
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is a country in North America. It is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and 88% of its population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.

The CaymanIslands is a self-governing British Overseas Territory, and the largest by population. The 264-square-kilometre (102-square-mile) territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located south of Cuba and north-east of Honduras, between Jamaica and Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula. The capital city is George Town on Grand Cayman, which is the most populous of the three islands.

The Channel Islands are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They are divided into two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, which is the largest of the islands; and the Bailiwick of Guernsey, consisting of Guernsey, Alderney, Sark, Herm and some smaller islands. Historically, they are the remnants of the Duchy of Normandy. Although they are not part of the United Kingdom, the UK is responsible for the defence and international relations of the islands as it is for the other Crown Dependency, the Isle of Man, and the British Overseas Territories. The Crown Dependencies are neither members of the Commonwealth of Nations, nor part of the European Union. They have a total population of about 171,916, and the bailiwicks' capitals, Saint Helier and Saint Peter Port, have populations of 33,500 and 18,207 respectively.

The Canary Islands, also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in Macaronesia in the Atlantic Ocean. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are 100 kilometres west of Morocco and the Western Sahara. They are the southernmost of the autonomous communities of Spain. The islands have a population of 2.2 million people and are the most populous special territory of the European Union.

Hawaii is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. It is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics.

Long Island is an island in southeastern New York state, constituting a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land area. The island extends from New York Harbor 118 miles (190 km) eastward into the North Atlantic Ocean with a maximum north–south width of 23 miles (37 km). With a land area of 1,401 square miles (3,630 km2), it is the largest island in the contiguous United States.

The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as Maldive Islands, is a country and archipelagic state in South Asia in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is named after the main island and capital, Malé. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, about 750 kilometres from the Asian continent's mainland. The Maldives' chain of 26 atolls stretches across the equator from Ihavandhippolhu Atoll in the north to Addu Atoll in the south.

Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about 2,000 kilometres off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island, as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga, and St. Brandon. The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion, are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans 2,040 square kilometres (790 sq mi) and has an exclusive economic zone covering 2,300,000 square kilometres.

Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples.

Oceania is a geographical region comprising Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western Hemispheres, at the centre of the water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about 9,000,000 square kilometres (3,500,000 sq mi) and a population of around 44.4 million as of 2022. When compared to the other continents, Oceania is the smallest in land area and the second-least populated after Antarctica.

The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of the Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east.

Rhode Island is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Island Sound; and shares a small maritime border with New York, east of Long Island. Rhode Island is the smallest U.S. state by area and the seventh-least populous, with slightly fewer than 1.1 million residents as of 2020; but it has grown at every decennial count since 1790 and is the second-most densely populated state, after New Jersey. The state takes its name from the eponymous island, though nearly all its land area is on the mainland. Providence is its capital and most populous city.

The Turks and Caicos Islands are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and northern West Indies. They are known primarily for tourism and as an offshore financial centre. The resident population in 2023 was estimated by The World Factbook at 59,367, making it the third-largest of the British overseas territories by population. However, according to a Department of Statistics estimate in 2022, the population was 47,720.

The Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons, is a country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, to the northeast of Australia. It is directly adjacent to Papua New Guinea to the northwest, Australia to the southwest, New Caledonia and Vanuatu to the southeast, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna, and Tuvalu to the east, and Nauru and the Federated States of Micronesia to the north. It has a total area of 28,896 square kilometres, and a population of 734,887 according to the official estimates for mid 2023. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands archipelago, which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands.

The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island countries and 19 dependencies in three archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago.

The Falkland Islands is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about 300 mi (480 km) east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about 752 mi (1,210 km) from Cape Dubouzet at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago, with an area of 4,700 sq mi (12,000 km2), comprises East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands. As a British overseas territory, the Falklands have internal self-governance, but the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The capital and largest settlement is Stanley on East Falkland.

Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of England, Scotland and Wales. With an area of 209,331 km2 (80,823 sq mi), it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The island of Ireland, with an area 40 per cent that of Great Britain, is to the west—these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago.

The Faroe or Faeroe Islands, or simply the Faroes, are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark. The official language of the country is Faroese, which is closely related to and partially mutually intelligible with Icelandic.
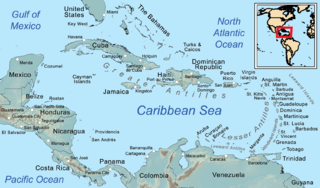
The Caribbean is a subregion of the Americas that includes the Caribbean Sea and its islands, some of which are surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some of which border both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean; the nearby coastal areas on the mainland are sometimes also included in the region. The region is south-east of the Gulf of Mexico and Northern America, east of Central America, and north of South America.



















