Related Research Articles

International development or global development is a broad concept denoting the idea that societies and countries have differing levels of economic or human development on an international scale. It is the basis for international classifications such as developed country, developing country and least developed country, and for a field of practice and research that in various ways engages with international development processes. There are, however, many schools of thought and conventions regarding which are the exact features constituting the "development" of a country.
Governance is the process of making and enforcing decisions within an organization or society. It is the process of interactions through the laws, social norms, power or language as structured in communication of an organized society over a social system. It is done by the government of a state, by a market, or by a network. It is the process of choosing the right course among the actors involved in a collective problem that leads to the creation, reinforcement, or reproduction of acceptable conduct and social order". In lay terms, it could be described as the political processes that exist in and between formal institutions.
Based on a long-standing research program of the World Bank, the Worldwide Governance Indicators capture six key dimensions of governance between 1996 and present. They measure the quality of governance in over 200 countries, based on close to 40 data sources produced by over 30 organizations worldwide and are updated annually since 2002.
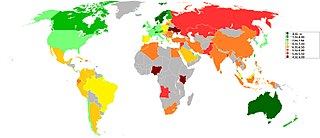
The Economist Intelligence Unit’s where-to-be-born index attempts to measure which country will provide the best opportunities for a healthy, safe and prosperous life in the years ahead.
Daniel Kaufmann is the president emeritus of the Natural Resource Governance Institute (NRGI), which resulted from the merger of the Revenue Watch Institute – Natural Resource Charter. He is also a nonresident senior fellow at the Brookings Institution, where he was previously a senior fellow, and until July 2019 served in the international board of the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative and in a number of advisory boards on governance, anti-corruption and natural resources and has also been in high-level expert commissions such as at the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, the Inter-American Development Bank and the Mo Ibrahim Foundation. Prior to that, he was a director at the World Bank Institute, leading work on governance and anti-corruption. He was also a senior manager and lead economist at the World Bank, writing and working on many countries around the world, and was a visiting scholar at Harvard University. He has also served in other boards and councils in the past, including at the World Economic Forum.
Human development involves studies of the human condition with its core being the capability approach. The inequality adjusted Human Development Index is used as a way of measuring actual progress in human development by the United Nations. It is an alternative approach to a single focus on economic growth, and focused more on social justice, as a way of understanding progress
This is a list of key international rankings of Costa Rica
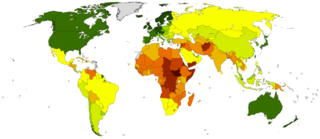
The Legatum Prosperity Index is an annual ranking developed by the Legatum Institute, an independent educational charity founded and part-funded by the private investment firm Legatum. The ranking is based on a variety of factors including wealth, economic growth, education, health, personal well-being, and quality of life.
The following are international rankings of Qatar.

Released by UNESCO, the Gender Parity Index (GPI) is a socioeconomic index usually designed to measure the relative access to education of males and females. It is used by international organizations, particularly in measuring the progress of developing countries. For example, some UNESCO documents consider gender parity in literacy.
The following are international rankings of Lebanon.
The following are international rankings of Tunisia.
Wikiprogress is a defunct online platform for sharing information on the measurement of social, economic and environmental progress. It is thought to facilitate sharing on ideas, initiatives and knowledge on "measuring the progress of societies". Like Wikipedia, it was open to all members and communities for contribution – anyone interested in "progress" could register.

The Women's Economic Opportunity Index is an index compiled by the Economist Intelligence Unit that measures the enabling environment for women's economic participation in 128 countries. The Economist Intelligence Unit's Women's Economic Opportunity Index is based on 29 indicators that measure a country's laws, regulations, practices, customs and attitudes that allow women to participate in the workforce under conditions roughly equal to those of men, whether as wage-earning employees or as owners of a business. The index was first produced in 2010, with an updated index produced in 2012. Three indicators were added and 15 new countries were assessed in the 2012 version of the Index.

The Sustainable Development Goals or Global Goals are a collection of seventeen interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future". The SDGs are: no poverty; zero hunger; good health and well-being; quality education; gender equality; clean water and sanitation; affordable and clean energy; decent work and economic growth; industry, innovation and infrastructure; reduced inequalities; sustainable cities and communities; responsible consumption and production; climate action; life below water; life on land; peace, justice, and strong institutions; and partnerships for the goals. The SDGs emphasize the interconnected environmental, social and economic aspects of sustainable development by putting sustainability at their center.
International comparisons, or national evaluation indicators, focuses on the quantitative, qualitative, and evaluative analysis of one country in relation to others. Often, the objective is to compare one country's performance to others in order to assess what countries have achieved, what needs to change in order for them to perform better, or a country's progress in reaching certain objectives.
Government competitiveness is a new concept created by Tobin Im, a scholar of public administration and a professor at the Graduate School of Public Administration at Seoul National University. Since 2011, Center for Government Competitiveness (CGC) at Seoul National University has developed the Government Competitiveness (GC) index which evaluates government achievements in the various fields and furthermore provides policy recommendations to increase competitiveness of government in the future.

Sustainable Development Goal 16 is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015, the official wording is: "Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels". The Goal has 12 targets and 23 indicators.

Sustainable Development Goal 1, one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015, calls for the end of poverty in all forms. The official wording is: "No Poverty". Member countries have pledged to "Leave No One Behind": underlying the goal is a "powerful commitment to leave no one behind and to reach those farthest behind first". SDG 1 aims to eradicate every form of extreme poverty including the lack of food, clean drinking water, and sanitation. Achieving this goal includes finding solutions to new threats caused by climate change and conflict. SDG 1 focuses not just on people living in poverty, but also on the services people rely on and social policy that either promotes or prevents poverty.
References
- ↑ "Worldwide Governance Indicators". World Bank. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ↑ "Worldwide Governance Indicators". World Bank. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ↑ "Worldwide Governance Indicators". World Bank. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ↑ See the first chapter of Global Governance on Wikipedia.
- ↑ This includes organizations like the United Nations and the Bretton Woods institutions.
- ↑ Among many similar diagnoses, see for example: World Humanity Action Trust (2000), "Governance for a Sustainable Future", Reports of the Commissions of the World Humanity Action Trust, Russell Press Ltd., Nottingham (UK), p. 30 Archived 2016-06-12 at the Wayback Machine ; (2009), O'Hara, P.A. (ed.), "Public Policy and Political Economy", International Encyclopedia of Public Policy - Governance in a Global Age, Vol. 3, Perth; "Environmental governance" on Wikipedia; "Current global governance systems lack capacity to deal with global risks" in Daily Financial Times, Wijeya Newspapers Ltd. Colombo (Sri Lanka), January 14, 2011 Archived March 3, 2016, at the Wayback Machine ; etc.