Taxonomy
The two species had previously been considered members of the genus Canis . In 2017, a taxonomic review recommended that these two species be recognised as genus Lupulella. [6] In response to this review, the American Society of Mammalogists recognised the new genus. [4]
In 2019, a workshop hosted by the IUCN/SSC Canid Specialist Group recommends that because DNA evidence shows the side-striped jackal (Canis adustus) and black-backed jackal (Canis mesomelas) to form a monophyletic lineage that sits outside of the Canis/Cuon/Lycaon clade, that they should be placed in a distinct genus, Lupulella (Hilzheimer, 1906) with the names Lupulella adusta and Lupulella mesomelas. [2]
Genus Lupulella – Schreber, 1775 – two species| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
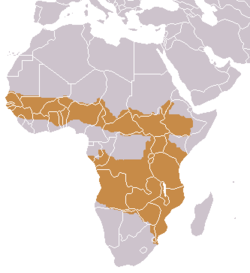
| Side-striped jackal  | Lupulella adusta
(Sundevall, 1847)
- L. a. adusta
- L. a. bweha
- L. a. centralis
- L. a. grayi
- L. a. kaffensis
- L. a. lateralis
- L. a. notatus
| central and southern Africa
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
|
|---|
| Black-backed jackal  | Lupulella mesomelas
(Schreber, 1775)
- Cape black-backed jackal, L. m. mesomelas
- East African black-backed jackal, L. m. schmidti
| eastern and southern Africa
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
|
|---|
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





