A number of suborbital spaceflights were conducted during 2008. These consist mostly of sounding rocket missions and missile tests, and include other flights such as an ASAT firing. Between the start of the year and 16 July, at least 43 publicly announced suborbital spaceflights were conducted, the first of them on 11 January.
LIDOS was an American ultraviolet astronomy mission, conducted using a Canadian Black Brant IX, serial number 36.243, launched from LC-36 at the White Sands Missile Range. The launch occurred at 05:32 UTC on 11 January, making it the first recorded spaceflight launch of 2008. The mission was conducted by NASA for Johns Hopkins University, and reached an apogee of 315 kilometres. It was declared a success. [1]
On 17 January, the Israeli Air Force was reported to have successfully launched the first Jericho-3 missile from Palmachim, on a test flight. [2]
SCIFER-2 (Sounding of the Cusp Ion Fountain Energization Region-2) was an American ionospheric and auroral research mission, launched from the Andøya Rocket Range in Norway. It was conducted by NASA using Black Brant XII 40.021. Research was conducted by Cornell University with Professor Paul Kintner as Principal Investigator, the Lynch Rocket Laboratory at Dartmouth College, and the Magnetosphere-Ionosphere Research Laboratory at the University of New Hampshire. Launch was delayed several times by high winds and poor scientific conditions, and finally occurred on 18 January at 07:30 UTC. The rocket reached an apogee of 1,460 kilometres during a successful flight. [3]
On 25 January, a Shaheen-1 missile was test fired from Sonmiani by the Army of Pakistan. The test was declared a success. [4]
The Norwegian HotPay-2 ionospheric and auroral research mission was launched from Andøya at 19:14:00 UTC on 31 January. The mission was conducted by Andøya Rocket Range (ARR) on behalf of the EU's Framework Programme for Research and Technological Development, FP6. The Principal Investigator for the mission was John Plane from the University of Leeds. The HotPay-2 payload, built by ARR contained instruments from School of Chemistry at University of Leeds (UK), Sodankyla Observatory (Finland), University of Stockholm (Sweden), Dartmouth College (US), Graz Technical University (Austria), Technical University of Kosice (Slovakia) and Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (Bulgaria). The successful research flight was conducted using a two-stage (VS-30/Orion) sounding rocket, which reached an apogee of 380.6 kilometres. [5]
On 28 January, Boeing, Lockheed Martin and the United States Navy announced that a test launch of a Standard Missile 3, on an undisclosed date in the previous month had been conducted successfully. The launch occurred from the USS Desert Ship, a US Navy base at the White Sands Missile Range. [6]
On 4 February, Iran conducted its second sounding rocket launch, and the maiden flight of the Kavoshgar-1 rocket, a derivative of the Shahab-3 missile. The launch occurred from a new space centre in Semnan Province. It is believed that the launch was a test of the Kavoshgar, which was being developed as a carrier rocket.
On 6 February at 09:14:40 UTC, JAXA launched an S-310 rocket from the Uchinoura Space Centre in Japan. The rocket was used to conduct research into the ionosphere.
TEXUS-44 was the 44th flight of the European TEXUS microgravity research programme. It was launched from Esrange in Sweden at 11:30 UTC on 7 February. A Brazilian VSB-30 sounding rocket was used, and the launch was conducted by the German Aerospace Centre (DLR) and the Swedish Space Corporation.
At 03:26 UTC on 21 February, a modified Standard Missile 3 was launched from the USS Lake Erie, stationed in the Pacific Ocean. The missile was fired at USA-193, a reconnaissance satellite which failed shortly after launch in December 2006. Acting as an anti-satellite weapon, the SM-3 was successful in destroying the satellite, by rupturing its hydrazine tank. Officially, the United States Government stated that they destroyed the satellite to prevent it falling over a populated area, however it was claimed that there were political motivations, such as proving that the United States had the capability to destroy a satellite in low Earth orbit, or to prevent the satellite from falling into the wrong hands, should it come down in a country not allied to the United States.
TEXUS-45, the 45th TEXUS microgravity research mission, was launched from Esrange in Sweden at 06:15 UTC on 21 February. A Brazilian VSB-30 rocket was used for the mission, which was conducted by the German Aerospace Centre (DLR) and the Swedish Space Corporation on behalf of the European Space Agency.
On 26 February, at 07:28 UTC, India test-fired a K-15 Sagarika submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) from the INS Kalinga, in the first K-15 test launch to be conducted underwater.
At 04:45 UTC on 23 March, the Indian Navy test fired an Agni-1 missile from Launch Complex 4 at Wheeler Island.
Mini-DUSTY 14 was a microgravity research mission launched on 28 March using an Indian RH-200 sounding rocket. The launch and mission were conducted by Andøya Rocket Range, and the launch occurred from their facilities in Norway.
Glory Trip 196GM (GT-196GM) was the first test of a Minuteman III missile to be conducted for nearly a year, due to a series of delays. The launch, from LF-09 at the Vandenberg Air Force Base occurred at 08:01 UTC on 2 April. It was conducted by the United States Air Force.
SEE was an Ultraviolet Astronomy mission launched from LC-36 at the White Sands Missile Range, using a Black Brant IX rocket. The serial number of the rocket was 36.240. Launch occurred at 16:58 UTC on 14 April. The launch was conducted by NASA for the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics of the University of Colorado.
On 15 April, an Israeli Blue Sparrow missile was test launched. The missile was fired from an F-15 aircraft, and flew a trajectory designed to imitate that flown by Iranian Shahab missiles. Later launches will be used to test Arrow missiles, designed to shoot down enemy missiles.
On 19 and 21 April, two Pakistani Shaheen-II missiles were launched from an undisclosed launch site, believed to be Sonmiani.
