Related Research Articles

Protein biosynthesis is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences.

Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In addition, other kinds of proteins include antibodies that protect an organism from infection, and hormones that send important signals throughout the body.

Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones.

Wolfgang Sawallisch was a German conductor and pianist.
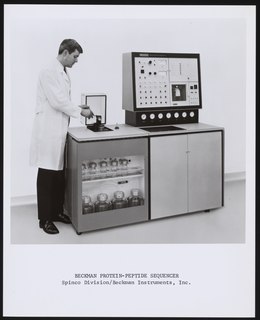
Protein sequencing is the practical process of determining the amino acid sequence of all or part of a protein or peptide. This may serve to identify the protein or characterize its post-translational modifications. Typically, partial sequencing of a protein provides sufficient information to identify it with reference to databases of protein sequences derived from the conceptual translation of genes.

The Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry (MPIB) is a research institute of the Max Planck Society located in Martinsried, a suburb of Munich. The institute was founded in 1973 by the merger of three formerly independent institutes: the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, the Max Planck Institute of Protein and Leather Research, and the Max Planck Institute of Cell Chemistry.
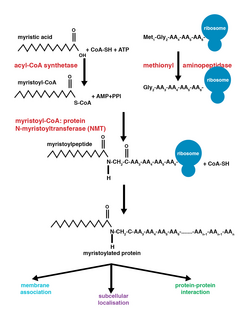
Myristoylation is a lipidation modification where a myristoyl group, derived from myristic acid, is covalently attached by an amide bond to the alpha-amino group of an N-terminal glycine residue. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid (14:0) with the systematic name of n-Tetradecanoic acid. This modification can be added either co-translationally or post-translationally. N-myristoyltransferase (NMT) catalyzes the myristic acid addition reaction in the cytoplasm of cells. This lipidation event is the most found type of fatty acylation and is common among many organisms including animals, plants, fungi, protozoans and viruses. Myristoylation allows for weak protein–protein and protein–lipid interactions and plays an essential role in membrane targeting, protein–protein interactions and functions widely in a variety of signal transduction pathways.
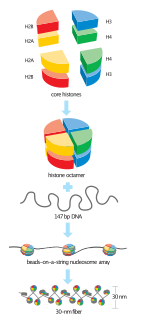
Histone H3 is one of the five main histones involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and a long N-terminal tail, H3 is involved with the structure of the nucleosomes of the 'beads on a string' structure. Histone proteins are highly post-translationally modified however Histone H3 is the most extensively modified of the five histones. The term "Histone H3" alone is purposely ambiguous in that it does not distinguish between sequence variants or modification state. Histone H3 is an important protein in the emerging field of epigenetics, where its sequence variants and variable modification states are thought to play a role in the dynamic and long term regulation of genes.

Horst Schumann was an SS-Sturmbannführer (major) and medical doctor who conducted sterilization and castration experiments at Auschwitz and was particularly interested in the mass sterilization of Jews by means of X-rays.
Histone H2B is one of the 5 main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and long N-terminal and C-terminal tails, H2B is involved with the structure of the nucleosomes.
Sulfation is the chemical reaction that entails the addition of SO3 group. In principle, many sulfations would involve reactions of sulfur trioxide (SO3). In practice, most sulfations are effected less directly. Regardless of the mechanism, the installation of a sulfate-like group on a substrate leads to substantial changes.

Scenes from Goethe's Faust is a musical-theatrical work by composer Robert Schumann. The work has been described as the height of his accomplishments in the realm of dramatic music. The work was written between 1844 and 1853 and is scored for SATB chorus, boys' chorus, orchestra, and a number of solo parts which, even with doubling, require seven solo singers, although eight is the usual number for a performance. Schumann never saw all three parts of the work performed in the same concert, or published together. Eric Sams comments 'There is no coherence in the orchestration, which audibly dates from two different periods ', leading him to conclude that Schumann did not conceive the work as a whole, although late nineteenth-century ideas of performance mean that in the modern era the piece is predominantly heard with all three parts.
The eastern blot, or eastern blotting, is a biochemical technique used to analyze protein post-translational modifications including the addition of lipids, phosphates, and glycoconjugates. It is most often used to detect carbohydrate epitopes. Thus, eastern blot can be considered an extension of the biochemical technique of western blot. Multiple techniques have been described by the term "eastern blot(ting)", most use phosphoprotein blotted from sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gel on to a polyvinylidene fluoride or nitrocellulose membrane. Transferred proteins are analyzed for post-translational modifications using probes that may detect lipids, carbohydrate, phosphorylation or any other protein modification. Eastern blotting should be used to refer to methods that detect their targets through specific interaction of the post-translational modifications and the probe, distinguishing them from a standard far-western blot. In principle, eastern blotting is similar to lectin blotting.
Thiazolines are a group of isomeric 5-membered heterocyclic compounds containing both sulfur and nitrogen in the ring. Although unsubstituted thiazolines are rarely encountered themselves, their derivatives are more common and some are bioactive. For example, in a common post-translational modification, cysteine residues are converted into thiazolines.
A biological pathway is a series of interactions among molecules in a cell that leads to a certain product or a change in a cell. Such a pathway can trigger the assembly of new molecules, such as a fat or protein. Pathways can also turn genes on and off, or spur a cell to move. Some of the most common biological pathways are involved in metabolism, the regulation of gene expression and the transmission of signals. Pathways play a key role in advanced studies of genomics.
The Unique Ingredient Identifier (UNII) is an alphanumeric identifier linked to a substance's molecular structure or descriptive information and is generated by the Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It classifies substances as chemical, protein, nucleic acid, polymer, structurally diverse, or mixture according to the standards outlined by the International Organization for Standardization in ISO 11238 and ISO DTS 19844. UNIIs are non-proprietary, unique, unambiguous, and free to generate and use. A UNII can be generated for substances at any level of complexity, being broad enough to include "any substance, from an atom to an organism."
Succinylation is a posttranslational modification where a succinyl group (-CO-CH2-CH2-CO2H) is added to a lysine residue of a protein molecule. This modification is found in many proteins, including histones. The potential role of succinylation is under investigation, but as addition of succinyl group changes lysine's charge from +1 to −1 (at physiological pH) and introduces a relatively large structural moiety (100 Da), bigger than acetylation (42 Da) or methylation (14 Da), it is expected to lead to more significant changes in protein structure and function.
The chaperone code refers to post-translational modifications of molecular chaperones that control protein folding. Whilst the genetic code specifies how DNA makes proteins, and the histone code regulates histone-DNA interactions, the chaperone code controls how proteins are folded to produce a functional proteome.
The Robert Schumann Prize for Poetry and Music Mainz is a classical music prize named after Robert Schumann, awarded biennially since 2012. The prize money is €15,000, donated by the Strecker Foundation, Mainz. The prize is awarded by the Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur in Mainz, for personalities with an outstanding lifetime achievement in the field of poetry and music.
Heidrun Schumann is a German computer scientist specializing in data visualization. She is a professor emerita in the Institute for Computer Science of the University of Rostock.
References
- ↑ Wolfgang Schumann; Wolfgang Schumann (Prof. Dr. rer. nat.) (2006). Dynamics of the bacterial chromosome: structure and function. Wiley-VCH. pp. 266–. ISBN 978-3-527-30496-7 . Retrieved 26 December 2010.