Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals.

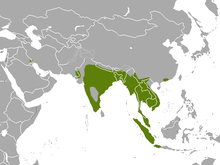
The Asian small-clawed otter, also known as the oriental small-clawed otter and the small-clawed otter, is an otter species native to South and Southeast Asia. It has short claws that do not extend beyond the pads of its webbed digits. With a total body length of 730 to 960 mm, it is the smallest otter species in the world.

Panthera tigris trinilensis, known as the Trinil tiger, is an extinct tiger subspecies dating from about 1.2 million years ago that was found at the locality of Trinil, Java, Indonesia. The fossil remains are now stored in the Dubois Collection of the National Museum of Natural History in Leiden, the Netherlands. Although these fossils have been found on Java, the Trinil tiger is probably not a direct ancestor of the Javan tiger. The Trinil tiger probably became extinct 50,000 years ago. The Bali tiger was also not closely related to the Trinil because of their time differences.

Candiacervus is an extinct genus of deer native to Pleistocene Crete. Due to a lack of other herbivores, the genus underwent an adaptive radiation, filling niches occupied by other taxa on the mainland. Due to the small size of Crete, the genus underwent insular dwarfism, the smallest species, C. ropalophorus, stood about 40 cm at the shoulders when fully grown, as can be inferred from a mounted skeleton. Some species are noted for their peculiar, spatula-shaped antlers, though other species have normal albeit miniaturized antlers. Other features are the relatively short limbs, the massivity of the bones and the simplified antler.

The smooth-coated otter is an otter species occurring in most of the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with a disjunct population in Iraq. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 1996 and is threatened by habitat loss, pollution of wetlands and poaching for the illegal wildlife trade. As its name indicates, its fur is smooth and shorter than that of other otter species.
Cyrnaonyx is an extinct genus of Lutrinae, otters from the Pleistocene. It was originally described by Helbing based on materials from France and he also attributed material from Corsica to it. The latter appeared to belong to another species and genus, Algarolutra majori. The only species of Cyrnaonyx is C. antiqua. It is known from the Pleistocene of Europe: France, Germany, Netherlands, Southern England and probably Italy.

Megalenhydris barbaricina is a Late Pleistocene giant otter from Sardinia. It is known from a single skeleton, discovered in the Grotta di Ispinigoli near Dorgali, and was described in 1987. The species is one of four extinct otter species from Sardinia and Corsica. The others are Algarolutra majori, Lutra castiglionis and Sardolutra ichnusae. This otter was large, possibly even larger than the extant Pteronura, which can reach two meters in length. The structure of the teeth points to a diet of shellfish and/or crustaceans. A special characteristic of the species is the flattening of the first few caudal vertebrae. This might point to a slightly flattened tail.

Sardolutra ichnusae is an extinct species of otter from the Late Pleistocene of Sardinia. It was originally described as Nesolutra ichnusae. It was a rather small species of otter, probably living in the sea. Among its characteristics is a relatively very large baculum, larger than in any living otter. The species probably evolved from a species of Lutra, maybe L. castiglionis.

Mycena adscendens, commonly known as the frosty bonnet, is a species of fungus in the family Mycenaceae. The fungus produces small white fruit bodies (mushrooms) with caps up to 7.5 mm (0.3 in) in diameter that appear to be dusted with sugar-like granules. Caps are supported by thin, hollow stems up to 20 mm (0.8 in) long, which are set on a disc-like base. Its distribution includes Europe, Turkey and the Pacific coast of the United States. The fruit bodies grow on fallen twigs and other woody debris on the forest floor, including fallen hazel nuts. The variety carpophila is known from Japan. There are several small white Mycena species that are similar in appearance to M. adscendens, some of which can be reliably distinguished only by examining microscopic characteristics.

Oriomeryx is an extinct genus of the family Moschidae, endemic to Europe from the early Miocene epoch, approximately 20 Ma. Fossils are known only from a single site in Zaragoza, Spain.

Adolph Cornelis 'Dolf' van Bruggen was a Dutch malacologist, entomologist, and botanist. His interest in the tropics and tropical Africa has dominated his broad scientific interest for more than 50 years now. He was an expert especially in the land snail families Streptaxidae, Achatinidae and Maizaniidae. As of 2008, he had authored some 655 scientific publications.
George François Cornelis Griss, usually cited as G. F. C. Griss, was a Dutch mathematician and philosopher, who was occupied with Hegelian idealism and Brouwers intuitionism and stated a negationless mathematics.

Otter fishing is a fishing technique which uses trained otters to fish in rivers. This method has been practised since the 6th century in various parts of the world, and is still practiced in southern Bangladesh.
Hemimachairodus is an extinct genus of saber-tooth cat of the tribe Machairodontini and subfamily Machairodontinae. The type species, Hemimachairodus zwierzyckii was previously assigned to the genus Homotherium.

Listriodon is an extinct genus of pig-like animals that lived in Eurasia during the Miocene.

Giant asian pangolin, is an extinct species of pangolin that was native to Asia.
The Cretan otter(Lutrogale cretensis) is an extinct otter that was endemic to Crete during the Pleistocene.
Lutra castiglionis, the Castiglione otter or Corsican otter, is an extinct species of otter that was endemic to Corsica during the Pleistocene.