At 05:30 UTC on 1 May a Black Brant IX, serial number 36.223 was launched by NASA, from LC-36 at the White Sands Missile Range, on an x-ray astronomy mission for the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
On 6 May, between 18:00 and 20:00 UTC, the maiden flight of the Mesquito rocket, serial number 12.065, was conducted by NASA from LC-2 at the Wallops Flight Facility. The flight was reported to be successful.
An Indian Agni-III missile was launched on a test mission from LC-4 at Wheeler Island, at 04:26 on 7 May. The test was reported to be successful.
About 24 hours after the maiden flight, the second Mesquito, 12.066, was launched from the same launch pad at the Wallops Flight Facility. The launch occurred early in the launch window, and was reported to have failed, due to a loss of control shortly after burnout of the solid rocket motor, and the loss of stabilisation fins during descent.
On 21 May Lockheed Martin announced that two Trident II missiles had been tested successfully earlier in the month. The launches were claimed to have broken a record for consecutive successful launches, with 122 such launches since 1989. Trident launches are typically conducted in pairs on the same day. The missiles were fired from the submarine USS Nebraska, submerged in the Pacific Ocean. The launches were later reported to have occurred on 8 May.
Maser 11 was a European sounding rocket mission, launched by a VSB-30 rocket at 04:00 UTC on 15 May. The launch occurred from Esrange in Sweden, was conducted by the Swedish Space Corporation, and reached an apogee of 252 kilometres. [7]
Glory Trip 197GM (GT-197GM) was the second test of a Minuteman III missile to be conducted in 2008. The launch, from LF-10 at Vandenberg AFB occurred at 10:04 UTC on 22 May. It was conducted by the 576th Flight Test Squadron of the USAF Space Command. The flight was a long range test aimed at Guam, approximately 8450 kilometres from the launch site, rather than the usual target, Kwajalein Atoll. Instrumentation was carried for the US National Nuclear Security Administration. The test was reported to have been successful. [8]
A Prithvi missile was launched by the Indian Army from the Integrated Test Range, at 05:00 UTC on 23 May, as part of a user training and test flight programme.
A Tszyuylan-2 missile was launched from the Chinese Navy's sole Soviet-designed Golf class submarine, located in the Yellow Sea, on 29 May.
A test of the terminal intercept capability of the United States AEGIS missile defence system was conducted on 5 June. A Threat-Representative Short Range Ballistic Missile was launched from the USS Tripoli, near Kauai. The missile reached space, and was intercepted by two SM-2 missiles launched from a destroyer, after re-entry. The SM-2 missiles did not reach space.
A further test of the AEGIS system was conducted on 13 June, when two Medium Range Target Missiles were launched from Barking Sands. The missiles were tracked by US Navy destroyers, and simulated SM-3 missiles were launched to intercept them.
On 26 June, the United States conducted its third ABM test of the month, when a THAAD missile was used to intercept a Threat Representative Ballistic Missile. The TRBM was launched from a C-17 Globemaster III aircraft, flying over the Pacific Ocean, at 02:16 UTC. A THAAD missile was launched from the Kwajalein Missile Range at 02:22, and the missile was successfully intercepted, during the stage at which the mock warhead separated from the missile. The THAAD did not leave the atmosphere, however the target did.
A Black Brant XI was used to conduct the Next Generation Sensor Producibility (NGSP-01) technology development mission for the US MDA. The rocket was launched from Wallops Island at 19:57 UTC on 26 June. The payload used infrared and optical sensors to track a number of objects released from the sounding rocket.
The first of three ECOMA aeronomy research missions to be conducted in 2008 was launched from the Andøya Rocket Range on 30 June. A Nike-Orion rocket was used.
The second ECOMA mission was launched at 21:30 UTC on 7 July. The mission used a Nike-Orion rocket launched from Andøya, to study Aeronomy. The mission was flown by ARR and DLR.
Iran conducted the Great Prophet III war games during July. These included a number of missile launches, several of which made suborbital spaceflights. Nine missiles were launched on 9 July, including a Shahab-3. Further launches, including another Shahab-3, were reported to have occurred on 10 July.
2008's third and final ECOMA Aeronomy mission was launched from Andøya atop a Nike-Orion at 10:46 UTC on 12 July. It reached an apogee of 123 kilometres (76 mi). [9]
SubTEC-II, a technology development flight, was launched from Wallops Flight Facility on 14 July at 10:10 UTC. A Terrier 70-Improved Orion sounding rocket was used, a derivative of the Terrier-Orion. The mission was reported to have been successful. [10]
FTX-03 was a missile defence test, conducted on 18 July by the US Air Force and MDA. A Polaris missile, in the STARS configuration, was launched from Kodiak Island at 22:47 UTC. [11] It was tracked by land and sea-based radar systems, and the US early warning satellite systems. Intercepts of the missile by SM-3 and THAAD missiles were simulated from ships in the Pacific Ocean, and ground-based systems at Vandenberg Air Force Base, respectively. The test was successful. [12]
A Russian SLBM test was conducted from the Delta III-class submarine Ryazan, located in the Barents Sea, on 1 August. The test was reported to have been successful. While the type of missile was not officially confirmed, Ryazan is believed to carry only R-29 missiles.
JAXA launched an S-520 from the Uchinoura Space Centre on 2 August at 08:30 UTC. The rocket conducted microgravity research, and reached an apogee of 293 kilometres.
A Minuteman III missile was launched from Vandenberg AFB at 08:01 UTC on 13 August, on a test flight aimed at Kwajalein Atoll. The test was successful, and the missile travelled about 6,790 kilometres downrange, deploying three re-entry vehicles.
The ALV X-1 test flight of the ATK Launch Vehicle was launched from LP-0B at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Wallops Island, at 09:10 UTC on 22 August. 27 seconds after launch, the flight ended in failure, when the rocket exploded.
