
The citric acid cycle —also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
Rhamnose is a naturally occurring deoxy sugar. It can be classified as either a methyl-pentose or a 6-deoxy-hexose. Rhamnose predominantly occurs in nature in its L-form as L-rhamnose (6-deoxy-L-mannose). This is unusual, since most of the naturally occurring sugars are in D-form. Exceptions are the methyl pentoses L-fucose and L-rhamnose and the pentose L-arabinose. However, examples of naturally-occurring D-rhamnose include some species of bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Helicobacter pylori.

UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase is a cytosolic enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UGDH gene.
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 6-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.136) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylmuramate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.98) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
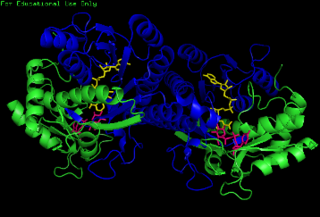
The enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, also known as UDP-galactose 4-epimerase or GALE, is a homodimeric epimerase found in bacterial, fungal, plant, and mammalian cells. This enzyme performs the final step in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, catalyzing the reversible conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. GALE tightly binds nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a co-factor required for catalytic activity.

In enzymology, a malate synthase (EC 2.3.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
UDP-glucuronic acid dehydrogenase (UDP-4-keto-hexauronic acid decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.305, UDP-GlcUA decarboxylase, ArnADH) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-glucuronate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (decarboxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
2-deoxy-scyllo-inosamine dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.329, neoA (gene name), kanK (gene name)) is an enzyme with systematic name 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosamine:NAD(P)+ 1-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.336, UDP-ManNAc 6-dehydrogenase, wecC (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-mannosamine:NAD+ 6-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
2-deoxy-scyllo-inosamine dehydrogenase (SAM-dependent) is an enzyme with systematic name 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosamine:S-adenosyl-L-methionine 1-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose formyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name 10-formyltetrahydrofolate:UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-beta-L-arabinose N-formyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
2-amino-3,7-dideoxy-D-threo-hept-6-ulosonate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde:1-deoxy-D-threo-hexo-2,5-diulose 6-phosphate methylglyoxaltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-2-acetamido-3-amino-2,3-dideoxy-glucuronate N-acetyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name acetyl-CoA:UDP-2-acetamido-3-amino-2,3-dideoxy-alpha-D-glucuronate N-acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine N-acetyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name acetyl-CoA:UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine N-acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine transaminase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-ribo-hexuluronate aminotransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-2-acetamido-3-amino-2,3-dideoxy-alpha-D-glucuronate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4,6-dehydratase (configuration-retaining) (EC 4.2.1.135, PglF) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-α-Dglucosamine hydro-lyase (configuration-retaining; UDP-2-acetamido-2,6-dideoxy-α-Dxylo-hex-4-ulose-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-2,3-diacetamido-2,3-dideoxyglucuronic acid 2-epimerase is an enzyme with systematic name 2,3-diacetamido-2,3-dideoxy-alpha-D-glucuronate 2-epimerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction





