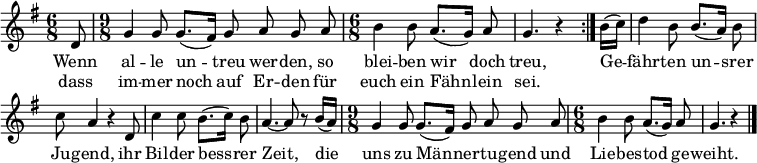Wenn alle untreu werden, so bleiben wir doch treu,
dass immer noch auf Erden für euch ein Fähnlein sei,
Gefährten unsrer Jugend, ihr Bilder bessrer Zeit,
die uns zu Männertugend, und Liebestod geweiht.
Wollt nimmer von uns weichen, uns immer nahe sein,
treu, wie die deutschen Eichen, wie Mond und Sonnenschein!
Einst wird es wieder helle in aller Brüder Sinn,
sie kehren zu der Quelle in Lieb und Reue hin.
Es haben wohl gerungen die Helden dieser Frist,
und nun der Sieg gelungen, übt Satan neue List.
Doch wie sich auch gestalten im Leben mag die Zeit,
du sollst uns nicht veralten, o Traum der Herrlichkeit.
Ihr Sterne, seid uns Zeugen, die ruhig niederschaun,
wenn alle Brüder schweigen und falschen Götzen traun:
wir wolln das Wort nicht brechen und Buben werden gleich,
wolln predigen und sprechen von Kaiser und von Reich! [4]