The US Navy launched two Trident II missiles from the USS Louisiana in the Pacific Ocean on 25 August. [13] The launches were part of the missile's operational test programme, and were both successful.
On 28 August the Russian military launched a test flight of the Topol-M missile from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome. The test was reported to have been successful. [14]
The US military intended to conduct a test of the THAAD anti-ballistic missile system on 18 September, launching two missiles against a single target. The target was launched from Kauai at 02:05 UTC, but failed before the interceptors could be launched. Both THAAD launches were cancelled. [15]
On 18 September the Russian Navy test fired a Bulava SLBM from the Dmitry Donskoi submarine in the White Sea. The missile was launched at 14:45 UTC, and impacted the test site at 15:05. [16]
A missile test using the NFIRE satellite to observe the launch was conducted on 24 September. Orbital Sciences Corporation launched a Chimera test vehicle from Vandenberg AFB at 06:57, on behalf of the US military. The missile passed close to the NFIRE satellite, before falling back to Earth. [17]
On 11 and 12 November, Russia conducted four missile tests in the space of two days. On 11 November, an R-29RMU Sineva missile was launched from the Delta IV-class submarine Tula (K-114), in the Barents Sea. The next day, an RS-12M Topol was launched from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome at 07:24 UTC. At an undisclosed time on the same day as the Topol, an R-29 Vysota and an R-29RM Shtil were launched from submarines. The R-29 was launched from the Delta III-class submarine Zelenograd (K-506), in the Sea of Okhotsk, while the R-29RM was launched from the Ekaterinburg (K-84), in the Barents Sea. All four tests were reported to have been successful.
On 20 October at 08:39 UTC, a Black Brant IX was launched from LC-36 at the White Sands Missile Range, to conduct an ultraviolet astronomy mission for NASA and the US Navy Research Laboratory. The flight lasted about ten minutes, and was successful.
A UR-100N missile was successfully test-launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome by the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces on 22 October at 09:10 UTC.
REXUS-4 was a student microgravity flight, launched from Esrange at 12:30 UTC on 22 October part of the REXUS programme. A Nike-Orion rocket was used. The flight was conducted by the Swedish Space Corporation and German Aerospace Centre, and the launch was conducted by EuroLaunch. The rocket reached an apogee of 175 kilometres.
On 1 November, the US Navy conducted two tests of the AEGIS missile defence system as part of the Pacific Blitz naval exercise. Two target missiles were launched from the Pacific Missile Range Facility at Barking Sands. SM-3 interceptors were launched from the USS Paul Hamilton and USS Hopper. The missile launched from the Paul Hamilton successfully intercepted its target, however the one launched from the Hopper failed to do so, due to a targeting fault.
GT-198GM was the fourth test of a Minuteman III missile to be conducted in 2008. The missile was launched from Vandenberg AFB at 09:00 UTC on 5 November. The missile travelled 6,740 kilometres downrange, and successfully impacted Kwajalein Atoll.
At 05:56 UTC on 12 November, an Indian Shaurya missile was launched on a successful test flight from LC-4 at the Integrated Test Range on Wheeler Island.
Iran tested a new solid-fuelled missile, named Sejjil, on 12 November. The test was reported to have been successful.
At 09:06 UTC on 13 November, the French Force Océanique Stratégique conducted a successful test flight of the M51 SLBM from the Centre d'Essais des Landes at Biscarosse.
On 14 November, a Black Brant IX was launched from LC-36 at the White Sands Missile Range on a Solar research mission for NASA and the US Navy Research Laboratory.
The Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force conducted a test of the AEGIS missile defence system, in conjunction with the US Navy and MDA. At 02:21 on 20 November, a target missile was launched from the Pacific Missile Range Facility at Barking Sands, by the US Navy. Three minutes later, an SM-3 interceptor was launched from the JDS Chōkai. The SM-3 failed to intercept the target due to an infrared sensor fault. It was the second consecutive failure of an AEGIS test, following a similar malfunction during the US Navy test on 1 November.
At 13:24 on 26 November, Russia successfully test-fired its third RS-24 ICBM from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome.
On 26 November, Iran launched the Kavoshgar-2 research flight. Some sources reported that a Safir was used, whilst images of the launch showed a smaller, solid-fuelled rocket. It is unclear whether the reports or the images were correct. The flight was reported to have lasted 40 minutes, with the payload being recovered by parachute.
An RSM-56 Bulava was tested on 28 November, with launch occurring from the Dmitry Donskoi submarine in the White Sea. The flight was reported to have been successful.
On 5 December, a VS-30-Orion was launched from SvalRak in Svalbard, on an Auroral research flight for the University of Oslo. Launch occurred at 10:35:10 UTC, and the rocket reached an apogee of 330 kilometres during its ten-minute flight, which was reported to have been successful.
FTG-05 was an American missile defence test which took place on 5 December. A Polaris missile, in the STARS configuration was launched as a target from Kodiak Launch Complex at 20:04 UTC, and a Ground Based Interceptor carrying an Exoatmospheric Kill Vehicle was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base at 20:21. At 20:29, the interceptor destroyed the target, completing the successful test.
An RSM-56 Bulava was tested on 23 December at 03:00 UTC. The missile was launched from the Dmitry Donskoi submarine in the White Sea. The missile went off course after one of the stage separation events, and self-destructed. This was the fifth reported failure of a Bulava out of ten test flights.

