Notes
- ↑ Applying the Stefan–Boltzmann law with a nominal solar effective temperature of 5,772 K:
This article is being considered for deletion in accordance with Wikipedia's deletion policy. Please share your thoughts on the matter at this article's deletion discussion page. |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Dorado [1] |
| Right ascension | 05h 29m 42.2038s [2] |
| Declination | −68° 57′ 17.351″ [2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.54 (var.) [3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Red supergiant |
| Spectral type | M2.5 Ia-Iab [4] |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 14.04 [5] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 12.15 [5] |
| Apparent magnitude (R) | 10.99 [5] |
| Apparent magnitude (J) | 7.922±0.024 [6] |
| Apparent magnitude (H) | 7.192±0.047 [6] |
| Apparent magnitude (K) | 6.886±0.029 [6] |
| B−V color index | 1.89 |
| V−R color index | 1.16 |
| J−H color index | 0.730 |
| J−K color index | 1.036 |
| Variable type | yes [3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 273.0±0.3 [5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 1.445 [2] mas/yr Dec.: 0.463 [2] mas/yr |
| Details | |
| Radius | 1,278 [lower-alpha 1] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 221,000 [7] – 251,000 [8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.5 [7] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,500 [7] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
SP77 46-44 (WOH S341) is a red supergiant star found in the Large Magellanic Cloud in the constellation of Dorado. It is one of the largest stars discovered, with a radius over 1,200 solar radii. If placed in the Solar System, its photosphere would engulf the orbit of Jupiter.
The apparent magnitude of SP77 46-44 varies by about 0.8 magnitudes around 11.5. [3] No variable star classification has been assigned. [10]

RT Aurigae is a yellow supergiant variable star in the constellation Auriga, about 1,500 light years from Earth.

Omicron1 Centauri is a star in the constellation Centaurus. It is approximately 10,000 light years from Earth.

Zeta Cephei is a star in the constellation of Cepheus. Zeta Cephei marks the left shoulder of Cepheus, the King of Joppa (Ethiopia). It is one of the fundamental stars of the MK spectral sequence, defined as type K1.5 Ib.

HD 37974 a variable B[e] hypergiant in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It is surrounded by an unexpected dust disk.

NO Aurigae is a pulsating variable star in the constellation Auriga. It is an unusually-luminous asymptotic giant branch star about 3,500 light years away.

V4381 Sagittarii is a variable star in the constellation Sagittarius. A white supergiant of spectral type A2/A3Iab, it is an Alpha Cygni variable that varies between apparent photographic magnitudes 6.57 and 6.62. Its visual apparent magnitude is about 6.54.

V381 Cephei is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Cepheus. Its apparent magnitude is slightly variable between 5.5 and 5.7.

RT Carinae, also known as CD-58 3538, is a variable star in the Carina Nebula in the constellation Carina. It has a mean apparent magnitude of +8.55.

HD 168607 is a blue hypergiant and luminous blue variable (LBV) star located in the constellation of Sagittarius, easy to see with amateur telescopes. It forms a pair with HD 168625, also a blue hypergiant and possible luminous blue variable, that can be seen at the south-east of M17, the Omega Nebula.

Sigma Ophiuchi, Latinized from σ Ophiuchi, is a single, orange-hued star in the equatorial constellation Ophiuchus. Its apparent visual magnitude is 4.31, which is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The annual parallax shift of 3.62 mas as seen from Earth provides a distance estimate of roughly 900 light years. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −28 km/s.

V1073 Scorpii is a variable star in the constellation Scorpius. It has a non-Greek Bayer designation of k Scorpii. The star has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around +4.87. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of approximately 2,920 ly (896 pc) from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +7 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −6.8
AH Scorpii is a red supergiant variable star located in the constellation Scorpius. It is one of the largest stars known by radius and is also one of the most luminous red supergiant stars in the Milky Way.

HV 2112 is a cool luminous variable star in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Until 2018, it was considered to be the most likely candidate for a Thorne–Żytkow object, but it is now thought to be an asymptotic giant branch star.

HDE 316285 is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Sagittarius. It is a candidate luminous blue variable and lies about 6,000 light years away in the direction of the galactic centre.

HV 11423 is a red supergiant star in the Small Magellanic Cloud. It is about 200,000 light-years away towards the constellation of Tucana.

BI Cygni(BI Cyg, IRC +40408, BD+36 4025) is a red supergiant in the constellation Cygnus. It is an irregular variable star with a maximum brightness of magnitude 8.4 and a minimum of magnitude 9.9. It is considered a member of the stellar Cygnus OB1 association, its distance is around 2,600 parsecs (8,500 ly) of the Solar System. It is less than a degree south of another variable red supergiant, BC Cygni.

BO Carinae, also known as HD 93420, is an irregular variable star in the constellation Carina.

HV 888, also known as WOH S140, is a red supergiant (RSG) star located in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It is among the largest known stars, with estimates of its radius ranging from 765 R☉ to over 1,700 R☉, and is also one of the most luminous of its type with a range of nearly 300,000 to over 500,000 times that of the Sun (L☉). The effective temperature is estimated to be around 3,500 K. If placed at the center of the Solar System, its photosphere would engulf the orbit of Jupiter and possibly even Saturn.

MZ Puppis is a red supergiant star in the constellation of Puppis. It has a radius of 400 R☉.
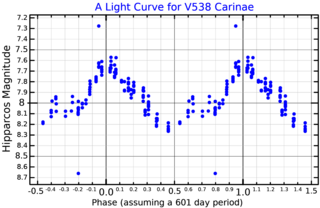
V538 Carinae is a variable star in the constellation of Carina, and a possible red supergiant. If this star replaced the Sun in the Solar System, its photosphere would at least engulf the orbit of Mars.