
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the progenitor, either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months.

A super-luminous supernova is a type of stellar explosion with a luminosity 10 or more times higher than that of standard supernovae. Like supernovae, SLSNe seem to be produced by several mechanisms, which is readily revealed by their light-curves and spectra. There are multiple models for what conditions may produce an SLSN, including core collapse in particularly massive stars, millisecond magnetars, interaction with circumstellar material, or pair-instability supernovae.
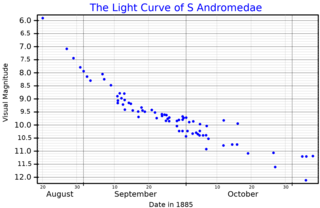
SN 1885A was a supernova in the Andromeda Galaxy, the only one seen in that galaxy so far by astronomers. It was the first supernova ever seen outside the Milky Way, though it was not appreciated at the time how far away it was. It is also known as "Supernova 1885".

SN 2005df was a Type Ia supernova in the barred spiral galaxy NGC 1559, which is located in the southern constellation of Reticulum. The event was discovered in Australia by Robert Evans on the early morning of August 5, 2005 with a 13.8 magnitude, and was confirmed by A. Gilmore on August 6. The supernova was classified as Type Ia by M. Salvo and associates. It was positioned at an offset of 15.0″ east and 40.0″ north of the galaxy's nucleus, reaching a maximum brightness of 12.3 on August 18. The supernova luminosity appeared unreddened by dust from its host galaxy.

A Type Ia supernova is a type of supernova that occurs in binary systems in which one of the stars is a white dwarf. The other star can be anything from a giant star to an even smaller white dwarf.

SN 1994D was a Type Ia supernova event in the outskirts of galaxy NGC 4526. It was offset by 9.0″ west and 7.8″ south of the galaxy center and positioned near a prominent dust lane. It was caused by the explosion of a white dwarf star composed of carbon and oxygen. This event was discovered on March 7, 1994 by R. R. Treffers and associates using the automated 30-inch telescope at Leuschner Observatory. It reached peak visual brightness two weeks later on March 22. Modelling of the light curve indicates the explosion would have been visible around March 3-4. A possible detection of helium in the spectrum was made by W. P. S. Meikle and associates in 1996. A mass of 0.014 to 0.03 M☉ in helium would be needed to produce this feature.

NGC 1309 is a spiral galaxy located approximately 120 million light-years away, appearing in the constellation Eridanus. It is about 75,000 light-years across, and is about 3/4s the width of the Milky Way. Its shape is classified as SA(s)bc, meaning that it has moderately wound spiral arms and no ring. Bright blue areas of star formation can be seen in the spiral arms, while the yellowish central nucleus contains older-population stars. NGC 1309 is one of over 200 members of the Eridanus Group of galaxies.

NGC 1032 is a spiral galaxy that is about 117 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus. It was discovered on 18 December 1783 by German-British astronomer William Herschel.

Type Ib and Type Ic supernovae are categories of supernovae that are caused by the stellar core collapse of massive stars. These stars have shed or been stripped of their outer envelope of hydrogen, and, when compared to the spectrum of Type Ia supernovae, they lack the absorption line of silicon. Compared to Type Ib, Type Ic supernovae are hypothesized to have lost more of their initial envelope, including most of their helium. The two types are usually referred to as stripped core-collapse supernovae.

A Type II supernova or SNII results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least eight times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun (M☉) to undergo this type of explosion. Type II supernovae are distinguished from other types of supernovae by the presence of hydrogen in their spectra. They are usually observed in the spiral arms of galaxies and in H II regions, but not in elliptical galaxies; those are generally composed of older, low-mass stars, with few of the young, very massive stars necessary to cause a supernova.
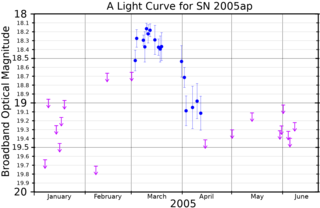
SN 2005ap was an extremely energetic type Ic supernova in the galaxy SDSS J130115.12+274327.5. With a peak absolute magnitude of around −22.7, it is the second-brightest superluminous supernova yet recorded, twice as bright as the previous record holder, SN 2006gy, though SN 2005ap was eventually surpassed by ASASSN-15lh. It was initially classified as type II-L, but later revised to type Ic. It was discovered on 3 March 2005, on unfiltered optical images taken with the 0.45 m ROTSE-IIIb telescope, which is located at the McDonald Observatory in West Texas, by Robert Quimby, as part of the Texas Supernova Search that also discovered SN 2006gy. Although it was discovered before SN 2006gy, it was not recognized as being brighter until October 2007. As it occurred 4.7 billion light years from Earth, it was not visible to the naked eye.