The Aerobee rocket was one of the United States' most produced and productive sounding rockets. Developed by the Aerojet Corporation, the Aerobee was designed to combine the altitude and launching capability of the V-2 with the cost effectiveness and mass production of the WAC Corporal. More than 1000 Aerobees were launched between 1947 and 1985, returning vast amounts of astronomical, physical, aeronomical, and biomedical data.

A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites; the maximum altitude for balloons is about 40 km and the minimum for satellites is approximately 121 km. Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between 1,000 and 1,500 km, such as the Black Brant X and XII, which is the maximum apogee of their class. Sounding rockets often use military surplus rocket motors. NASA routinely flies the Terrier Mk 70 boosted Improved Orion, lifting 270–450-kg (600–1,000-pound) payloads into the exoatmospheric region between 97 and 201 km.

Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
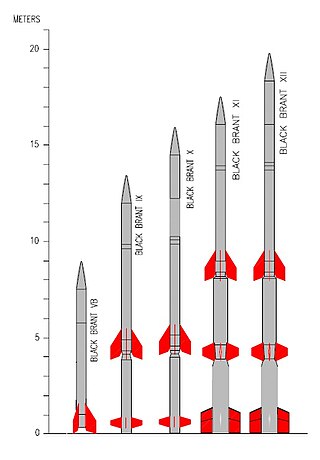
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.

