
The Mustelidae are a diverse family of carnivoran mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, polecats, martens, grisons, and wolverines. Otherwise known as mustelids, they form the largest family in the suborder Caniformia of the order Carnivora with about 66 to 70 species in nine subfamilies.

Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals.

Moorhens—sometimes called marsh hens—are medium-sized water birds that are members of the rail family (Rallidae). Most species are placed in the genus Gallinula, Latin for "little hen." They are close relatives of coots. They are often referred to as (black) gallinules. Recently, one of the species of Gallinula was found to have enough differences to form a new genus Paragallinula with the only species being the lesser moorhen.

Gargano is a historical and geographical sub-region in the province of Foggia, Apulia, southeast Italy, consisting of a wide isolated mountain massif made of highland and several peaks and forming the backbone of the Gargano Promontory projecting into the Adriatic Sea, the "spur" on the Italian "boot".

Lutrogale was proposed as generic name by John Edward Gray in 1865 for otters with a convex forehead and nose, using the smooth-coated otter L. perspicillata as type species.

Prolagus is an extinct genus of lagomorph. Over 20 species have been named, and the genus was abundant and widespread in Europe during the Neogene. However, by the end of the Middle Pleistocene, it was confined to a single species, the Sardinian pika, on the Corsica, Sardinia, and surrounding islands, where it survived into historical times. In North Africa and Western Asia, the genus is known from the Miocene and Pliocene. The scientific name may mean "before hares" or "primitive hares". Its taxonomy is disputed, with it either being considered a member of the family Ochotonidae, which includes living pikas, or the only member of the family Prolagidae.

A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus Gazella. There are also seven species included in two further genera; Eudorcas and Nanger, which were formerly considered subgenera of Gazella. A third former subgenus, Procapra, includes three living species of Asian gazelles.

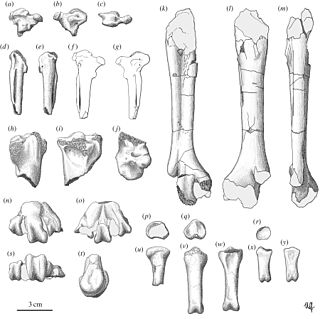
Megalenhydris barbaricina is an extinct species of giant otter from the Late Pleistocene of Sardinia. It is known from a single partial skeleton, discovered in the Grotta di Ispinigoli near Dorgali, and was described in 1987. It was larger than any living otter, exceeding the size of South American giant otters (Petrolutra), which can reach two meters in length. The species is one of four extinct otter species from Sardinia and Corsica. The others are Algarolutra majori, Lutra castiglionis and Sardolutra ichnusae. It is suggested to have ultimately originated from the much smaller European mainland species "Lutra" simplicidens, which may be more closely related to Lutrogale than to modern Lutra species. The structure of the teeth points to a diet of bottom dwelling fish and crustaceans. A special characteristic of the species is the flattening of the first few caudal vertebrae. This might point to a slightly flattened tail.

Sardolutra ichnusae is an extinct species of otter from the Late Pleistocene of Sardinia. It was originally described as Nesolutra ichnusae. It was a rather small species of otter, probably living in the sea. Among its characteristics is a relatively very large baculum, larger than in any living otter. The species probably evolved from a species of Lutra, maybe L. castiglionis.

The Shungura Formation is a stratigraphic formation located in the Omo river basin in Ethiopia. It dates to the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene. Oldowan tools have been found in the formation, suggesting early use of stone tools by hominins. Among many others, fossils of Panthera were found in Member G of the formation.
Algarolutra is an extinct endemic genus of otter from the Pleistocene of Corsica and Sardinia. The single species A. majori was originally attributed to the genus Cyrnaonyx and its type species C. antiqua, which was based on fossils from Corsica and also from mainland France. From mainland Europe, only lower dentition was known, whereas from Corsica and Sardinia only upper dentition was known. When a Cyrnaonyx antiqua fossil with both upper and lower dentition was found in England, it became clear that the species majori was too different to keep even in the same genus and the genus Algarolutra was described. appearing to belong to separate genera. A. majori is known only from very sparse evidence.

Enhydriodon is an extinct genus of mustelids known from Africa, Pakistan, and India that lived from the late Miocene to the early Pleistocene. It contains nine confirmed species, two debated species, and at least a few other undescribed species from Africa. The genus belongs to the tribe Enhydriodontini in the otter subfamily Lutrinae. Enhydriodon means "otter tooth" in Ancient Greek and is a reference to its dentition rather than to the Enhydra genus, which includes the modern sea otter and its two prehistoric relatives.
Garganornis is an extinct genus of enormous flightless anatid waterfowl from the Late Miocene of Gargano, Italy. The genus contains one species, G. ballmanni, named by Meijer in 2014. Its enormous size is thought to have been an adaptation to living in exposed, open areas with no terrestrial predators, and as a deterrent to the indigenous aerial predators like the eagle Garganoaetus and the giant barn owl Tyto gigantea.

Talpa tyrrhenica, also known as the Tyrrhenian mole, is an extinct species of mole belonging to the genus Talpa. It was endemic to the Mediterranean islands of Corsica and Sardinia during the Pleistocene epoch.
Microtus (Tyrrhenicola) henseli is an extinct species of vole belonging to the genus Microtus that was endemic to Sardinia and Corsica during the Pleistocene and Holocene.
Lontra weiri is a fossil species in the carnivoran family Mustelidae from the Hagerman Fossil Beds of Idaho. It shared its habitat with Satherium piscinarium, a probable ancestor of the giant otter of South America. It is named in honor of musician Bob Weir, and is the oldest known member of its genus. Prior to its discovery, Lontra was thought to have evolved from Lutra licenti, which dates from the Pleistocene of East Asia.
Hoplocetus is an extinct genus of raptorial cetacean of the sperm whale superfamily, Physeteroidea. Its remains have been found in the Miocene of Belgium, France, Germany and Malta, the Pliocene of Belgium and France, and the Pleistocene of the United Kingdom and South Carolina.
The Cretan otter(Lutrogale cretensis) is an extinct otter that was endemic to Crete during the Pleistocene.
Lutra castiglionis, the Castiglione otter or Corsican otter, is an extinct species of otter that was endemic to Corsica during the Pleistocene.
Proadinotherium is an extinct genus of toxodontid. It lived between the Late Oligocene and the Early Miocene in what is now South America.



















