
Antidesma is a genus of tropical plant in the family Phyllanthaceae formally described by Linnaeus in 1753. It is native to tropical Africa, S + E + SE Asia, Australia, and various oceanic islands. The greatest diversity occurs in Southeast Asia.

Canarium is a genus of about 120 species of tropical and subtropical trees, in the family Burseraceae. They grow naturally across tropical Africa, south and southeast Asia, Indochina, Malesia, Australia and western Pacific Islands; including from southern Nigeria east to Madagascar, Mauritius, Sri Lanka and India; from Burma, Malaysia and Thailand through the Malay Peninsula and Vietnam to south China, Taiwan and the Philippines; through Borneo, Indonesia, Timor and New Guinea, through to the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, New Caledonia, Fiji, Samoa, Tonga and Palau.

Aporosa is a genus of flowering plant belonging to the family Phyllanthaceae, first described as a genus in 1825. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Papuasia, and Queensland.

Daphniphyllum is the sole genus in the flowering plant family Daphniphyllaceae and was described as a genus in 1826. The genus includes evergreen shrubs and trees mainly native to east and southeast Asia, but also found in the Indian Subcontinent and New Guinea.

Arenga is a genus of palms, native to Southeast Asia, southern China, New Guinea, and northern Australia. They are small to medium-sized palms, growing to 2–20 m tall, with pinnate leaves 2–12 m long. Arenga palms can grow in areas with little sunlight and relatively infertile soil.

Corybas, commonly known as helmet orchids, is a genus of about 120 species of plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Helmet orchids are small, perennial, deciduous herbs and are nearly always terrestrial. They have a single leaf at their base and a single flower on a short stalk, the flower dominated by its large dorsal sepal and labellum. Species of Corybas are found in Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea, Southeast Asia, the Himalayas, southern China, many Pacific islands and a few sub-Antarctic islands.
Pothos is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, Australia, New Guinea, Southeast Asia, and various islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans.

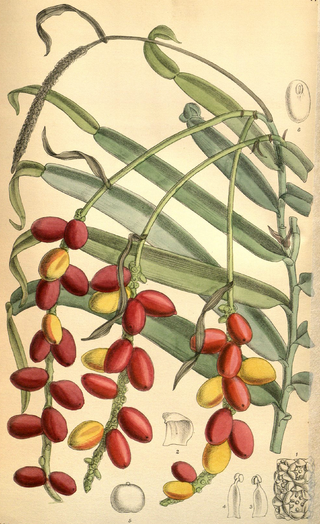
Barringtonia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lecythidaceae first described as a genus with this name in 1775. It is native to Africa, southern Asia, Australia, and various islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. The genus name commemorates Daines Barrington.

Acriopsis, commonly known as chandelier orchids or 合萼兰属 is a genus of flowering plants in the family Orchidaceaes. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic herbs with spherical or cylindrical pseudobulbs, creeping, branched rhizomes, thin white roots, two or three leaves and many small flowers. The flowers are non-resupinate with the lateral sepals joined along their edges and have spreading petals and a three-lobed labellum. The column has projections that extend hood-like beyond the anther.

Scindapsus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to Southeast Asia, New Guinea, Queensland, and a few western Pacific islands. The species Scindapsus pictus is common in cultivation.

Pholidota, commonly known as rattlesnake orchids, is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are clump-forming epiphytes or lithophytes with pseudobulbs, each with a single large leaf and a large number of small, whitish flowers arranged in two ranks along a thin, wiry flowering stem that emerges from the top of the pseudobulb. There are about thirty five species native to areas from tropical and subtropical Asia to the southwestern Pacific.

Rhodamnia rubescens, the scrub stringybark, brush turpentine, or brown malletwood, is an evergreen rainforest tree of the myrtle family Myrtaceae, that is native to Eastern Australia. Identified by a stringy type of bark and triple-veined leaves, it grows in a variety of different rainforests from the Batemans Bay region of southeastern New South Wales to Gympie in southeastern Queensland. It is not seen in the cool temperate rainforests. The pathogen myrtle rust threatens the existence of Rhodamnia rubescens.

Vrydagzynea, commonly called tonsil orchids, is a genus of orchids in the tribe Cranichideae. About forty five species of Vrydagzynea have been formally described. They are native to India, Taiwan, Southeast Asia, Malesia, Melanesia and Polynesia. A single species in Australia is possibly extinct. They have thinly textured, stalked leaves and small, dull-coloured resupinate flowers with the dorsal sepal and petals overlapping to form a hood over the column.

Thelasis, commonly known as fly orchids, is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are usually epiphytes, sometimes lithophytes or rarely terrestrials. Some species have pseudobulbs with up to three leaves, whilst others have several leaves in two ranks. A large number of small, white or greenish yellow flowers are borne on a thin, arching flowering stem. There are about thirty species, distributed from tropical and subtropical Asia to the southwest Pacific.

Gossia is a genus of rainforest trees in the myrtle family first described as a genus in 2003 by Neil Snow, Gordon Guymer and Sawvel. It is native to northeastern Australia as well as several islands of Papuasia and New Caledonia.

Rhodamnia argentea is a rainforest tree of eastern Australia. Commonly known asmalletwood, white myrtle, silver leaf, silver malletwood and white turpentine. The natural habitat is a variety of different rain forests, at sea level or in the adjacent ranges. Growing on sand, alluvium and volcanic based soils. From the Hastings River, New South Wales to Bowen, Queensland.

Rhodamnia whiteana, known as the cliff malletwood or White's malletwood is a sub-tropical rainforest plant of eastern Australia. It was first formally described in 1986 by Gordon Guymer and Laurence Jessup from a specimen collected from Mount Cordeaux.

Phrynium is a genus of flowering plants native to China, India, Southeast Asia, New Guinea and Melanesia. It was described as a genus in 1797.

Myxopyrum is a plant genus native to India, southern China, Southeast Asia and New Guinea. There are at present 4 recognized species:

Hornstedtia is a genus of plants in the Zingiberaceae. It is native to Southeast Asia, the Himalayas, southern China, New Guinea, Melanesia and Queensland.




