Little Joe II was an American rocket used from 1963 to 1966 for five uncrewed tests of the Apollo spacecraft launch escape system (LES), and to verify the performance of the command module parachute recovery system in abort mode. It was named after a similar rocket designed for the same function in Project Mercury. Launched from White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, it was the smallest of four launch rockets used in the Apollo program.
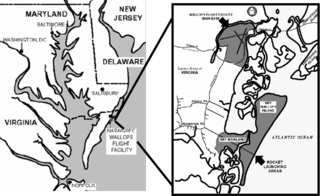
Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately 100 miles (160 km) north-northeast of Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and primarily serves to support science and exploration missions for NASA and other Federal agencies. WFF includes an extensively instrumented range to support launches of more than a dozen types of sounding rockets; small expendable suborbital and orbital rockets; high-altitude balloon flights carrying scientific instruments for atmospheric and astronomical research; and, using its Research Airport, flight tests of aeronautical research aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles.

Orion is the designation of a small American sounding rocket. The Orion has a length of 5.60 meters, a diameter of 0.35 m, a launch weight of 400 kg, a launch thrust of 7 kN and a ceiling of 85 kilometers. The Orion, built by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center's Wallops Flight Facility, is also used as an upper stage of sounding rockets, usually paired with a Terrier missile as the first stage, although Nike, Taurus and VS-30 rockets are also used.
Malemute is the designation of an American sounding rocket family. The original Malemute had a maximum flight altitude of 165 km, a liftoff thrust of 57.00 kN, a total mass of 100 kg, a diameter of 0.41 m and a total length of 2.40 m. It was a single stage vehicle powered by a Thiokol Malemute TU-758 engine, operated by Sandia National Laboratories (SNL).

A boilerplate spacecraft, also known as a mass simulator, is a nonfunctional craft or payload that is used to test various configurations and basic size, load, and handling characteristics of rocket launch vehicles. It is far less expensive to build multiple, full-scale, non-functional boilerplate spacecraft than it is to develop the full system. In this way, boilerplate spacecraft allow components and aspects of cutting-edge aerospace projects to be tested while detailed contracts for the final project are being negotiated. These tests may be used to develop procedures for mating a spacecraft to its launch vehicle, emergency access and egress, maintenance support activities, and various transportation processes.

The Eastern Range (ER) is an American rocket range (Spaceport) that supports missile and rocket launches from the two major launch heads located at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. The range has also supported Ariane launches from the Guiana Space Centre as well as launches from the Wallops Flight Facility and other lead ranges. The range also uses instrumentation operated by NASA at Wallops and KSC.

