The Chʼol are an Indigenous people of Mexico, mainly in the northern Chiapas highlands in the state of Chiapas. As one of the Maya peoples, their indigenous language is from the Mayan language family, known also as Chʼol. According to the 2000 Census, there were 140,806 speakers of Chʼol in Chiapas, including 40,000 who were monolingual.

Mexicali Municipality is a municipality in the Mexican state of Baja California. Its municipal seat is located in the city of Mexicali. As of 2020, the municipality had a total population of 1,049,792. The municipality has an area of 13,700 km2 (5,300 sq mi). This includes many smaller outlying communities as well as the city of Mexicali. Also, the islands of Baja California located in the Gulf of California are part of the municipality, among them the mudflat islands at the mouth of the Colorado River, Isla Ángel de la Guarda and the islands of the San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park. Mexicali is the northernmost municipality of Latin America.

Altamirano is a municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas. The municipality covers an area of 1120 km2. As of 2010, the municipality had a total population of 29,865, up from 21,948 as of 2005.

Villaflores Municipality is a municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico, and the name of its largest settlement and seat of the municipal government. Situated in the Sierra Madre de Chiapas range, the municipality has an area of approximately 1232 km2 at an average elevation of 540m above mean sea level.
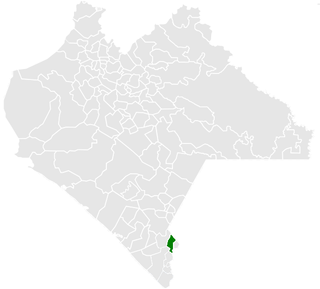
Cacahoatán is a city and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas, in southern Mexico. It covers an area of 173.9 km2. The land of Cocoa. Nahuatl orig.
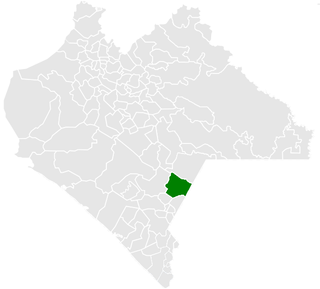
Frontera Comalapa is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico. It covers an area of 717.90 km².

La Concordia is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.
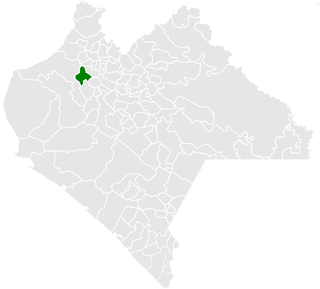
Copainalá is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico. It covers an area of 330.4 km2.

Huitiupán is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.

Ixtapangajoya is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.
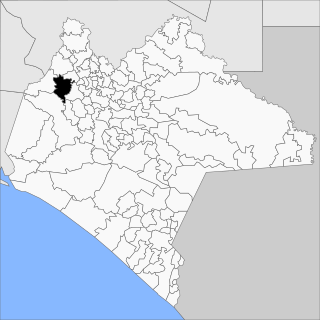
Tecpatán is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.

Juárez is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.
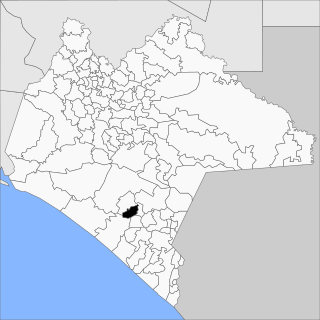
Montecristo de Guerrero is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.

San Juan Cancuc is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.

Sabanilla is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.
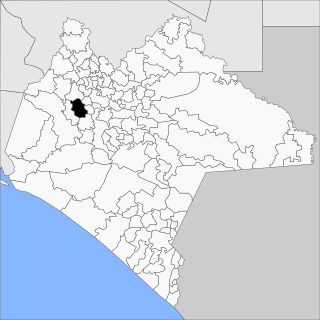
San Fernando is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.
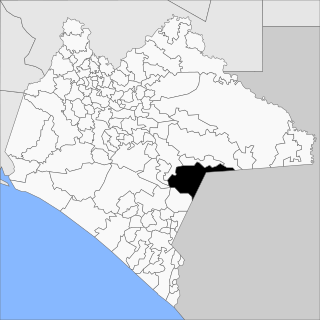
La Trinitaria is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.

Unión Juárez is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico. The majority of the population in the municipality is Mam people that preserves the Mam traditions and Mam language.

Lerdo is a municipality in the Mexican state of Durango. The municipal seat lies at Ciudad Lerdo. The municipality covers an area of 1868.8 km2.

The Chiapas conflict consisted of the 1994 Zapatista uprising, the 1995 Zapatista crisis, and the subsequent tension between the Mexican state, the indigenous peoples and subsistence farmers of Chiapas from the 1990s to the 2010s.





















