
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies, and later with East Asia. The company gained control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time.

Ghanshyam Das Birla was an Indian businessman and member of the Birla Family.
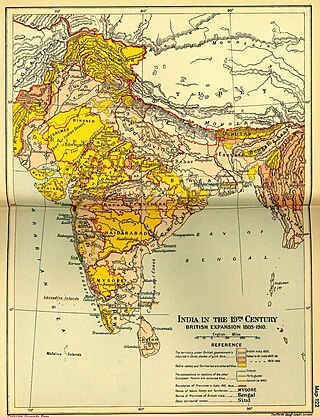
Company rule in India was the rule of the British East India Company on the Indian subcontinent. This is variously taken to have commenced in 1757, after the Battle of Plassey, when the Nawab of Bengal Siraj ud-Daulah was defeated and replaced with Mir Jafar, who had the support of the East India Company; or in 1765, when the Company was granted the diwani, or the right to collect revenue, in Bengal and Bihar; or in 1773, when the Company abolished local rule (Nizamat) in Bengal and established a capital in Calcutta, appointed its first Governor-General of Fort William, Warren Hastings, and became directly involved in governance. The East India Company significantly expanded its influence throughout the Indian subcontinent after the Anglo-Mysore Wars, Anglo-Maratha Wars, and Anglo-Sikh Wars. Lord William Bentinck became the first Governor General of India in 1834 under the Government of India Act 1833. The Company India ruled until 1858, when, after the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and the Government of India Act 1858, the India Office of the British government assumed the task of directly administering India in the new British Raj.

Scottish Church College is a college affiliated by Calcutta University, India. It offers selective co-educational undergraduate and postgraduate studies and is the oldest continuously running Christian liberal arts and sciences college in Asia. It has been rated (A) by the Indian National Assessment and Accreditation Council. Students and alumni call themselves "Caledonians" in the name of the college festival, "Caledonia". The Scottish Church College has been embellished as GRADE-I Heritage Building with this plaque on 8th November, 2023.

Alexander Duff, was a Christian missionary in India; where he played a large part in the development of higher education. He was a Moderator of the General Assembly and convener of the foreign missions committee of the Free Church of Scotland and a scientific liberal reformer of anglicized evangelism across the Empire. He was the first overseas missionary of the Church of Scotland to India. On 13 July 1830 he founded the General Assembly's Institution in Calcutta, now known as the Scottish Church College. He also played a part in establishing the University of Calcutta. He was twice Moderator of the Free Church of Scotland in 1851 and 1873, the only person to serve the role twice.

The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal, later the Bengal Province, was the largest of all three presidencies of British India during Company rule and later a province of India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal. Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the governor of Bengal was concurrently the governor-general of India and Calcutta was the capital of India until 1911.

The former communities of Jewish migrants and their descendants from Baghdad and elsewhere in the Middle East are traditionally called Baghdadi Jews or Iraqi Jews. They settled primarily in the ports and along the trade routes around the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea.
Education in West Bengal is provided by both the public sector as well as the private sector. Health Sciences, University of North Bengal and University of Calcutta.
Bhowanipore is a neighbourhood of South Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
The Calcutta Scottish was a regiment of volunteers of Scottish descent raised in 1914 as an infantry regiment of the British Indian Army. The regiment formed part of the army reserves of the Auxiliary Force, India (AFI). The regimental dress uniform was Hunting Stewart tartan. The regiment was disbanded following India's independence in 1947.

John Borthwick Gilchrist was a Scottish surgeon, linguist, philologist and Indologist. Born and educated in Edinburgh, he spent most of his early career in India, where he made a study of the local languages. In later life, he returned to Britain and lived in Edinburgh and London. In his final years, he moved to Paris, where he died at the age of 81.

The Regulating Act 1773 was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain intended to overhaul the management of the East India Company's rule in India (Bengal). The Act did not prove to be a long-term solution to concerns over the company's affairs. Pitt's India Act was therefore subsequently enacted in 1784 as a more radical reform. It marked the first step towards parliamentary control over the company and centralised administration in India.

The Scottish Cemetery at Calcutta was established in 1820 catering to the specific needs of the large Scottish population in the Kolkata area. These Scots, including soldiers, missionaries, jute traders and businessmen, were attached to numerous enterprises in the area such as the headquarters of the East India Company, and the administration of the British India, whose capital was here. The cemetery was utilised until the 1940s but was abandoned in the 1950s and neglected following India's independence. Well over 90% of those buried bear recognisably Scots names such as Anderson, McGregor, Campbell and Ross. Around 10% are Bengali.

Coinage under British governance of the Indian subcontinent can be divided into two periods: East India Company (EIC) issues, pre-1835; and Imperial issues struck under direct authority of the crown. The EIC issues can be further subdivided into two subcategories: the Presidency issues, which comprise separate Madras Presidency, Bombay Presidency, and Bengal Presidency issues; and uniform coinage for all British territories from 1835 to 1858. Imperial issues bear obverse portraits of Queen Victoria, Edward VII, George V, and George VI. No British India coins were issued during the brief reign of Edward VIII.
John Anderson Graham was a Scottish minister and the first missionary from Young Men's Guild sent to North Eastern Himalayan region Kalimpong—then in British Sikkim, currently in West Bengal.
Andrew Yule was a businessman who founded Andrew Yule and Co.
Jardine, Skinner and Company was a trading company based in Calcutta, India. It was founded in 1825, initially dealing in textiles. Later it branched out into opium, tea, timber and petroleum. The company was closely associated with Matheson & Company of London and Jardine Matheson & Co. of Hong Kong.

HCS Aurora was a sloop-of-war launched in 1809 at Bombay for the Bombay Marine, the naval arm of the British East India Company (EIC). Intended to protect EIC trade routes in the Indian Ocean from piracy, the French captured Aurora in September 1810, only to have the British recapture her in early December of that year. Aurora returned to the service of the Bombay Marine, assisting the British military in various campaigns in the East Indies and the Persian Gulf. The last mention of Aurora in EIC records was 1828, when she was listed on the rolls of the Bombay Marine on 1 January of that year.

Lady Nugent was built at Bombay in 1813. She made four voyages under contract to the British East India Company (EIC). She then made two voyages transporting convicts to Australia, one to New South Wales and one to Van Diemen's Land (Tasmania). She also made several voyages with emigrants to New Zealand under charter to the New Zealand Company or the Canterbury Association. She foundered in May 1854 with the loss of some 400 persons, most of them soldiers that she was carrying from Madras to Rangoon.
James Sibbald was launched at Bombay in 1803. She was a "country ship", a British vessel that traded only east of the Cape of Good Hope. A French privateer captured her in late 1804, but she quickly returned to British ownership in Bombay in a process that is currently obscure. She made several voyages for the British East India Company (EIC).













