
V354 Cephei is a red supergiant star located within the Milky Way. It is an irregular variable located over 8,900 light-years away from the Sun. It has an estimated radius of 685 solar radii. If it were placed in the center of the Solar System, it would extend to between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.

MY Cephei is a red supergiant located in open cluster NGC 7419 in the constellation of Cepheus. It is a semiregular variable star with a maximum brightness of magnitude 14.4 and a minimum of magnitude 15.5.

WOH G64 is an unusual red supergiant (RSG) star in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) satellite galaxy in the southern constellation of Dorado. It is one of the largest known stars, being described as possibly being the largest star known. It is also one of the most luminous and massive red supergiants, with a radius calculated to be around 1,540 times that of the Sun (R☉) and a luminosity around 282,000 times the solar luminosity (L☉).

NML Cygni or V1489 Cygni is a red hypergiant or red supergiant (RSG) in the constellation Cygnus. It is one of the largest stars currently known by radius, and is also one of the most luminous and massive cool hypergiants, as well as one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way.
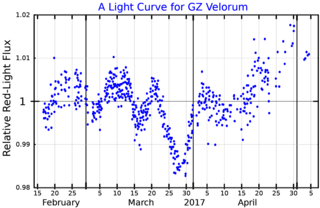
GZ Velorum is a single, orange-hued star in the southern constellation of Vela. It is a faint star but visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.58. The star is located around 1,300 light years from Earth, as determined from its annual parallax shift of 2.4 mas. It is moving further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of +13 km/s.

UY Scuti (BD-12°5055) is an extreme red hypergiant or red supergiant star in the constellation Scutum. It is considered one of the largest known stars by radius and is also a pulsating variable star, with a maximum brightness of magnitude 8.29 and a minimum of magnitude 10.56. It has an estimated radius of 1,708 solar radii (1.188×109 kilometres; 7.94 astronomical units), thus a volume nearly 5 billion times that of the Sun. It is approximately 2.9 kiloparsecs (9,500 light-years) from Earth. If placed at the center of the Solar System, its photosphere would at least engulf the orbit of Jupiter.

Westerlund 1 W26 or Westerlund 1 BKS AS is a red supergiant located at the outskirts of the Westerlund 1 super star cluster. It is one of the largest known stars and the most luminous supergiant stars discovered so far with radius calculated to be in excess of a thousand times the solar radius, and a luminosity of over 200,000 times the solar luminosity. If placed at the center of the Solar System, its photosphere would engulf the orbit of Jupiter.

HV 11423 is a red supergiant star in the Small Magellanic Cloud. It is about 200,000 light-years away towards the constellation of Tucana.

RW Cygni is a semiregular variable star in the constellation Cygnus, about a degree east of 2nd magnitude γ Cygni. Its apparent magnitude varies between 8.05 and 9.70 and its spectral type between M3 and M4.

HD 143183 is a red supergiant variable star of spectral type M3Ia in constellation Norma. It is a member of the Norma OB1 association, at a distance of about 2 kiloparsecs. It is one of the most luminous red supergiants with a luminosity over 100,000 times greater than the Sun (L☉), and is as well one of the largest stars with a radius more than a thousand times that of the Sun (R☉). Older studies frequently calculated higher luminosities and radii. It has an estimated mass loss rate of 5×10−5 M☉ per year and has been once described as a cool hypergiant. It is surrounded by a dozen early-type stars and a circumstellar nebula which extends 0.12 parsecs (0.39 ly).

HV 888, also known as WOH S140, is a red supergiant (RSG) star located in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It is among the largest known stars, with estimates of its radius ranging from 765 R☉ to over 1,700 R☉, and is also one of the most luminous of its type with a range of nearly 300,000 to over 500,000 times that of the Sun (L☉). The effective temperature is estimated to be around 3,500 K. If placed at the center of the Solar System, its photosphere would engulf the orbit of Jupiter and possibly even Saturn.

Westerlund 1-20 (abbreviated to Wd 1-20 or just W20) is a red supergiant (RSG) located in the Westerlund 1 super star cluster. Its radius was calculated to be around 965 solar radii (6.72 × 108 km, 4.48 au), making it one of the largest stars discovered so far. This corresponds to a volume 899 million times bigger than the Sun. If placed at the center of the Solar System, the photosphere of Westerlund 1-20 would almost reach the orbit of Jupiter.

Westerlund 1-75 or Wd 1-75 is a red supergiant (RSG) located in the Westerlund 1 super star cluster. Its radius is calculated to be around 668 solar radii (4.65 × 108 km, 3.10 au). This corresponds to a volume 298 million times bigger than the Sun. If placed at the center of the Solar System, Westerlund 1-75 would engulf the inner limits of the asteroid belt.

IRAS 05280–6910 is a red supergiant star or OH/IR supergiant star located in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Its radius is calculated to be more than a thousand times that of the Sun, making it one of the largest stars discovered so far. If placed at the center of the Solar System, its photosphere would engulf the orbit of Jupiter. It has an estimated mass loss rate of 5.4×10−4 M☉ per year, one of the highest known for any red supergiant star.
WOH S279 is a red supergiant located in the constellation of Dorado. It is currently among the largest known stars with an radius of about 1,300 solar radii. If placed at the center of the solar system, its photosphere would engulf the orbit of Jupiter.
SP77 46-44 is a red supergiant star found in the Large Magellanic Cloud in the constellation of Dorado. It is one of the largest stars discovered, with a radius over 1,200 solar radii. If placed in the Solar System, its photosphere would engulf the orbit of Jupiter.
SP77 31-18 is a red supergiant or red hypergiant of the largest stars found, with a size of around 1,200 solar radii. If it replaced the Sun as the central body of the Solar System, its photosphere would engulf the orbit of Jupiter.

IRAS 18357–0604 is a yellow hypergiant (YHG) star located in the constellation of Scutum, estimated to be about 19,600 light years, or 6,000 parsecs, away. IRAS 18357–0604 is remarkably similar to IRC +10420, another yellow hypergiant in the constellation of Aquila.

WOH S264 is a large, highly luminous red supergiant star in the Large Magellanic Cloud.

V1027 Cygni is a luminous yellow supergiant star located in the constellation of Cygnus, about 14,000 light years away. For a time, it was thought that it could be a low-mass post-AGB star, however recent parallax measurements published in Gaia DR3 have shown this to likely not be the case, and instead it is likely a massive yellow supergiant star.
















