In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabling operating systems and other computer programs to access hardware functions without needing to know precise details about the hardware being used.

In computer science, a microkernel is the near-minimum amount of software that can provide the mechanisms needed to implement an operating system (OS). These mechanisms include low-level address space management, thread management, and inter-process communication (IPC).
Mach is an operating system kernel developed at Carnegie Mellon University by Richard Rashid and Avie Tevanian to support operating system research, primarily distributed and parallel computing. Mach is often considered one of the earliest examples of a microkernel. However, not all versions of Mach are microkernels. Mach's derivatives are the basis of the operating system kernel in GNU Hurd and of Apple's XNU kernel used in macOS, iOS, iPadOS, tvOS, and watchOS.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
OS-9 is a family of real-time, process-based, multitasking, multi-user operating systems, developed in the 1980s, originally by Microware Systems Corporation for the Motorola 6809 microprocessor. It was purchased by Radisys Corp in 2001, and was purchased again in 2013 by its current owner Microware LP.
A modern computer operating system usually uses virtual memory to provide separate address spaces or separate regions of a single address space, called user space and kernel space. Primarily, this separation serves to provide memory protection and hardware protection from malicious or errant software behaviour.
The Internetworking Operating System (IOS) is a family of proprietary network operating systems used on several router and network switch models manufactured by Cisco Systems. The system is a package of routing, switching, internetworking, and telecommunications functions integrated into a multitasking operating system. Although the IOS code base includes a cooperative multitasking kernel, most IOS features have been ported to other kernels, such as Linux and QNX, for use in Cisco products.
In computing, Quark is an operating system kernel used in MorphOS. It is a microkernel designed to run fully virtualized computers, called boxes. As of 2020, only one box is available, the ABox, that lets users run extant AmigaOS software compiled for Motorola 68000 series and PowerPC central processing units (CPUs).

XNU is the computer operating system (OS) kernel developed at Apple Inc. since December 1996 for use in the Mac OS X operating system and released as free and open-source software as part of the Darwin OS, which, in addition to being the basis for macOS, is also the basis for Apple TV Software, iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, visionOS, and tvOS.

Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality performed by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MACs), accompanied on-chip by a microcontroller. It was designed for a unified low-power processor architecture that can run operating systems while simultaneously handling complex numeric tasks such as real-time H.264 video encoding.
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM) or virtualizer, is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine, and each virtual machine is called a guest machine. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Unlike an emulator, the guest executes most instructions on the native hardware. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources: for example, Linux, Windows, and macOS instances can all run on a single physical x86 machine. This contrasts with operating-system–level virtualization, where all instances must share a single kernel, though the guest operating systems can differ in user space, such as different Linux distributions with the same kernel.

The architecture of Windows NT, a line of operating systems produced and sold by Microsoft, is a layered design that consists of two main components, user mode and kernel mode. It is a preemptive, reentrant multitasking operating system, which has been designed to work with uniprocessor and symmetrical multiprocessor (SMP)-based computers. To process input/output (I/O) requests, it uses packet-driven I/O, which utilizes I/O request packets (IRPs) and asynchronous I/O. Starting with Windows XP, Microsoft began making 64-bit versions of Windows available; before this, there were only 32-bit versions of these operating systems.
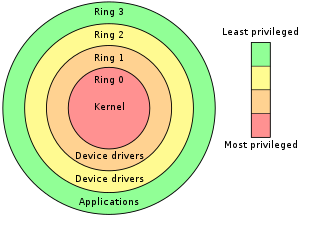
In computer science, hierarchical protection domains, often called protection rings, are mechanisms to protect data and functionality from faults and malicious behavior.
A hybrid kernel is an operating system kernel whose architecture attempts to combine aspects and benefits of microkernel and monolithic kernel architectures used in operating systems.
Bartok is an optimizing compiler and managed runtime system for Common Intermediate Language, being developed by Microsoft Research.
The Mac OS nanokernel is an operating system kernel that serves as the basis of most PowerPC based system software versions 7 through 9 of the classic Mac OS, predating Mac OS X.

ChibiOS/RT is a compact and fast real-time operating system supporting multiple architectures and released under a mix of the GNU General Public License version 3 (GPL3) and the Apache License 2.0. It is developed by Giovanni Di Sirio.

C# Open Source Managed Operating System (Cosmos) is a toolkit for building GUI and command-line based operating systems, written mostly in the programming language C# and small amounts of a high-level assembly language named X#. Cosmos is a backronym, in that the acronym was chosen before the meaning. It is open-source software released under a BSD license.

A kernel is a computer program at the core of a computer's operating system that always has complete control over everything in the system. The kernel is also responsible for preventing and mitigating conflicts between different processes. It is the portion of the operating system code that is always resident in memory and facilitates interactions between hardware and software components. A full kernel controls all hardware resources via device drivers, arbitrates conflicts between processes concerning such resources, and optimizes the utilization of common resources e.g. CPU & cache usage, file systems, and network sockets. On most systems, the kernel is one of the first programs loaded on startup. It handles the rest of startup as well as memory, peripherals, and input/output (I/O) requests from software, translating them into data-processing instructions for the central processing unit.
An embedded hypervisor is a hypervisor that supports the requirements of embedded systems.