The year 2008 contained several significant events in spaceflight, including the first flyby of Mercury by a spacecraft since 1975, the discovery of water ice on Mars by the Phoenix spacecraft, which landed in May, the first Chinese spacewalk in September, the launch of the first Indian Lunar probe in October, and the first successful flight of a privately developed orbital launch vehicle by SpaceX's Falcon 1.

The NOTS-EV-2 Caleb, also known as NOTS-500, Hi-Hoe and SIP was an expendable launch system, which was later used as a sounding rocket and prototype anti-satellite weapon. It was developed by the United States Navy's Naval Ordnance Test Station (NOTS) as a follow-up to the NOTS-EV-1 Pilot, which had been abandoned following ten launches officially classified as failed missions. Two were launched in July and October 1960, before the cancellation of the project. Following cancellation, two leftover Calebs were used in the Satellite Interceptor Program (SIP), while three more were used as sounding rockets, under the designation Hi-Hoe. These derivatives flew until July 1962, when the Hi-Hoe made its final flight.

The year 2012 saw a number of significant events in spaceflight. In May and October, the first Commercial Orbital Transportation Services resupply missions took place, during which the SpaceX Dragon became the first private spacecraft to dock with the International Space Station (ISS). In June, China launched the crewed Shenzhou 9 orbital mission, and North Korea achieved its first successful orbital launch in December. 2012 also saw China's first successful asteroid exploration mission, and the landing of NASA's Curiosity rover on Mars. The Vega and Unha-3 rockets made their maiden flights in 2012, while the Proton-K made its last.
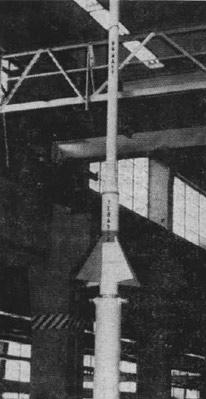
Terasca, or Terrier-ASROC-Cajun, was an American three-stage sounding rocket developed and launched by the United States Navy. Derived from a combination of the Terrier, ASROC and Cajun rockets, three launches were attempted during 1959, but only one was successful.

The Terrier Malemute is a two-stage American sounding rocket typically used for smaller payloads. Both the Terrier first stage and the Malemute second stage use solid fuel. The Terrier burns for approximately 5.2 seconds, and the Malemute burns for approximately 21.5 seconds. The first stage booster consists of a surplus Navy Terrier MK 12 Mod 1 rocket motor with four 0.22 m2 (340 sq in) fin panels arranged in a cruciform configuration. The Terrier rocket booster has a diameter of 460 mm (18 in). The second stage solid rocket is a Thiokol Malemute TU-758 rocket motor, specially designed for high altitude research rocket applications. Apogee is approximately 400 km (220 nmi) for a 230 kg (510 lb) payload or 700 km (380 nmi) for a 41 kg (90 lb) payload. For a payload weight of 200 lb (91 kg), the acceleration during the boost phase is 26 g. Its first flight was on November 11, 1974, from Barking Sands. Other launch sites have included Poker Flat, Wallops Island and Fort Yukon, Alaska.
Space Vector Corporation (SVC) is a United States-based company that provides aerospace products and services to government and commercial customers. Space Vector is headquartered in Chatsworth, California and is a privately held small business. Its primary products are flight safety and system batteries, GPS tracking systems, custom avionics and structures, attitude control systems, pneumatic components, and separation systems. Space Vector also provides launch services as a prime contractor under the Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC) Sounding Rocket Program (SRP-3) which includes performing vehicle integration activities, end-to-end system testing, payload integration, launch operations, and mission analysis and design.

Jaguar was a three-stage sounding rocket developed by the United States Air Force in the early 1960s. Designed for air launch to allow soundings from remote areas without infrastructure, it was only launched twice before the project was abandoned.

The NASA Sounding Rocket Program (NSRP) is a NASA run program of sounding rockets which has been operating since 1959. The missions carried out by this program are primarily used for scientific research, particularly low gravity and material based research. NASA's sounding rocket program is commonly used by colleges and universities for upper atmosphere research.