
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
In organic chemistry, hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention: production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resultant aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in speciality chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and pharmaceuticals. The development of hydroformylation is one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.

In chemistry, the term phosphonium describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula PR+
4. These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic red-brown solids. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is the usual compound of commerce. It is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis.
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.
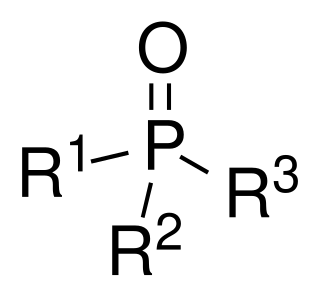
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3). The parent phosphine oxide (H3PO) remains rare and obscure.
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PRnH3−n, where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of n: primary phosphines (n = 1), secondary phosphines (n = 2), tertiary phosphines (n = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3).

In coordination chemistry, the bite angle is the angle on a central atom between two bonds to a bidentate ligand. This ligand–metal–ligand geometric parameter is used to classify chelating ligands, including those in organometallic complexes. It is most often discussed in terms of catalysis, as changes in bite angle can affect not just the activity and selectivity of a catalytic reaction but even allow alternative reaction pathways to become accessible.

Diphenylphosphine, also known as diphenylphosphane, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PH. This foul-smelling, colorless liquid is easily oxidized in air. It is a precursor to organophosphorus ligands for use as catalysts.

Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride (THPC) is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula [P(CH2OH)4]Cl. It is a white water-soluble salt. THPC has applications as a precursor to fire-retardant materials, as well as a microbiocide in commercial and industrial water systems.

Organorhodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a rhodium-carbon chemical bond, and the study of rhodium and rhodium compounds as catalysts in organic reactions.

Cobalt tetracarbonyl hydride is an organometallic compound with the formula HCo(CO)4. It is a volatile, yellow liquid that forms a colorless vapor and has an intolerable odor. The compound readily decomposes upon melt and in absentia of high CO partial pressures forms Co2(CO)8. Despite operational challenges associated with its handling, the compound has received considerable attention for its ability to function as a catalyst in hydroformylation. In this respect, HCo(CO)4 and related derivatives have received significant academic interest for their ability to mediate a variety of carbonylation (introduction of CO into inorganic compounds) reactions.

A metal-phosphine complex is a coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).

Carbonyl hydrido tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) [Carbonyl(hydrido)tris(triphenylphosphane)rhodium(I)] is an organorhodium compound with the formula [RhH(CO)(PPh3)3] (Ph = C6H5). It is a yellow, benzene-soluble solid, which is used industrially for hydroformylation.
Hydrophosphination is the insertion of a carbon-carbon multiple bond into a phosphorus-hydrogen bond forming a new phosphorus-carbon bond. Like other hydrofunctionalizations, the rate and regiochemistry of the insertion reaction is influenced by the catalyst. Catalysts take many forms, but most prevalent are bases and free-radical initiators. Most hydrophosphinations involve reactions of phosphine (PH3).
In chemistry, phosphorochloridites are a class of organophosphorus compound with the formula (RO)2PCl (R = organic substituent). They are pyramidal in shape, akin to regular phosphites (P(OR)3). They are usually colorless and sensitive toward hydrolysis and, to some extent, oxidation to the corresponding phosphorochloridates ((RO)2P(O)Cl).

1,1,1-Tris(diphenylphosphinomethyl)ethane, also called Triphos, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH3C[CH2PPh2]3. An air-sensitive white solid, it is a tripodal ligand ("three-legged") of idealized C3v symmetry. It was originally prepared by the reaction of sodium diphenylphosphide and CH3C(CH2Cl)3:





















