of April 2023, no new smart motorways will be built.

Trunk roads in Wales were created in the Trunk Roads Act of 1936 when the UK Ministry of Transport took direct control over 30 of the principal roads in Great Britain from English, Welsh and Scottish local authorities. The number of trunk roads was increased from 30 to 101 in the Trunk Roads Act of 1946. These roads formed what the Act called "the national system of routes for through traffic". Since Welsh devolution the trunk road system in Wales has been managed by the South Wales Trunk Road Agent and the North and Mid Wales Trunk Road Agent on behalf of the Welsh Government. As of April 2019, out of a total of 34,850 miles (56,090 km) of roads in Wales, 1,576 miles (2,536 km) are trunk roads.




















