
Fusicoccins are organic compounds produced by a fungus. It has detrimental effect on plants and causes their death.

Isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase, also known as Isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase, is an isomerase that catalyzes the conversion of the relatively un-reactive isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) to the more-reactive electrophile dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). This isomerization is a key step in the biosynthesis of isoprenoids through the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway.

In enzymology, bornyl diphosphate synthase (BPPS) (EC 5.5.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
The enzyme ent-kaurene synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (EC 2.2.1.7) is an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, chlorophyll synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
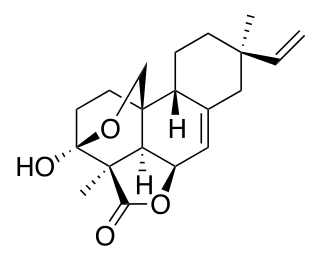
Momilactone B is an allelopathic agent produced from the roots of rice. It has been shown to be produced in high concentrations by the roots of rice seedlings. The production of momilactone B has also been induced in response to infection by blast fungus or irradiated with UV light. More recently it has been shown to be a potential chemotherapeutic agent against human colon cancer.

In molecular biology, YgbB is a protein domain. This entry makes reference to a number of proteins from eukaryotes and prokaryotes which share this common N-terminal signature and appear to be involved in terpenoid biosynthesis. The YgbB protein is a putative enzyme thought to aid terpenoid and isoprenoid biosynthesis, a vital chemical in all living organisms. This protein domain is part of an enzyme which catalyses a reaction in a complex pathway.
Futalosine hydrolase (EC 3.2.2.26, futalosine nucleosidase, MqnB) is an enzyme with systematic name futalosine ribohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
ent-Sandaracopimaradiene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name ent-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase [ent-sandaracopimara-8(14),15-diene-forming]. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
ent-Pimara-9(11),15-diene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name ent-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Stemar-13-ene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 9α-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (stemar-13-ene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
syn-Pimara-7,15-diene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 9α-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (9β-pimara-7,15-diene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aphidicolan-16β-ol synthase (EC 4.2.3.42, PbACS) is an enzyme with systematic name 9α-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (aphidicolan-16β-ol-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phyllocladan-16α-ol synthase (EC 4.2.3.45, PaDC1) is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (phyllocladan-16α-ol-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Miltiradiene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-copaly-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Terpentedienyl-diphosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name terpentedienyl-diphosphate lyase (decyclizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Halimadienyl-diphosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name halima-5,13-dien-15-yl-diphosphate lyase (decyclizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction







