
The Caridea, commonly known as caridean shrimp or true shrimp, from the Greek word καρίς, καρίδος, are an infraorder of shrimp within the order Decapoda. This infraorder contains all species of true shrimp. They are found widely around the world in both fresh and salt water. Many other animals with similar names – such as the mud shrimp of Axiidea and the boxer shrimp of Stenopodidea – are not true shrimp, but many have evolved features similar to true shrimp.

Dendrobranchiata is a suborder of decapods, commonly known as prawns. There are 540 extant species in seven families, and a fossil record extending back to the Devonian. They differ from related animals, such as Caridea and Stenopodidea, by the branching form of the gills and by the fact that they do not brood their eggs, but release them directly into the water. They may reach a length of over 330 millimetres (13 in) and a mass of 450 grams (1.0 lb), and are widely fished and farmed for human consumption.

Malacostraca is the second largest of the six classes of pancrustaceans behind insects, containing about 40,000 living species, divided among 16 orders. Its members, the malacostracans, display a great diversity of body forms and include crabs, lobsters, spiny lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, amphipods, mantis shrimp, tongue-eating lice and many other less familiar animals. They are abundant in all marine environments and have colonised freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are segmented animals, united by a common body plan comprising 20 body segments, and divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen.

The Decapoda or decapods are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 extant species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp and Anomura including hermit crabs, king crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossils of the group date to the Devonian.

The Achelata is an infra-order of the decapod crustaceans, holding the spiny lobsters, slipper lobsters and their fossil relatives.

The Stenopodidea or boxer shrimps are a small group of decapod crustaceans. Often confused with Caridea shrimp or Dendrobranchiata prawns, they are neither, belonging to their own group.

Astacidea is an infraorder of decapod crustaceans including lobsters, crayfish, and their close relatives.

Eucarida is a superorder of the Malacostraca, a class of the crustacean subphylum, comprising the decapods, krill, and Angustidontida. They are characterised by having the carapace fused to all thoracic segments, and by the possession of stalked eyes.

Axiidea is an infraorder of decapod crustaceans. They are colloquially known as mud shrimp, ghost shrimp, or burrowing shrimp; however, these decapods are only distantly related to true shrimp. Axiidea and Gebiidea are divergent infraorders of the former infraorder Thalassinidea. These infraorders have converged ecologically and morphologically as burrowing forms. Based on molecular evidence as of 2009, it is now widely believed that these two infraorders represent two distinct lineages separate from one another. Since this is a recent change, much of the literature and research surrounding these infraorders still refers to the Axiidea and Gebiidea in combination as "thalassinidean" for the sake of clarity and reference. This division based on molecular evidence is consistent with the groupings proposed by Robert Gurney in 1938 based on larval developmental stages.

Cumacea is an order of small marine crustaceans of the superorder Peracarida, occasionally called hooded shrimp or comma shrimp. Their unique appearance and uniform body plan makes them easy to distinguish from other crustaceans. They live in soft-bottoms such as mud and sand, mostly in the marine environment. There are more than 1,500 species of cumaceans formally described. The species diversity of Cumacea increases with depth.

Synalpheus is a genus of snapping shrimp of the family Alpheidae, presently containing more than 160 species; new ones are described on a regular basis, and the exact number even of described species is disputed.

Upogebiidae is a family of mud shrimp crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Gebiidea, within the order Decapoda. They are infauna, living their entire adult lives in seafloor burrows. Over 100 species have been identified, with different species often highly specialized for different types of substrate, even including sea sponges or coral. They are filter feeders, although some species also deposit feed.

Polychelida is an infraorder of decapod crustaceans. Fossil representatives are known dating from as far back as the Upper Triassic. A total of 38 extant species, all in the family Polychelidae, and 55 fossil species have been described.
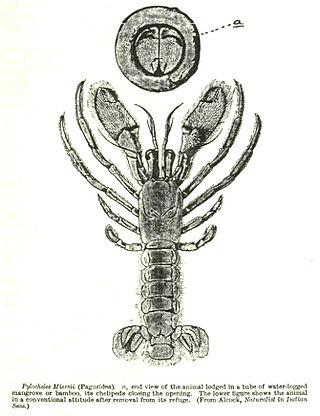
The Pylochelidae are a family of hermit crabs. Its members are commonly called the 'symmetrical hermit crabs'. They live in all the world's oceans, except the Arctic and the Antarctic, at depths of 2,000 m (6,600 ft). Due to their cryptic nature and relative scarcity, only around 60 specimens had been collected before 1987, when a monograph was published detailing a further 400.

Crustaceans may pass through a number of larval and immature stages between hatching from their eggs and reaching their adult form. Each of the stages is separated by a moult, in which the hard exoskeleton is shed to allow the animal to grow. The larvae of crustaceans often bear little resemblance to the adult, and there are still cases where it is not known what larvae will grow into what adults. This is especially true of crustaceans which live as benthic adults, more-so than where the larvae are planktonic, and thereby easily caught.

Stenopodidae is a family of decapods in the order Decapoda, sometimes known as boxer shrimp. There are about 6 genera and more than 30 described species in Stenopodidae. The oldest record of the family dates to the Devonian.
Juxtastenopus spinulatus is a species of stenopodidean shrimp. It lives in the Red Sea, and across the Indian Ocean as far east as the Philippines. It is red or pink, up to 28 mm (1.1 in) long, with enlarged third pereiopods. Originally described in the genus Engystenopus, it is now placed in the monotypic genus Juxtastenopus, in the family Stenopodidae.

Crustaceans are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are a part of the subphylum Crustacea, a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans.

Oziidae is a family of crabs in the order Decapoda. There are about 7 genera and more than 30 described species in Oziidae.

Periclimenes, commonly known as glass shrimp or cleaner shrimp, is a commensal and often symbiotic genus of semi-transparent shrimp within the family Palaemonidae. Species of this large genus feature a wide variety of coloration and patterns, widespread distribution throughout much of the world's tropical oceans, and are often sought out for aquarium trade.



















