
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of three types of bone: cranial bones, facial bones, and ear ossicles. Two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium (braincase) and the viscerocranium that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans, these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton.

In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is a unpaired bone which consists of two portions. These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word frons.

The lacrimal bones are two small and fragile bones of the facial skeleton; they are roughly the size of the little fingernail and situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. They each have two surfaces and four borders. Several bony landmarks of the lacrimal bones function in the process of lacrimation. Specifically, the lacrimal bones help form the nasolacrimal canal necessary for tear translocation. A depression on the anterior inferior portion of one bone, the lacrimal fossa, houses the membranous lacrimal sac. Tears, from the lacrimal glands, collect in this sac during excessive lacrimation. The fluid then flows through the nasolacrimal duct and into the nasopharynx. This drainage results in what is commonly referred to a runny nose during excessive crying or tear production. Injury or fracture of the lacrimal bone can result in posttraumatic obstruction of the lacrimal pathways.

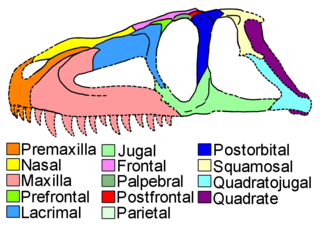
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.

Quaesitosaurus is a genus of nemegtosaurid sauropod containing only the type species, Q. orientalis, described in 1983. It lived from 72 to 71 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous epoch in the Barun Goyot Formation. With long, low and horse-like with frontally located peg-teeth, the skull of Quaesitosaurus is similar enough to the skull of Diplodocus and its kin to have prompted informed speculation that the missing body was built like those of diplodocids.

Tsintaosaurus is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from China. It was about 8.3 metres (27 ft) long and weighed 2.5 tonnes. The type species is Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus, first described by Chinese paleontologist C. C. Young in 1958.

The ethmoidal labyrinth or lateral mass of the ethmoid bone consists of a number of thin-walled cellular cavities, the ethmoid air cells, arranged in three groups, anterior, middle, and posterior, and interposed between two vertical plates of bone; the lateral plate forms part of the orbit, the medial plate forms part of the nasal cavity. In the disarticulated bone many of these cells are opened into, but when the bones are articulated, they are closed in at every part, except where they open into the nasal cavity.

The frontal process of the maxilla is a strong plate, which projects upward, medialward, and backward from the maxilla, forming part of the lateral boundary of the nose.

Dipnorhynchus is an extinct genus of marine lungfish from the middle Devonian period (Emsian) of Australia.
Luperosuchus is an extinct genus of loricatan pseudosuchian reptile which contains only a single species, Luperosuchus fractus. It is known from the Chañares Formation of Argentina, within strata belonging to the latest Ladinian stage of the late Middle Triassic, or the earliest Carnian of the Late Triassic. Luperosuchus was one of the largest carnivores of the Chañares Formation, although its remains are fragmentary and primarily represented by a skull with similarities to Prestosuchus and Saurosuchus.

The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes and all land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium.
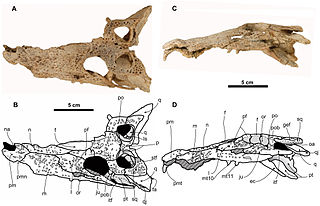
Arenysuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of allodaposuchid eusuchian crocodylomorph from Late Cretaceous deposits of north Spain. It is known from the holotype MPZ ELI-1, a partial skull from Elías site, and from the referred material MPZ2010/948, MPZ2010/949, MPZ2010/950 and MPZ2010/951, four teeth from Blasi 2 site. It was found by the researchers José Manuel Gasca and Ainara Badiola from the Tremp Formation, in Arén of Huesca, Spain. It was first named by Eduardo Puértolas, José I. Canudo and Penélope Cruzado-Caballero in 2011 and the type species is Arenysuchus gascabadiolorum.

Jesairosaurus is an extinct genus of early archosauromorph reptile known from the Illizi Province of Algeria. It is known from a single species, Jesairosaurus lehmani. Although a potential relative of the long-necked tanystropheids, this lightly-built reptile could instead be characterized by its relatively short neck as well as various skull features.
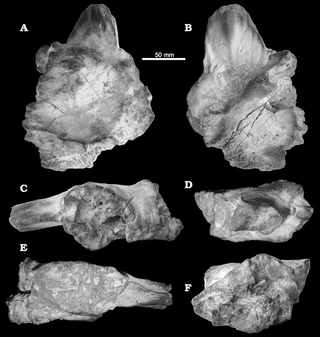
Sauroniops is a controversial genus of carnivorous basal carcharodontosaurid theropod dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Gara Sbaa Formation, and possibly also the Kem Kem Formation, both of Morocco. The type, and currently only, species is S. platytholus.
This glossary explains technical terms commonly employed in the description of dinosaur body fossils. Besides dinosaur-specific terms, it covers terms with wider usage, when these are of central importance in the study of dinosaurs or when their discussion in the context of dinosaurs is beneficial. The glossary does not cover ichnological and bone histological terms, nor does it cover measurements.

Avicranium is a genus of extinct drepanosaur reptile known from the Chinle Formation of the late Triassic. The type species of Avicranium is Avicranium renestoi. "Avicranium" is Latin for "bird cranium", in reference to its unusual bird-like skull, while "renestoi" references Silvio Renesto, a paleontologist known for studies of Italian drepanosaurs.

Thanatotheristes is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Laramidia, approximately 80.1-79.5 Ma. Thanatotheristes contains only one species, T. degrootorum. Fossils of this taxon are found in the Foremost Formation of Alberta, Canada, coexisting with medium-sized ceratopsids like Xenoceratops foremostensis and small pachycephalosaurids like Colepiocephale lambei.

Rugarhynchos is an extinct genus of doswelliid archosauriform from the Late Triassic of New Mexico. The only known species is Rugarhynchos sixmilensis. It was originally described as a species of Doswellia in 2012, before receiving its own genus in 2020. Rugarhynchos was a close relative of Doswellia and shared several features with it, such as the absence of an infratemporal fenestra and heavily textured skull bones. However, it could also be distinguished by many unique characteristics, such as a thick diagonal ridge on the side of the snout, blunt spikes on its osteoderms, and a complex suture between the quadratojugal, squamosal, and jugal. Non-metric multidimensional scaling and tooth morphology suggest that Rugarhynchos had a general skull anatomy convergent with some crocodyliforms, spinosaurids, and phytosaurs. However, its snout was somewhat less elongated than those other reptiles.

Bagualia, is an extinct genus of eusauropod dinosaur, from the Early Jurassic Epoch in what is now the Chubut Province of Argentina. The type species, B. alba, was formally described in 2020. Bagualia represents the oldest definitive Eusauropod, and due to the completeness of its material it represents one of the most important taxa for understanding the early evolution of the group.
The postfrontal is a paired cranial bone found in many tetrapods. It occupies an area of the skull roof between and behind the orbits, lateral to the frontal and parietal bones, and anterior to the postorbital bone.


















