
Sinosauropteryx is a compsognathid dinosaur. Described in 1996, it was the first dinosaur taxon outside of Avialae to be found with evidence of feathers. It was covered with a coat of very simple filament-like feathers. Structures that indicate colouration have also been preserved in some of its feathers, which makes Sinosauropteryx the first non-avialian dinosaurs where colouration has been determined. The colouration includes a reddish and light banded tail. Some contention has arisen with an alternative interpretation of the filamentous impression as remains of collagen fibres, but this has not been widely accepted.

Confuciusornis is a genus of basal crow-sized avialan from the Early Cretaceous Period of the Yixian and Jiufotang Formations of China, dating from 125 to 120 million years ago. Like modern birds, Confuciusornis had a toothless beak, but closer and later relatives of modern birds such as Hesperornis and Ichthyornis were toothed, indicating that the loss of teeth occurred convergently in Confuciusornis and living birds. It was thought to be the oldest known bird to have a beak, though this title now belongs to an earlier relative Eoconfuciusornis. It was named after the Chinese moral philosopher Confucius. Confuciusornis is one of the most abundant vertebrates found in the Yixian Formation, and several hundred complete specimens have been found.

Beipiaosaurus is a genus of therizinosauroid theropod dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Early Cretaceous in the Yixian Formation. The first remains were found in 1996 and formally described in 1999. Before the discovery of Yutyrannus, Beipiaosaurus were among the heaviest dinosaurs known from direct evidence to be feathered. Beipiaosaurus is known from three reported specimens. Numerous impressions of feather structures were preserved that allowed researchers to determine the feathering color which turned out to be brownish.
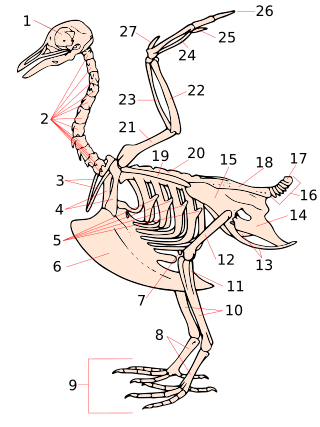
Pygostyle describes a skeletal condition in which the final few caudal vertebrae are fused into a single ossification, supporting the tail feathers and musculature. In modern birds, the rectrices attach to these. The pygostyle is the main component of the uropygium, a structure colloquially known as the bishop's nose, parson's nose, pope's nose, or sultan's nose. This is the fleshy protuberance visible at the posterior end of a bird that has been dressed for cooking. It has a swollen appearance because it also contains the uropygial gland that produces preen oil.

Jeholornis is a genus of avialans that lived between approximately 122 and 120 million years ago during the early Cretaceous Period in China. Fossil Jeholornis were first discovered in the Jiufotang Formation in Hebei Province, China and additional specimens have been found in the older Yixian Formation.

The South Georgia pintail, also misleadingly known as the South Georgian teal, is the nominate subspecies of the yellow-billed pintail, a duck in the dabbling duck subfamily Anatinae. It is endemic to the large (3,756 km2) subantarctic island of South Georgia and its accompanying archipelago, and is a vagrant to the South Sandwich Islands. It was among the birds noted by James Cook in January 1775, on the occasion of the first recorded landing on South Georgia, and was formerly considered a full species.

Longipteryx is a genus of prehistoric bird which lived during the Early Cretaceous. It contains a single species, Longipteryx chaoyangensis. Its remains have been recovered from the Jiufotang Formation at Chaoyang in Liaoning Province, China. Apart from the holotype IVPP V 12325 - a fine and nearly complete skeleton — another entire skeleton and some isolated bones are known to date.

Flight feathers are the long, stiff, asymmetrically shaped, but symmetrically paired pennaceous feathers on the wings or tail of a bird; those on the wings are called remiges, singular remex, while those on the tail are called rectrices, singular rectrix. The primary function of the flight feathers is to aid in the generation of both thrust and lift, thereby enabling flight. The flight feathers of some birds perform additional functions, generally associated with territorial displays, courtship rituals or feeding methods. In some species, these feathers have developed into long showy plumes used in visual courtship displays, while in others they create a sound during display flights. Tiny serrations on the leading edge of their remiges help owls to fly silently, while the extra-stiff rectrices of woodpeckers help them to brace against tree trunks as they hammer on them. Even flightless birds still retain flight feathers, though sometimes in radically modified forms.

