Shelikhov Gulf is a large gulf off the northwestern coast of Kamchatka, Russia. It is located in the northeastern corner of the Sea of Okhotsk and it branches into two main arms, Gizhigin Bay to the west and Penzhina Bay to the east. Its southwest corner is formed by the P'yagin Peninsula, Yam Gulf and the Yamsky Islands.
Sakhalin Gulf is a gulf in the Sea of Okhotsk between continental Russia and the northern tip of Sakhalin Island. The width of the gulf reaches up to 160 km. It is covered with ice from mid-November until late April, but north winds can leave the bay blocked with ice until July.

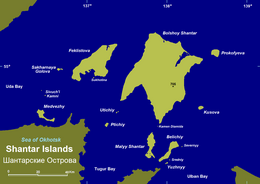
Bolshoy Shantar is an island in the Sea of Okhotsk, Russia. It is the main island of the Shantar Islands. Its area is 1766 km². It is about 72 km (44.7 mi) in length and 49 km (30.4 mi) in width. It has a large brackish lake on its north side which is connected to the sea through a narrow passage. Yakshin Bay indents the southwest side of the island.

Feklistova or Feklistov Island is one of the Shantar Islands in Sea of Okhotsk. With an area of 372 km², it is the second largest in the archipelago.

Iony Island, or Jonas' Island, formerly Ostrov Svyatogo Iony, is a small island in the Sea of Okhotsk.

Taui Bay is a body of water in the Sea of Okhotsk off the coast of the Magadan Oblast in Russia. The bay opens to the south.
Konstantina Bay is a small bay in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk, just south of the Shantar Islands. It is a western branch of the larger Academy Bay to the east. The bay is about 9.6 km (6 mi) in diameter and its entrance is about 4.8 km (3 mi) wide. Spring tides rise 3.8 m (12.5 ft), while neaps rise 2.7 m (9 ft).
Nikolaya Bay, formerly Usalginsky Bay, is a small, narrow bay in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk, just south of the Shantar Islands. It is a southeastern branch of the larger Academy Bay to the north. Its northern and southern points, Lamsdorf Point and Cape Grote, are separated by only 8 km (5 mi), while the bay itself is about 59.5 km (37 mi) deep in a southerly direction. The Tokara Peninsula separates it from Ulban Bay to the west. The Usalgin River runs into its head. Spring tides rise 5.5 m (18 ft), while neaps rise 2.4–3 m (8–10 ft). There is ice in the bay from mid-November to mid-July.

Tugur Bay or Tugursky Bay is a large bay in the Tuguro-Chumikansky District of Khabarovsk Krai, Russian Federation.

Maly Shantar Island is a small, narrow island in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk, one of the Shantar Islands.

Medvezhy Island is a long, narrow island in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk, the westernmost of the Shantar Islands. It lies on the eastern side of Uda Gulf. It is 12.9 km long. It is separated from the mainland by Shevchenko Straight.
Lindholm Strait is a strait in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk. It separates Malyy Shantar and Belichiy Islands to the north from the Tugur Peninsula to the south. At its narrowest it is only 3.2 km wide. Tides are semidiurnal. Springs rise 4.9 m, while neaps rise 3.6 m. The flood current sets west, while the stronger ebb current flows in the opposite direction. The former creates large eddies and whirlpools. Tidal currents vary from 3.5 to 6 knots.

Ptichy Island is a small island in the Sea of Okhotsk.

Sakharnaya Golova is a small island in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk. It is part of the Shantar Islands National Park.

Academy Bay is a large bay in the Tuguro-Chumikansky District of Khabarovsk Krai, Russian Federation.
Lebyazhya Bay is a small bay that indents the south side of Feklistova Island, one of the Shantar Islands, in the western Sea of Okhotsk. Its entrance is 11.3 kilometers (7.0 mi) wide and it is 5.6 kilometers (3.5 mi) deep. There are three small bays at its head: Enegelma Road to the west, Soboleva to the north, and Rosseta to the east. A small island, Sukhotina, lies to its southeast. In the spring and summer it is host to a small nesting colony of thick-billed murre. A number of streams of fresh water flow down the hills into the bay. Spring tides rise 6.5 meters (21 ft) while neaps rise 2.4 meters.
Abrek Bay is a small bay on the southeast coast of Maly Shantar Island, one of the Shantar Islands, in the western Sea of Okhotsk. It is 2.4 km (1.5 mi) wide at its entrance and about 1.6 km (1 mi) deep. Spring tides rise about 4.5 m (15 ft) and neaps about 2.7 m (9 ft).
Cape Bol'shoy Dugandzha is a headland in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia.
Commercial open-boat whaling by American and European ships occurred in the Sea of Okhotsk from the 1830s to the early 1900s. They primarily caught right and bowhead whales. Both populations of these species declined drastically, with the latter once thought to be extinct by western historians. Peak catches were made in the 1840s and 1850s. It's estimated that as many as 15,200 bowheads and 2,400 rights were taken in the sea.