
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates.

Amino acid biosynthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids.

Cystathionine-β-synthase, also known as CBS, is an enzyme (EC 4.2.1.22) that in humans is encoded by the CBS gene. It catalyzes the first step of the transsulfuration pathway, from homocysteine to cystathionine:

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
The enzyme L-3-cyanoalanine synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme S-carboxymethylcysteine synthase catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme ectoine synthase (EC ) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.19) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme isohexenylglutaconyl-CoA hydratase (EC 4.2.1.57) catalyzes the chemical reaction
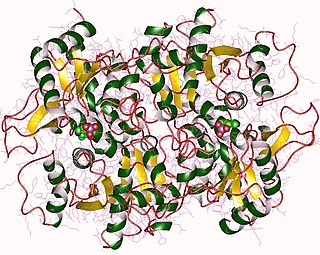
The enzyme threonine synthase (EC 4.2.3.1) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-pyrazolylalanine synthase (EC 2.5.1.51) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cysteine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-mimosine synthase (EC 2.5.1.52) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an uracilylalanine synthase (EC 2.5.1.53) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a zeatin 9-aminocarboxyethyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
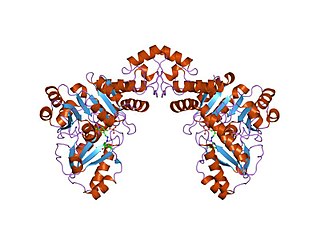
In molecular biology, the Cys/Met metabolism PLP-dependent enzyme family is a family of proteins including enzymes involved in cysteine and methionine metabolism which use PLP (pyridoxal-5'-phosphate) as a cofactor.
Tryptophan synthase (indole-salvaging) (EC 4.2.1.122, tryptophan synthase beta2) is an enzyme with systematic name L-serine hydro-lyase (adding indole, L-tryptophan-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
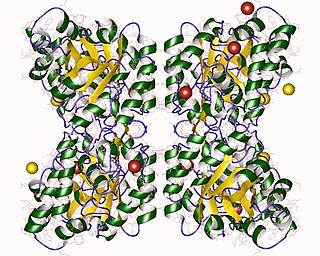
4-Hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase (EC 4.3.3.7, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydropicolinate synthetase, dihydrodipicolinic acid synthase, L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing), dapA (gene)) is an enzyme with the systematic name L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing; (4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-(2S)-dipicolinate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction








