
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants. In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) is pumped under high pressure to the reactor core where it is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms. The heated, high pressure water then flows to a steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to lower pressure water of a secondary system where steam is generated. The steam then drives turbines, which spin an electric generator. In contrast to a boiling water reactor (BWR), pressure in the primary coolant loop prevents the water from boiling within the reactor. All light-water reactors use ordinary water as both coolant and neutron moderator. Most use anywhere from two to four vertically mounted steam generators; VVER reactors use horizontal steam generators.

A nuclear meltdown is a severe nuclear reactor accident that results in core damage from overheating. The term nuclear meltdown is not officially defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency or by the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission. It has been defined to mean the accidental melting of the core of a nuclear reactor, however, and is in common usage a reference to the core's either complete or partial collapse.

A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a generator that produces electricity. As of September 2023, the International Atomic Energy Agency reported that there were 410 nuclear power reactors in operation in 32 countries around the world, and 57 nuclear power reactors under construction.

The RBMK is a class of graphite-moderated nuclear power reactor designed and built by the Soviet Union. It is somewhat like a boiling water reactor as water boils in the pressure tubes. It is one of two power reactor types to enter serial production in the Soviet Union during the 1970s, the other being the VVER reactor. The name refers to its design where instead of a large steel pressure vessel surrounding the entire core, the core is surrounded by a cylindrical annular steel tank inside a concrete vault and each fuel assembly is enclosed in an individual 8 cm (inner) diameter pipe. The channels also contain the coolant, and are surrounded by graphite.
Passive nuclear safety is a design approach for safety features, implemented in a nuclear reactor, that does not require any active intervention on the part of the operator or electrical/electronic feedback in order to bring the reactor to a safe shutdown state, in the event of a particular type of emergency. Such design features tend to rely on the engineering of components such that their predicted behaviour would slow down, rather than accelerate the deterioration of the reactor state; they typically take advantage of natural forces or phenomena such as gravity, buoyancy, pressure differences, conduction or natural heat convection to accomplish safety functions without requiring an active power source. Many older common reactor designs use passive safety systems to a limited extent, rather, relying on active safety systems such as diesel-powered motors. Some newer reactor designs feature more passive systems; the motivation being that they are highly reliable and reduce the cost associated with the installation and maintenance of systems that would otherwise require multiple trains of equipment and redundant safety class power supplies in order to achieve the same level of reliability. However, weak driving forces that power many passive safety features can pose significant challenges to effectiveness of a passive system, particularly in the short term following an accident.

State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom, also known as Rosatom State Nuclear Energy Corporation,, or Rosatom State Corporation, is a Russian state corporation headquartered in Moscow that specializes in nuclear energy, nuclear non-energy goods and high-tech products. It was established in 2007 and comprises more than 350 enterprises, including scientific research organizations, a nuclear weapons complex, and the world's only nuclear icebreaker fleet.
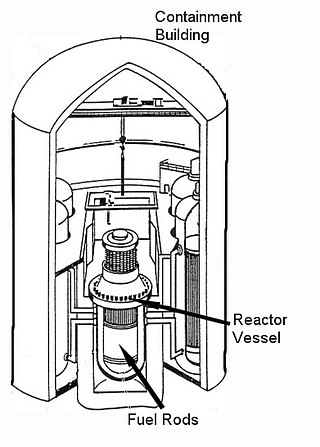
A containment building is a reinforced steel, concrete or lead structure enclosing a nuclear reactor. It is designed, in any emergency, to contain the escape of radioactive steam or gas to a maximum pressure in the range of 275 to 550 kPa. The containment is the fourth and final barrier to radioactive release, the first being the fuel ceramic itself, the second being the metal fuel cladding tubes, the third being the reactor vessel and coolant system.

The advanced boiling water reactor (ABWR) is a Generation III boiling water reactor. The ABWR is currently offered by GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) and Toshiba. The ABWR generates electrical power by using steam to power a turbine connected to a generator; the steam is boiled from water using heat generated by fission reactions within nuclear fuel. Kashiwazaki-Kariwa unit 6 is considered the first Generation III reactor in the world.

