
A pika is a small, mountain-dwelling mammal native to Asia and North America. With short limbs, a very round body, an even coat of fur, and no external tail, they resemble their close relative, the rabbit, but with short, rounded ears. The large-eared pika of the Himalayas and nearby mountains lives at elevations of more than 6,000 m (20,000 ft).

Castoridae is a family of rodents that contains the two living species of beavers and their fossil relatives. A formerly diverse group, only a single genus is extant today, Castor. Two other genera of "giant beavers", Castoroides and Trogontherium, became extinct in the Late Pleistocene.

Ground squirrels are rodents of the squirrel family (Sciuridae) that generally live on the ground or in burrows, rather than in trees like the tree squirrels. The term is most often used for the medium-sized ground squirrels, as the larger ones are more commonly known as marmots or prairie dogs, while the smaller and less bushy-tailed ground squirrels tend to be known as chipmunks.

The mountain beaver is a North American rodent. It is the only living member of its genus, Aplodontia, and family, Aplodontiidae. It should not be confused with true North American and Eurasian beavers, to which it is not closely related; the mountain beaver is instead more closely related to squirrels, although its less-efficient renal system was thought to indicate greater relative antiquity for the species. There are seven subspecies of mountain beavers, six of which are found in California and three of which are endemic to the state.

Mystacinidae is a family of unusual bats, the New Zealand short-tailed bats. There is one living genus, Mystacina, with two species, one of which could have possibly become extinct in the 1960s. They are medium-sized bats, about 6 centimetres (2.4 in) in length, with grey, velvety fur.
Yurlunggur is a genus of fossil snake in the extinct family Madtsoiidae containing the species Yurlunggur camfieldensis known from the Oligocene and Miocene of Australia.

Sparassodonta is an extinct order of carnivorous metatherian mammals native to South America, related to modern marsupials. They were once considered to be true marsupials, but are now thought to be a separate side branch that split before the last common ancestor of all modern marsupials.

Megistotherium is an extinct genus of hyaenodont belonging to the family Hyainailouridae that lived in Africa.

Palaeocastor is an extinct genus of beavers that lived in the North American Badlands during the late Oligocene period to early Miocene. Palaeocastor was much smaller than modern beavers. There are several species including Palaeocastor fossor, Palaeocastor magnus,Palaeocastor wahlerti, and Palaeocastor peninsulatus. The animals first became known on grounds of their fossilized burrows, the "Devil's corkscrews".

Daeodon is an extinct genus of entelodont even-toed ungulates that inhabited North America about 29 to 15.97 million years ago during the latest Oligocene and earliest Miocene. The type species is Daeodon shoshonensis, described from a very fragmentary holotype by Cope. Some authors synonymize it with Dinohyus hollandi and several other species, but due to the lack of diagnostic material, this may be questionable.

Barbourofelidae is an extinct family of carnivorans of the suborder Feliformia, sometimes known as false saber-toothed cats, that lived in North America, Eurasia and Africa during the Miocene epoch and existed for about 7.9 million years. Thought to be an independent lineage from the Nimravidae and Machairodontinae, which had all attained elongated canines, recent research argues that it may be a subfamily of the Nimravidae, extending its biochronological range into the Miocene, although this issue is not yet fully resolved.
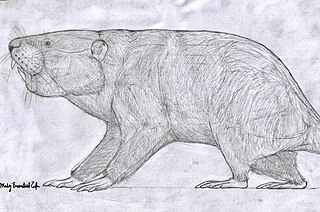
Migmacastor is an extinct member of the beaver family, Castoridae, known from a single species, Migmacastor procumbodens. Only a single specimen has been reported, a skull from the late Oligocene or early Miocene of Nebraska. Features of the incisor teeth of Migmacastor indicate they were used to dig. Other extinct beavers, including the better-known Palaeocastor, were also fossorial (digging), but Migmacastor may have become a burrower independently.
Cyonasua is an extinct genus of procyonid from the Late Miocene to Middle Pleistocene of South America. Fossils of Cyonasua have been found in Argentina, Bolivia, Uruguay, and Venezuela. The oldest well-dated fossils of Cyonasua are approximately 7.3 million years old. Most fossils of Cyonasua are late Miocene to early late Pliocene in age, but a single early Pleistocene specimen indicates that members of this genus survived until at least 0.99 million years ago.

Umbridae is a family of ray-finned fish in the order Salmoniformes. The single living genus, Umbra, occupies weed-choked freshwater habitats in eastern North America and eastern Europe. While the family traditionally contained the genera Umbra, Novumbra, and Dallia, recent genetic and paleontological research have recovered this grouping as paraphyletic, with Novumbra and Dallia being moved to the family Esocidae.

Megalictis is an extinct genus of large predatory mustelids that existed in North America during the "cat gap" from the Late Arikareean (Ar4) in the Miocene epoch. It is thought to have resembled a huge, jaguar-sized ferret, weighing up to 60–100 kilograms (130–220 lb).
Promartes is a genus of mustelids, now extinct, which existed during the Miocene period.

Langstonia is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorph of the family Sebecidae. It lived in the middle Miocene, in the "Monkey Beds" of the Colombian Villavieja Formation. Langstonia was named in 2007 by Alfredo Paolillo and Omar Linares for fossils originally described by Langston in 1965 as Sebecus huilensis. Thus, the type species is L. huilensis.

Arctoidea is a clade of mostly carnivorous mammals which include the extinct Hemicyonidae (dog-bears), and the extant Musteloidea, Pinnipedia, and Ursidae (bears), found in all continents from the Eocene, 46 million years ago, to the present. The oldest group of the clade is the bears, as their CMAH gene is still intact. The gene became non-functional in the common ancestor of the Mustelida. Arctoids are caniforms, along with dogs (canids) and extinct bear dogs (Amphicyonidae). The earliest caniforms were superficially similar to martens, which are tree-dwelling mustelids. Together with feliforms, caniforms compose the order Carnivora; sometimes Arctoidea can be considered a separate suborder from Caniformia and a sister taxon to Feliformia.

Livyatan is an extinct genus of macroraptorial sperm whale containing one known species: L. melvillei. The genus name was inspired by the biblical sea monster Leviathan, and the species name by Herman Melville, the author of the famous novel Moby-Dick about a white bull sperm whale. Herman Melville often referred to whales as "Leviathans" in his book. It is mainly known from the Pisco Formation of Peru during the Tortonian stage of the Miocene epoch, about 9.9–8.9 million years ago (mya); however, finds of isolated teeth from other locations such as Chile, Argentina, the United States (California), South Africa and Australia imply that either it or a close relative survived into the Pliocene, around 5 mya, and may have had a global presence. It was a member of a group of macroraptorial sperm whales and was probably an apex predator, preying on whales, seals and so forth. Characteristically of raptorial sperm whales, Livyatan had functional, enamel-coated teeth on the upper and lower jaws, as well as several features suitable for hunting large prey.

Diegoaelurus is an extinct genus of placental mammals from the extinct subfamily Machaeroidinae within extinct family Oxyaenidae. This genus contains only one species Diegoaelurus vanvalkenburghae, which was found in the Santiago Formation in California. This mammal lived during the Uintan stage of the Middle Eocene Epoch around 46.2 to 39.7 million years ago.























