Related Research Articles

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.
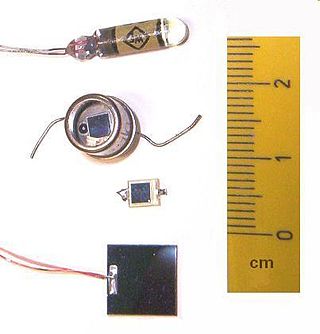
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and measurement applications, or for the generation of electrical power in solar cells. Photodiodes are used in a wide range of applications throughout the electromagnetic spectrum from visible light photocells to gamma ray spectrometers.

Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG). The digital interface is used to connect a video source, such as a video display controller, to a display device, such as a computer monitor. It was developed with the intention of creating an industry standard for the transfer of uncompressed digital video content.

In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths of laser light. This technique enables bidirectional communications over a single strand of fiber as well as multiplication of capacity.

In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal is an electronic logic signal which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions.

In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels.

A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that most common spectrum analyzers measure is electrical; however, spectral compositions of other signals, such as acoustic pressure waves and optical light waves, can be considered through the use of an appropriate transducer. Spectrum analyzers for other types of signals also exist, such as optical spectrum analyzers which use direct optical techniques such as a monochromator to make measurements.

Boundary scan is a method for testing interconnects on printed circuit boards or sub-blocks inside an integrated circuit (IC). Boundary scan is also widely used as a debugging method to watch integrated circuit pin states, measure voltage, or analyze sub-blocks inside an integrated circuit.
A general-purpose input/output (GPIO) is an uncommitted digital signal pin on an integrated circuit or electronic circuit board which may be used as an input or output, or both, and is controllable by software.
Networking hardware, also known as network equipment or computer networking devices, are electronic devices that are required for communication and interaction between devices on a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data transmission in a computer network. Units which are the last receiver or generate data are called hosts, end systems or data terminal equipment.
Power-system automation is the act of automatically controlling the power system via instrumentation and control devices. Substation automation refers to using data from Intelligent electronic devices (IED), control and automation capabilities within the substation, and control commands from remote users to control power-system devices.
In computer science, a data buffer is a region of memory used to store data temporarily while it is being moved from one place to another. Typically, the data is stored in a buffer as it is retrieved from an input device or just before it is sent to an output device ; however, a buffer may be used when data is moved between processes within a computer, comparable to buffers in telecommunication. Buffers can be implemented in a fixed memory location in hardware or by using a virtual data buffer in software that points at a location in the physical memory.
Soundstream Inc. was the first United States audiophile digital audio recording company, providing commercial services for recording and computer-based editing.
The Fibre Channel electrical interface is one of two related Fibre Channel standards that can be used to physically interconnect computer devices. The other standard is a Fibre Channel optical interface, which is not covered in this article.

Power dividers and directional couplers are passive devices used mostly in the field of radio technology. They couple a defined amount of the electromagnetic power in a transmission line to a port enabling the signal to be used in another circuit. An essential feature of directional couplers is that they only couple power flowing in one direction. Power entering the output port is coupled to the isolated port but not to the coupled port. A directional coupler designed to split power equally between two ports is called a hybrid coupler.
Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical or optical connectors for carrying audio or video signals. Audio interfaces or video interfaces define physical parameters and interpretation of signals. Some connectors and interfaces carry either audio only or video only, whereas others carry both, audio and video.

Active cables are copper cables used for data transmission that use an electronic circuit to boost their performance. Without an electronic circuit, a cable is considered passive. Unlike passive cables, which can suffer from data degradation due to issues such as attenuation, crosstalk, and group velocity distortion, active cables contain one or more integrated circuits to address these problems. This active boosting allows cables to be more compact, thinner, and longer, and to transmit data faster than passive cables.
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes some unwanted components or features from a signal. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal. Most often, this means removing some frequencies or frequency bands. However, filters do not exclusively act in the frequency domain; especially in the field of image processing many other targets for filtering exist. Correlations can be removed for certain frequency components and not for others without having to act in the frequency domain. Filters are widely used in electronics and telecommunication, in radio, television, audio recording, radar, control systems, music synthesis, image processing, computer graphics, and structural dynamics.

TOSLINK is a standardized optical fiber connector system. Generically known as optical audio, the most common use of the TOSLINK optical fiber connector is in consumer audio equipment in which the digital optical socket carries (transmits) a stream of digital audio signals from audio equipment to an AV receiver that can decode two channels of uncompressed, pulse-code modulated (PCM) audio; or decode compressed 5.1/7.1 surround sound audio signals, such as Dolby Digital and DTS. Unlike an HDMI connector cable, a TOSLINK optical fiber connector does not possess the bandwidth capacity to carry the uncompressed audio signals of Dolby TrueHD and of DTS-HD Master Audio; nor carry more than two channels of PCM audio.
This glossary of computer hardware terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related to computer hardware, i.e. the physical and structural components of computers, architectural issues, and peripheral devices.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.- FAA Glossary of Optical Communications Terms