Archaeorhynchus is a genus of beaked avialan stem-birds from the early Cretaceous period. A fossil of its only known species, Archaeorhynchus spathula, was first reported in 2005 by Zhou & Zhang to have been found in Yixian Formation rocks at Yixian, Liaoning province, China, showing a well-preserved and essentially complete skeleton. Two more complete specimens were found in Lower Cretaceous deposits of Jianchang, Liaoning, northeastern China, preserving new anatomical information. These deposits are 120 million years old, whereas the original specimen was 125 million years old, meaning the age range for this species is 125-120Ma.
Paraprotopteryx is a genus of enantiornithean birds from the Mesozoic of China.

Protopteryx is an extinct bird and the most basal enantiornithean, from the Cretaceous period. The type species is P. fengningensis. It was first discovered in the Sichakou Member of the Yixian Formation or Huajiying Formation of Hebei Province, northern China, dating from 131 Ma ago. Protopteryx has been found in the Daibeigou formation, as well. The name Protopteryx means "primitive feather": "proto-" meaning "the first of" and "-pteryx" meaning "feather" or "wing." The name comes from the fact that Protopteryx feathers are more primitive than those of modern birds, such as the two elongated tail feathers that lack barbs and rami.

Similicaudipteryx, meaning "similar to Caudipteryx", is a genus of theropod dinosaur of the family Caudipteridae.

Dinosaur coloration is generally one of the unknowns in the field of paleontology, as skin pigmentation is nearly always lost during the fossilization process. However, recent studies of feathered dinosaurs and skin impressions have shown the colour of some species can be inferred through the use of melanosomes, the colour-determining pigments within the feathers.

Euornithes is a natural group which includes the most recent common ancestor of all avialans closer to modern birds than to Sinornis.

Bohaiornithidae is a group of early predatory enantiornitheans from the early Cretaceous Period of China. All known specimens come from the Jiufotang Formation and Yixian Formation, dating to the early Aptian age, 125–120 million years ago. Bohaiornithidae was first coined as a family of enantiornithean birds by Wang and colleagues in 2014. They defined it as the natural group formed by all descendants of the common ancestor of the type species, Bohaiornis guoi, and Shenqiornis mengi.

Archaeornithura is an extinct genus of ornithuromorphs from the early Cretaceous period. It is known from two fossil specimens of a single species, Archaeornithura meemannae. The specimens have been dated to the Hauterivian age, 130.7 million years ago, making A. meemannae the oldest known ornithuromorph, the lineage that gave rise to modern birds, and contains all living birds as well as many of their extinct relatives.

Parapengornis is an extinct genus of enantiornithine bird from the Lower Cretaceous of what is now China. The holotype specimen was discovered in the Jiufotang Formation near Lingyuan, western Liaoning province, and was catalogued as IVPP V18687. The nearly complete, articulated specimen is preserved on a slab and has impressions of pennaceous feathers. Only parts of the sternum, the left hand, and right foot are missing. In 2015, it became the basis of the new genus and species Parapengornis eurycaudatus, named by the Chinese palaeontologists Han Hu, Jingmai K. O’Connor, and Zhonghe Zhou. The generic name consists of the Latin word para and the name of the related genus Pengornis, indicating their close relationship. The name Pengornis is itself derived from "Peng", a mythological bird from Chinese folklore, and ornis, which means bird in Greek. The specific name is derived from the Latin words eury, meaning broad, and caudatus, meaning tail, in reference to the broad and expanded pygostyle. A nearly complete specimen formerly assigned to Pengornis was also reassigned to Parapengornis by these authors.

Chiappeavis is a genus of enantiornithean bird from Early Cretaceous of northeastern China. The only species is Chiappeavis magnapremaxillo. Chiappeavis is classified within the family Pengornithidae. It is known from a single, almost complete skeleton including feather impressions discovered in the Jiufotang Formation of the Jehol Group. Long feathers formed a fan-shaped tail that was probably employed in flight.

Wulong is a genus of microraptorine dromaeosaurid dinosaurs from the Early Cretaceous (Aptian) Jiufotang Formation of China. The genus includes a single species, Wulong bohaiensis. The skeletal remains, which include preserved feathers, represent a juvenile.
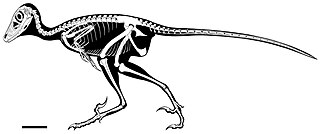
Daurlong is an extinct genus of dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (Aptian) Longjiang Formation of China. The genus contains a single species, D. wangi, known from a nearly complete skeleton. Daurlong represents the first described occurrence of a preserved intestinal region in a theropod closely related to birds.





