The AP1000 is a nuclear power plant designed and sold by Westinghouse Electric Company. The plant is a pressurized water reactor with improved use of passive nuclear safety and many design features intended to lower its capital cost and improve its economics.

The water-water energetic reactor (WWER), or VVER is a series of pressurized water reactor designs originally developed in the Soviet Union, and now Russia, by OKB Gidropress. The idea of such a reactor was proposed at the Kurchatov Institute by Savely Moiseevich Feinberg. VVER were originally developed before the 1970s, and have been continually updated. They were one of the initial reactors developed by the USSR, the other being the infamous RBMK. As a result, the name VVER is associated with a wide variety of reactor designs spanning from generation I reactors to modern generation III+ reactor designs. Power output ranges from 70 to 1300 MWe, with designs of up to 1700 MWe in development. The first prototype VVER-210 was built at the Novovoronezh Nuclear Power Plant.

Generation III reactors, or Gen III reactors, are a class of nuclear reactors designed to succeed Generation II reactors, incorporating evolutionary improvements in design. These include improved fuel technology, higher thermal efficiency, significantly enhanced safety systems, and standardized designs intended to reduce maintenance and capital costs. They are promoted by the Generation IV International Forum (GIF).

The Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR) is a passively safe generation III+ reactor design derived from its predecessor, the Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (SBWR) and from the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR). All are designs by GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH), and are based on previous Boiling Water Reactor designs.

Russia is one of the world's largest producers of nuclear energy. In 2020 total electricity generated in nuclear power plants in Russia was 215.746 TWh, 20.28% of all power generation. The installed gross capacity of Russian nuclear reactors is 29.4 GW in December 2020.
State Enterprise National Nuclear Energy Generating Company "Energoatom", commonly known as just Energoatom, is a state enterprise operating all four nuclear power plants in Ukraine. It is the largest power producer in Ukraine.

The Belene Nuclear Power Plant is an abandoned nuclear power plant 3 km from Belene and 11 km from Svishtov in Pleven Province, northern Bulgaria, near the Danube River. It was intended to substitute four VVER-440 V230 reactors of the Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant that were decommissioned as a prerequisite for Bulgaria to join the European Union.

The Mochovce Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power plant located between the towns of Nitra and Levice, on the site of the former village of Mochovce, Slovakia. Two up-rated 470 MW reactors plus a 471 MW VVER 440 reactor are presently in operation, with a fourth of the same type under construction. In 2022 it generated almost 7,000 GWh of electricity, the power plant provided approximately 20% of Slovakia's electricity needs.

The Kursk Nuclear Power Plant is one of the three biggest nuclear power plants (NPPs) in Russia and one of the four biggest electricity producers in the country. It is located on the bank of the Seym River about 40 kilometers west of the city of Kursk, midway between it and the town of Lgov, in western Russia. The nearby city of Kurchatov was founded when construction of the plant began. The plant feeds the grid for Kursk Oblast and 19 other regions. As of 2024, the site houses two active reactors and two decommissioned older units. It also houses the partially built Kursk 5 and Kursk 6 units which had construction halted, and two new VVER designs are under construction.

Smolensk Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power station in Russia. It is located in the Smolensk region, in Desnogorsk province, approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi) from Smolensk, 115 kilometres (71 mi) from Bryansk and 320 kilometres (200 mi) from Moscow. Smolensk Nuclear Power Plant is the biggest power generating station in the north-western region of the united energy system of the Russian Federation. Smolensk NPP has an outer appearance similar to that of Chernobyl NPP units 3-4, as both are later generation RBMKs.
The three primary objectives of nuclear reactor safety systems as defined by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission are to shut down the reactor, maintain it in a shutdown condition and prevent the release of radioactive material.

The Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant (Bengali: রূপপুর পারমাণবিক বিদ্যুৎকেন্দ্র) is a 2.4 GWe nuclear power plant project in Bangladesh. The nuclear power plant is being constructed at Rooppur of Ishwardi Upazila on the bank of the river Padma, about 160 km northwest of Dhaka. It will be the country's first nuclear power plant, and the first of the two units is expected to go into operation in 2025.














