
Apiaceae or Umbelliferae is a family of mostly aromatic flowering plants named after the type genus Apium and commonly known as the celery, carrot or parsley family, or simply as umbellifers. It is the 16th-largest family of flowering plants, with more than 3,800 species in about 446 genera, including such well-known and economically important plants as ajwain, angelica, anise, asafoetida, caraway, carrot, celery, chervil, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel, lovage, cow parsley, parsley, parsnip and sea holly, as well as silphium, a plant whose exact identity is unclear and which may be extinct.

Scilla is a genus of about 30 to 80 species of bulb-forming perennial herbaceous plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. Sometimes called the squills in English, they are native to woodlands, subalpine meadows, and seashores throughout Europe, Africa and the Middle East. A few species are also naturalized in Australasia and North America. Their flowers are usually blue, but white, pink, and purple types are known; most flower in early spring, but a few are autumn-flowering. Several Scilla species are valued as ornamental garden plants.

Lamium (dead-nettles) is a genus of about 30 species of flowering plants in the family Lamiaceae, of which it is the type genus. They are all herbaceous plants native to Europe, Asia, and northern Africa, but several have become very successful weeds of crop fields and are now widely naturalised across much of the temperate world.

Coriaria is the sole genus in the family Coriariaceae, which was described by Linnaeus in 1753. It includes 14 species of small trees, shrubs and subshrubs, with a widespread but disjunct distribution across warm temperate regions of the world, occurring as far apart as the Mediterranean region, southern and eastern Asia, New Zealand, the Pacific Ocean islands, and Central and South America.

Bifora is a cosmopolitan genus of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, of disjunct distribution, with 3 species, two Eurasian and one American.

Selinum carvifolia is a flowering plant of the genus Selinum in the family Apiaceae. The specific name carvifolia signifies 'having leaves resembling those of Caraway'. It is a plant of fens and damp meadows, growing in most of Europe, with the exception of much of the Mediterranean region, eastwards to Central Asia. Its common name in English is Cambridge milk parsley, because it is confined, in the UK, to the county of Cambridgeshire and closely resembles milk parsley, an umbellifer of another genus, but found in similar habitats. The two plants are not only similar in appearance, but also grow in similar moist habitats, although they may be told apart in the following manner: P. palustre has hollow, often purplish stems, pinnatifid leaf lobes and deflexed bracteoles; while S. carvifolia has solid, greenish stems, entire or sometimes lobed leaf-lobes and erecto-patent bracteoles. Also, when the two plants are in fruit, another difference becomes apparent: the three dorsal ridges on the fruit of S. carvifolia are winged, while those on the fruit of P. palustre are not. Yet a further difference lies in the respective leaflets of the plants : those of Peucedanum palustre are blunt and pale at the tip, while those of Selinum carvifolia are sharply pointed and of a darker green. S. carvifolia used also to occur in the English counties of Nottinghamshire and Lincolnshire but is now extinct in both. Growing in only three small Cambridgeshire fens, it is one of England's rarest umbellifers. It is naturalized in the United States, where it is known by the common name little-leaf angelica.

Laser is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the Umbelliferae family (Apiaceae). The only species is Laser trílobum, an herbaceous plant, a Pliocene relict.

Tordylium apulum, commonly known as the Mediterranean hartwort, is an annual forb or herb. It is classified within the family Apiaceae, the carrot family. It is native to Europe and Western Asia, but has been introduced to the United States, where it is now found only in Arizona. This plant's seeds are suggested as the plant model used for the famous gold "Malia Pendant", a jewel of high quality gold-smithery of the Minoan times now on display at the Heraklion Archaeological Museum.

Andryala is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. It is native to Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.

Thapsia villosa, commonly known as the villous deadly carrot, is a species of poisonous herbaceous plants in the genus Thapsia. It grows to about 70 to 190 cm in height. It has pinnate hairy leaves with sheath-like petioles. The flowers are yellow in color and borne on compound umbels. They develop into fruits with four wings characteristic of the genus. It is native to southwestern Europe and northwestern Africa surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. The plant was used extensively for traditional medicine since around the 3rd century BC.

Vella is a genus of plants in the family Brassicaceae, under which there are no fewer than six species. Species are many branched, and have hairy, sessile, entire leaves that are narrower in width at their bases, widening out to form ovals. Fruits are stiff follicles. Vella is endemic to that area of land encompassing Algeria, Morocco, and Spain.
Selinum is a Eurasiatic genus of flowering plants in the parsley family Apiaceae.
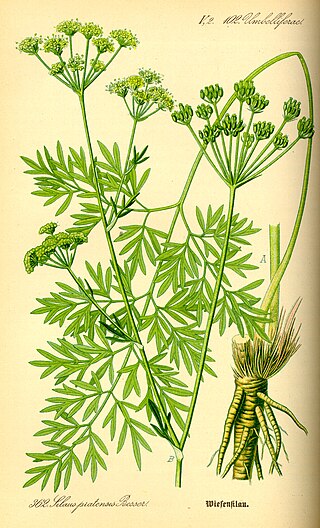
Silaum silaus, commonly known as pepper-saxifrage, is a perennial plant in the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) found across south-eastern, central, and western Europe, including the British Isles. It grows in damp grasslands on neutral soils.

Leontice is a group of perennial, tuberous herbs in the Berberidaceae described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753.

Tordylium maximum, known as hartwort, is an annual or biennial flowering plant in the carrot family (Apiaceae).
Tordylium trachycarpum is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to Western Asia and European Turkey. It was first described by Pierre Edmond Boissier in 1849 as Ainsworthia trachycarpa.

Oenanthe aquatica, fine-leaved water-dropwort, is an aquatic flowering plant in the carrot family. It is widely distributed from the Atlantic coast of Europe to central Asia.
Stenotaenia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae, native to Anatolia, the Transcaucasus, and Iran. Their fruit have numerous vittae on their dorsal and commissural surfaces, a trait shared with the genus Opopanax.

Oenanthe fistulosa, tubular water-dropwort, is a flowering plant in the carrot family, native to Europe, North Africa and western parts of Asia. It is an uncommon plant of wetlands, growing around pools and along ditches, mainly in areas of high conservation value.

Sison is a genus of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to western and southern Europe and north Africa. The genus was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753, in his book Species Plantarum.

