SN 1993J is a supernova observed in Bode's Galaxy. It was discovered on 28 March 1993 by F. Garcia in Spain. At the time, it was the second-brightest type II supernova observed in the twentieth century behind SN 1987A, peaking at a visible apparent magnitude of 10.7 on March 30, with a second peak of 10.86 on April 18.

SN 2008ax was a helium-rich type Ib core-collapse supernova in the interacting galaxy NGC 4490. It was independently discovered on 3 March 2008 by LOSS and 4 March by Koichi Itagaki. The site had been monitored six hours before discovery, thus constraining the time of the explosion breakout. It was the third-brightest supernova of 2008. The brightness in the B-band peaked about 20 days after the explosion. X-ray emissions were detected from the event, which are most likely the result of shock heating from the supernova ejecta and circumstellar material.

SN 1994I is a Type Ic supernova discovered on April 2, 1994 in the Whirlpool Galaxy by amateur astronomers Tim Puckett and Jerry Armstrong of the Atlanta Astronomy Club. Type Ic supernova are a rare type of supernova that result from the explosion of a very massive star that has shed its outer layers of hydrogen and helium. The explosion results in a highly luminous burst of radiation that then dims over the course of weeks or months. SN 1994I was a relatively nearby supernova, and provided an important addition to the then small collection of known Type Ic supernova. Very early images were captured of SN 1994I, as two high school students in Oil City, Pennsylvania serendipitously took images of the Whirlpool Galaxy using the 30-inch telescope at Leuschner Observatory on March 31, 1994, which included SN 1994I just after it began to brighten.

SN 2011fe, initially designated PTF 11kly, was a Type Ia supernova discovered by the Palomar Transient Factory (PTF) survey on 24 August 2011 during an automated review of images of the Messier 101 from the nights of 22 and 23 August 2011. It was located in Messier 101, the Pinwheel Galaxy, 21 million light years from Earth. It was observed by the PTF survey very near the beginning of its supernova event, when it was approximately 1 million times too dim to be visible to the naked eye. It is the youngest type Ia ever discovered. About 13 September 2011, it reached its maximum brightness of apparent magnitude +9.9 which equals an absolute magnitude of about -19, equal to 2.5 billion Suns. At +10 apparent magnitude around 5 September, SN 2011fe was visible in small telescopes. As of 30 September the supernova was at +11 apparent magnitude in the early evening sky after sunset above the northwest horizon. It had dropped to +13.7 as of 26 November 2011.
In astronomy, a calcium-rich supernova is a subclass of supernovae that, in contrast to more well-known traditional supernova classes, are fainter and produce unusually large amounts of calcium. Since their luminosity is located in a gap between that of novae and other supernovae, they are also referred to as "gap" transients. Only around 15 events have been classified as a calcium-rich supernova – a combination of their intrinsic rarity and low luminosity make new discoveries and their subsequent study difficult. This makes calcium-rich supernovae one of the most mysterious supernova subclasses currently known.

ASASSN-15lh is an extremely luminous astronomical transient event discovered by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN), with the appearance of a superluminous supernova event. It was first detected on June 14, 2015, located within a faint galaxy in the southern constellation Indus, and was the most luminous supernova-like object ever observed. At its peak, ASASSN-15lh was 570 billion times brighter than the Sun, and 20 times brighter than the combined light emitted by the Milky Way Galaxy. The emitted energy was exceeded by PS1-10adi.

SN 2018cow was a very powerful astronomical explosion, 10–100 times brighter than a normal supernova, spatially coincident with galaxy CGCG 137-068, approximately 200 million ly (60 million pc) distant in the Hercules constellation. It was discovered on 16 June 2018 by the ATLAS-HKO telescope, and had generated significant interest among astronomers throughout the world. Later, on 10 July 2018, and after AT 2018cow had significantly faded, astronomers, based on follow-up studies with the Nordic Optical Telescope (NOT), formally described AT 2018cow as SN 2018cow, a type Ib supernova, showing an "unprecedented spectrum for a supernova of this class"; although others, mostly at first but also more recently, have referred to it as a type Ic-BL supernova. An explanation to help better understand the unique features of AT 2018cow has been presented. AT2018cow is one of the few reported Fast Blue Optical Transients (FBOTs) observed in the Universe. In May 2020, however, a much more powerful FBOT than AT 2018cow was reportedly observed.

NGC 4589 is an elliptical galaxy located in the Draco constellation. It was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel on November 22, 1797. This galaxy lies at a distance of 73.0 million light-years (22.39 Mpc) from the Milky Way, and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 2,002 km/s. It is known by its designations PGC 42139 or UGC 7797.
Ken'ichi Nomoto is a Japanese astrophysicist and astronomer, known for his research on stellar evolution, supernovae, and the origin of heavy elements.
















